QUIZ: How Much Do You Know About The Cold War?
Following World War II, the Cold War was a time of great tension between the United States and the communist Soviet Union, along with their respective allies, with the conflict continuing to span from the 1947 Truman Doctrine to the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Although there was no large-scale fighting between the two sides, it sparked many regional conflicts known as proxy wars, and almost resulted in full-blown nuclear warfare. Think you’re educated about this dark period of time in human history? Take this quiz to test your knowledge!
Which leader coined the term “Iron Curtain” referencing the divide in Europe during the Cold War?

A. Harry Truman
B. John F. Kennedy
C. Joseph Stalin
D. Winston Churchill
Answer: Winston Churchill
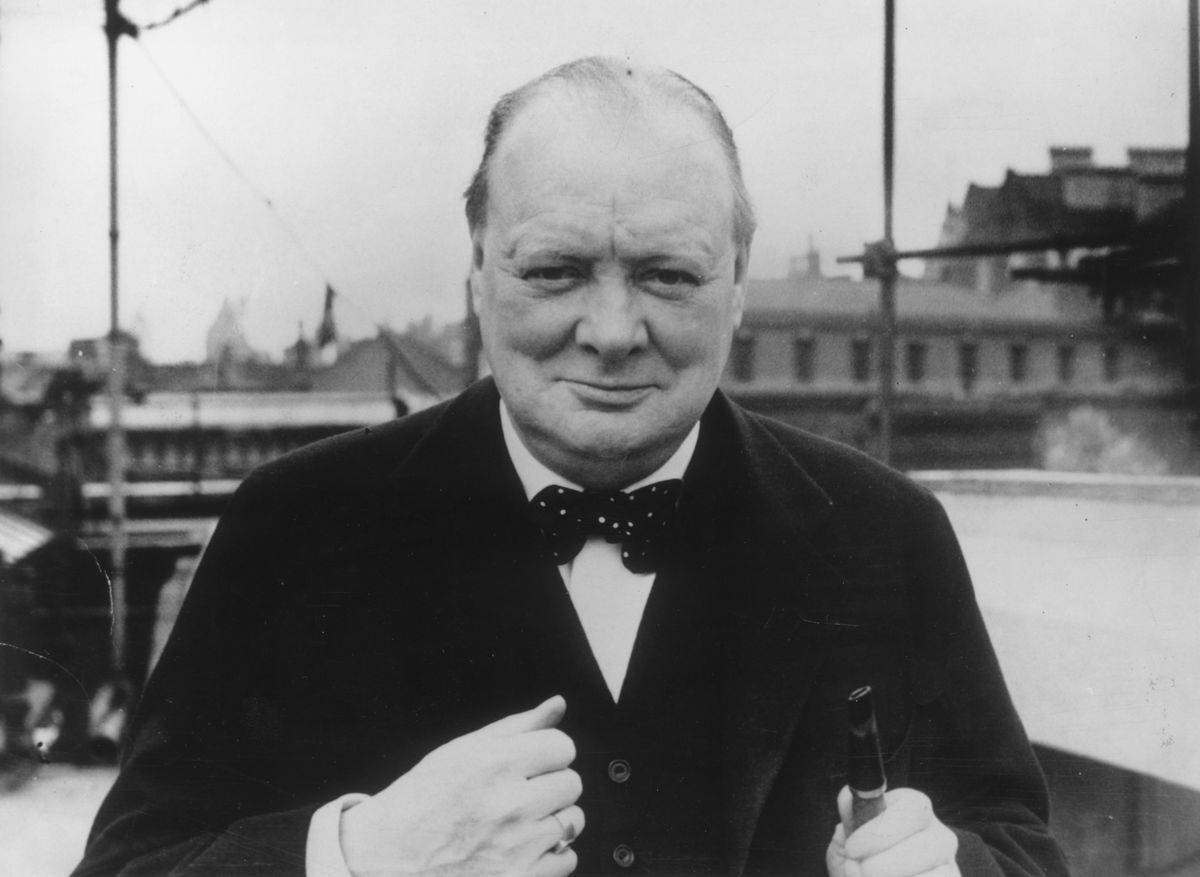

Winston Churchill first referred to the divide as the “Iron Curtain” in a speech at Westminster College in Missouri on March 5, 1946. He stated, “From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an Iron Curtain has descended across the continent.”
What was the name of the doctrine formed by U.S. diplomat George Kennan that was the basis of U.S. Foreign policy during the Cold War?

A. The Truman Doctine
B. Total War
C. Flexible Response
D. Containment
Answer: Containment

Kennan outlined the doctrine known as the X article, which advocated “a policy of firm containment, designed to confront the Russians with unalterable counterforce at every point where they show signs of encroaching upon the interest of a peaceful and stable world.”
The United States and the United Kingdom conducted an airlift to bring supplies to which city in 1948 and 1949?
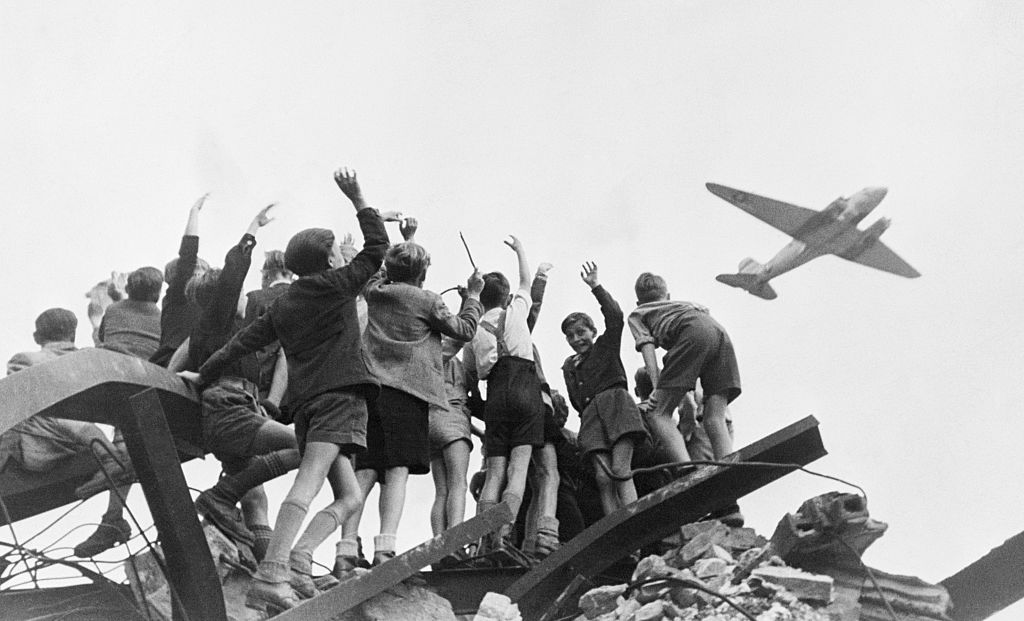

A. Warsaw
B. Berlin
C. Prague
D. Moscow
Answer: Berlin
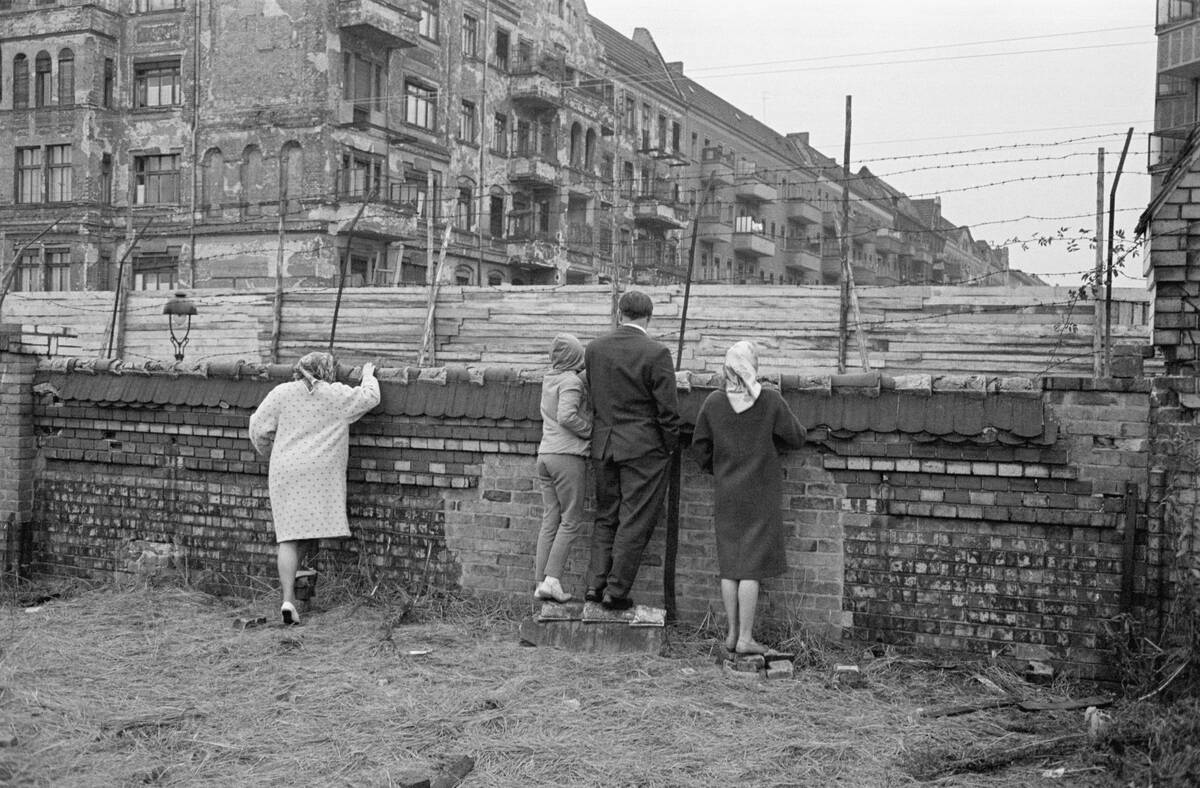

On June 24, 1948, the Soviet Union blocked ground access to West Berlin, also cutting off food, water, electricity, and other supplies. Days later, the United States and the United Kingdom launched an airlift of supplies that lasted for more than a year.
In 1961, the United States and Soviet Tanks had a staredown through a crossing point in the Berlin Wall known as…
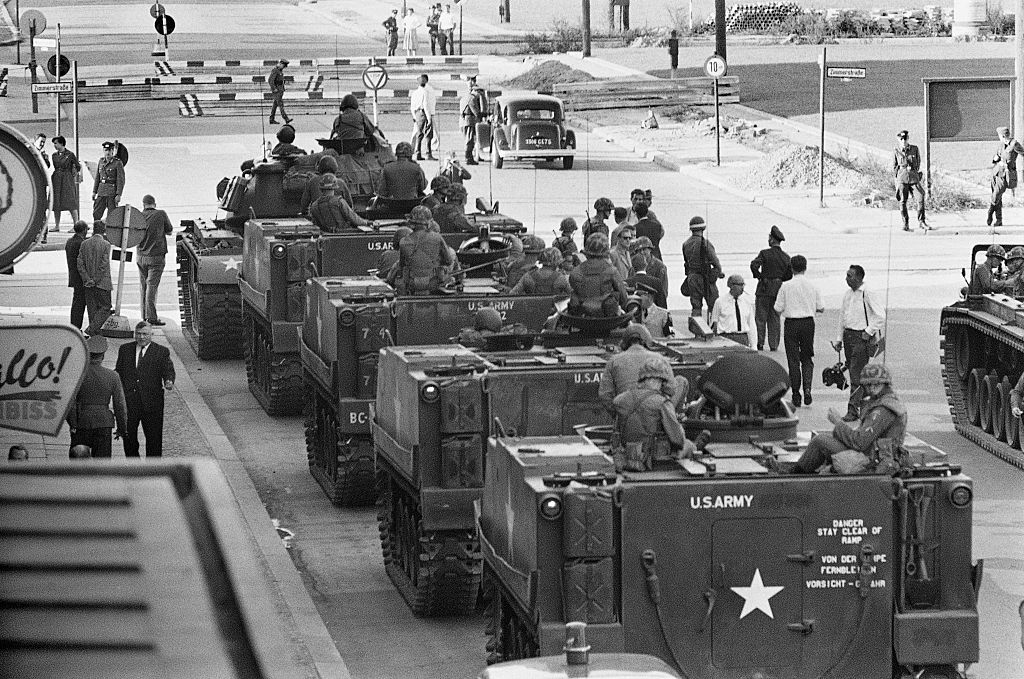

A. Checkpoint Charlie
B. No Man’s Land
C. The Western Door
D. The Closed Opening
Answer: Checkpoint Charlie
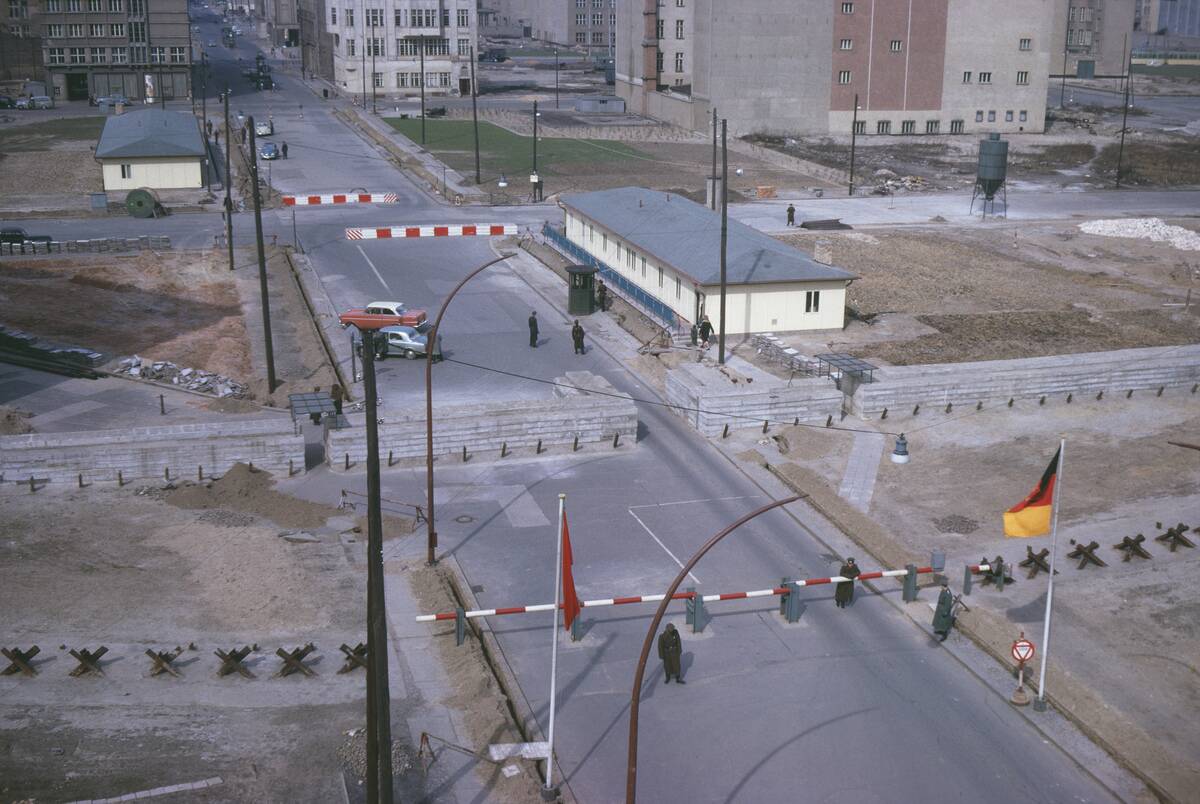

During the showdown, a spy from the KGB, otherwise known as the Soviet security intelligence agency, helped the two sides communicate in order to diffuse the situation before violence broke out in the streets.
The United States’ involvement in Vietnam was initiated by an event in what body of water?

A. The Gulf of Tonkin
B. The Persian Gulf
C. The Bay of Pigs
D. The Gulf of Mexico
Answer: The Gulf of Tonkin

The Gulf of Tonkin Incident in 1964, which may have been exaggerated by the U.S. Defense Department, led congress to pass the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, allowing for intervention in Asian countries that were under the threat of communism, leading the US to become more heavily involved in Vietnam.
What was the name of the East German secret police that spied on its own citizens?
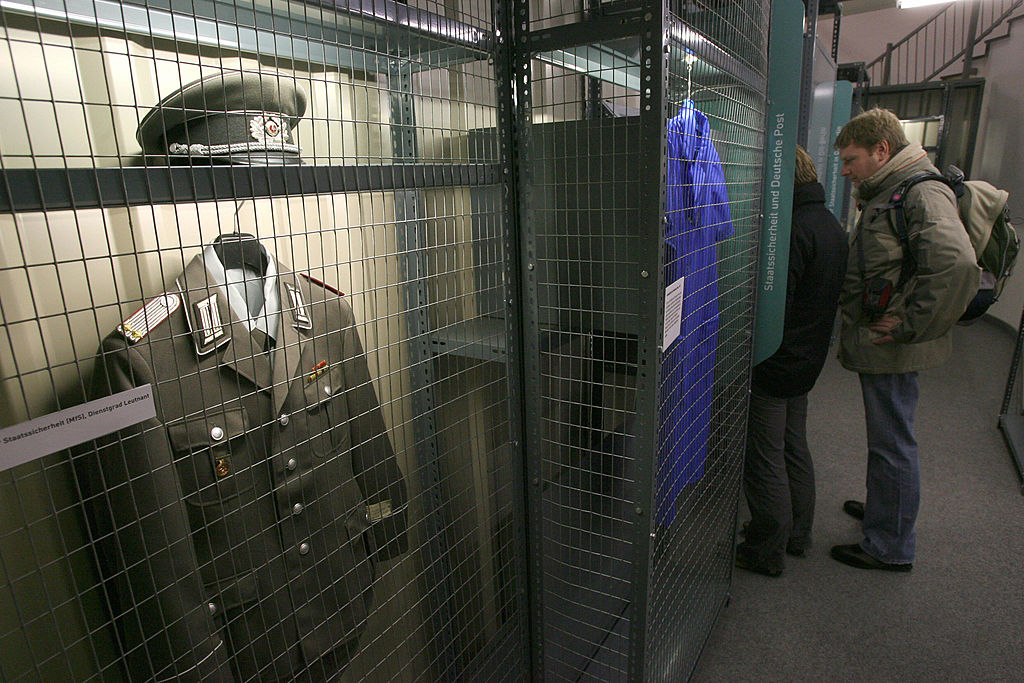

A. The Stasi
B. The KGB
C. The Enforcers
D. The Reds
Answer: The Stasi

The Stasi or State Security Service was the official security service of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany). They are regarded as one of the most effective secret police agencies to have ever existed.
The 13-day nuclear standoff in 1962 between the United States and the Soviet Union is referred to as what?

A. The Cuban Missile Crisis
B. The Days of Silence
C. The Standoff
D. Endgame Crisis
Answer: The Cuban Missile Crisis
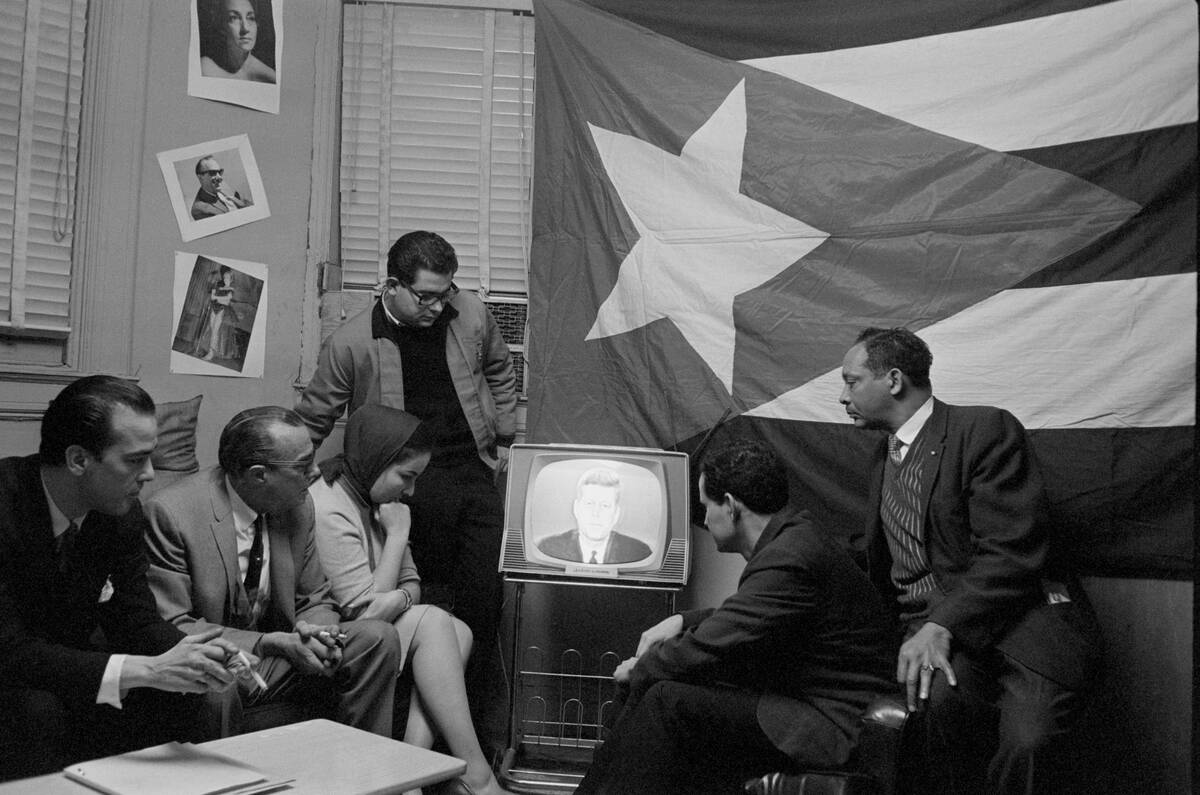

The 13-day nuclear standoff between the Soviet Union and the United States was initiated after the discovery of a Soviet ballistic missile deployment in Cuba. It is regarded as the closest the world has ever come to full-scale nuclear war.
What was the name of the failed United States invasion of Cuba in 1961?
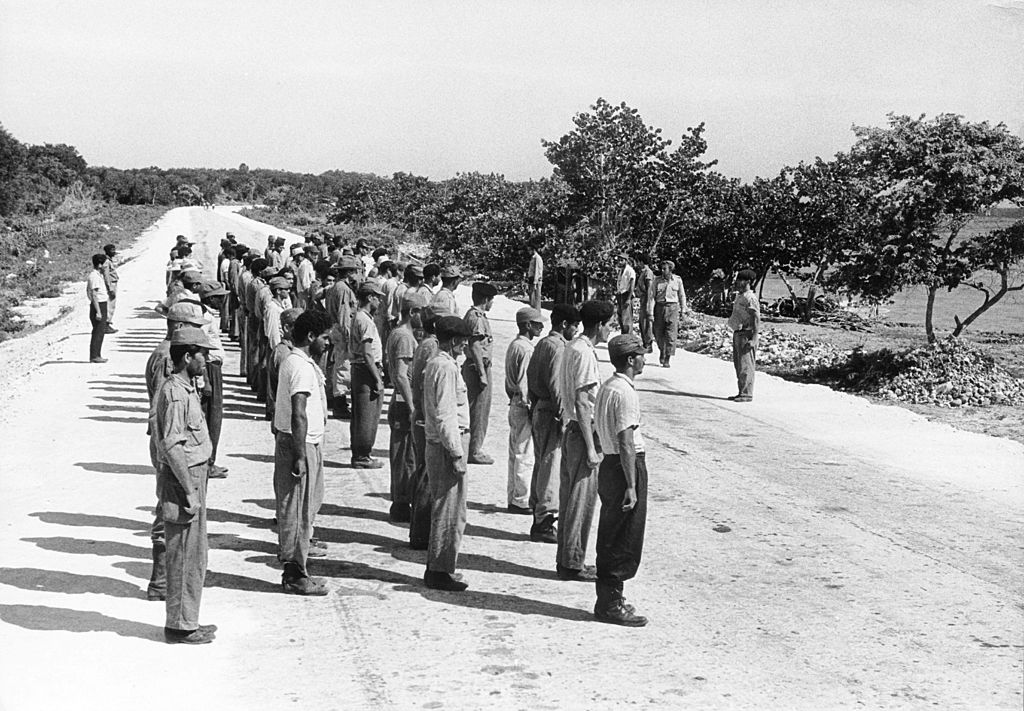

A. The Bay of Pigs
B. Mission X
C. Operation Scoundrel
D. Mission Seek and Capture
Answer: The Bay of Pigs

The Bay of Pigs invasion was a failed attempt by United States-sponsored Cuban exiles to stop Fidel Castro’s Cuban Revolution, starting with a military invasion of northern Cuba. The attempt lasted just three days.
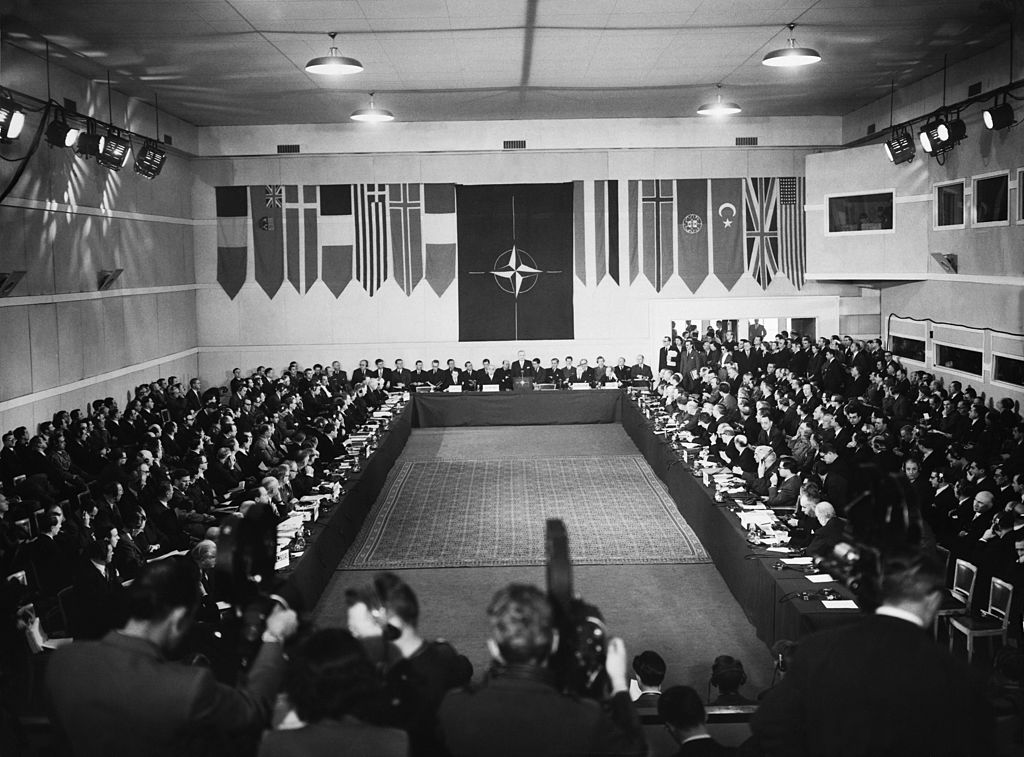
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), which was an alliance between the United States, Canada, and other Europeans was formed which year?

A. 1950
B. 1949
C. 1953
D. 1948
Answer: 1949
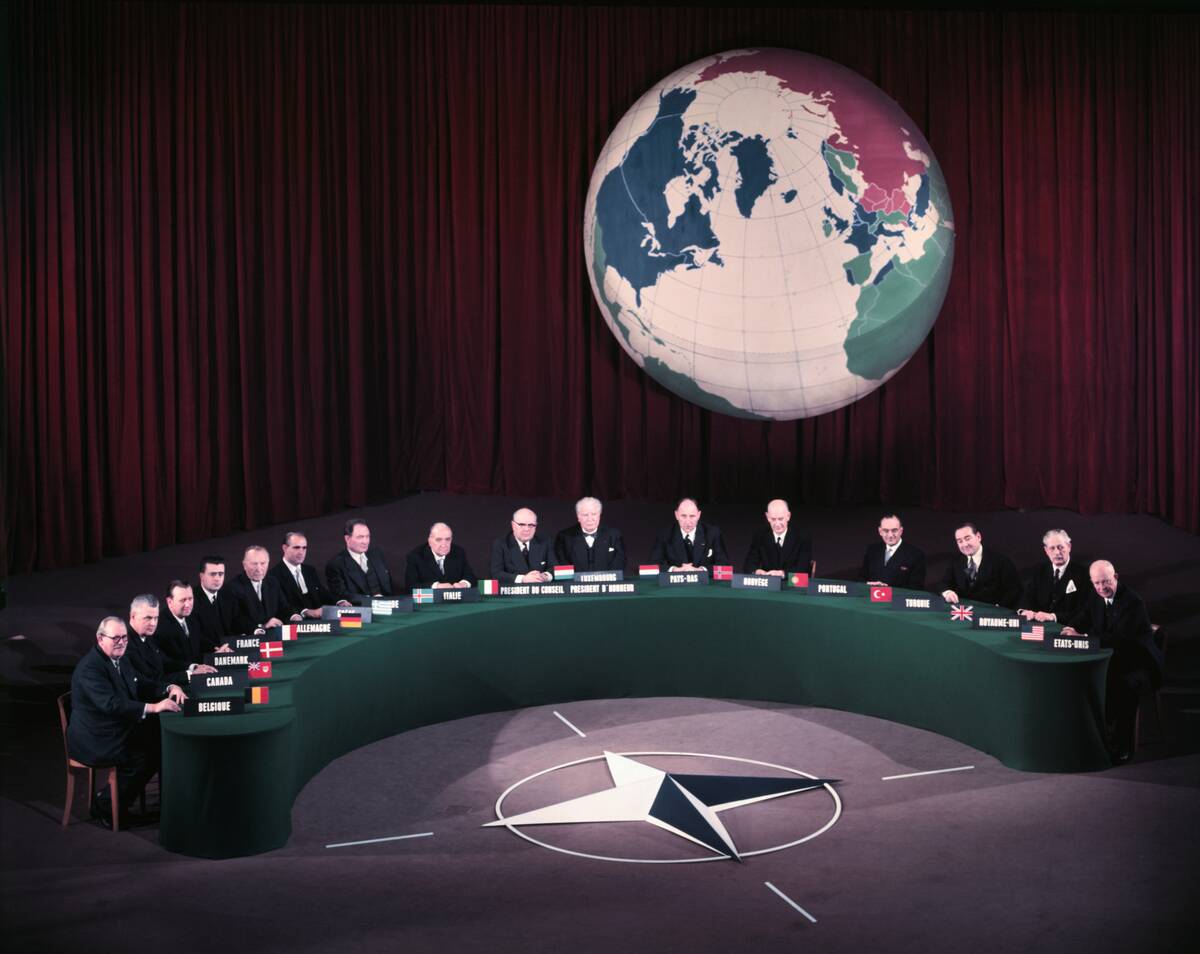

NATO is comprised of 29 North American and European counties, who implemented the North Atlantic Treaty that was signed in 1949. It is a military alliance in which the headquarters are located in Evere, Brussels, Belgium.
What military alliance did the Soviet Union and their communist allies form in response to NATO?

A. The Warsaw Pact
B. Eurasian Union
C. WTROP
D. Organization of Communists
Answer: The Warsaw Pact

The Soviet Union and its satellite states in Eastern Europe formed the Warsaw Pact on May 14, 1955, as a response to NATO and a way to establish Soviet influence in the area.
In 1989, what event marked the beginning of the end of the Cold War?

A. The fall of the Berlin Wall
B. The signing of the U.S.-Soviet Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty
C. The collapse of the Soviet Union
D. The failed mission of the Bay of Pigs
Answer: The fall of the Berlin Wall

The fall of the Berlin Wall began on November 9, 1989, which marked the destruction of the Iron Curtain and the beginning of the fall of communism in Eastern and Central Europe.
In 1956, this country was involved in a three-week uprising to resist the Soviet Union.
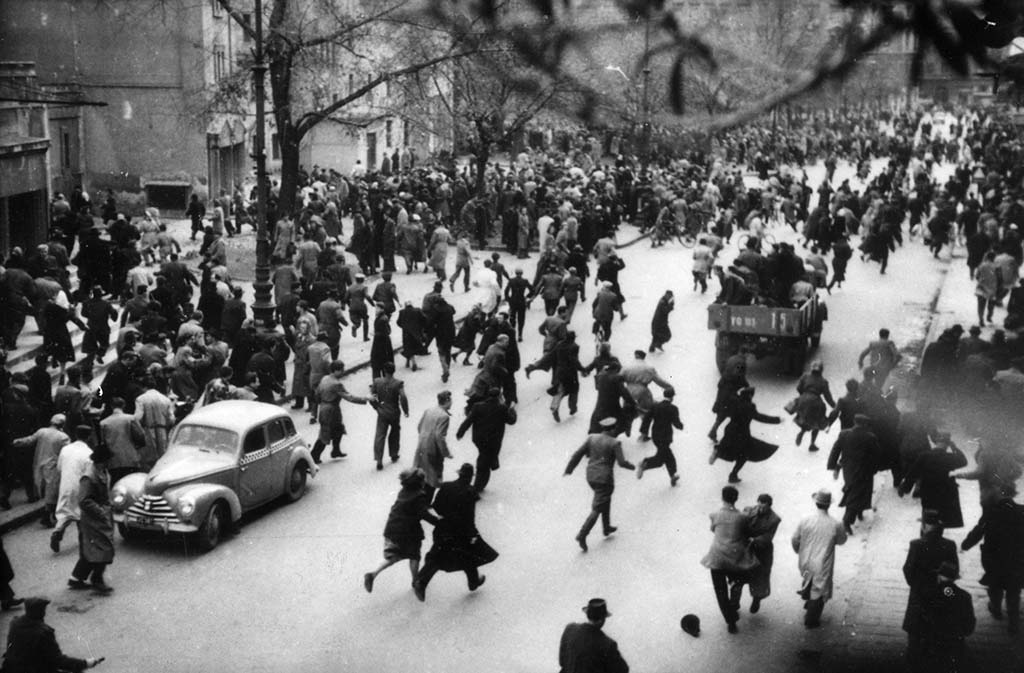
A. Hungary
B. Yugoslavia
C. Poland
D. Bulgaria
Answer: Hungary

Between October 23 and November 10, 1956, students, followed by thousands of Hungarians formed militias to fight against the threat of the Soviet Union. Unfortunately, their rebellion was brutally put down.
Détente was a policy of de-escalation of tensions between the Soviet Union and the United States. Which president was a major supporter of this policy?

A. Kennedy
B. Reagan
C. Eisenhower
D. Carter
Answer: Carter
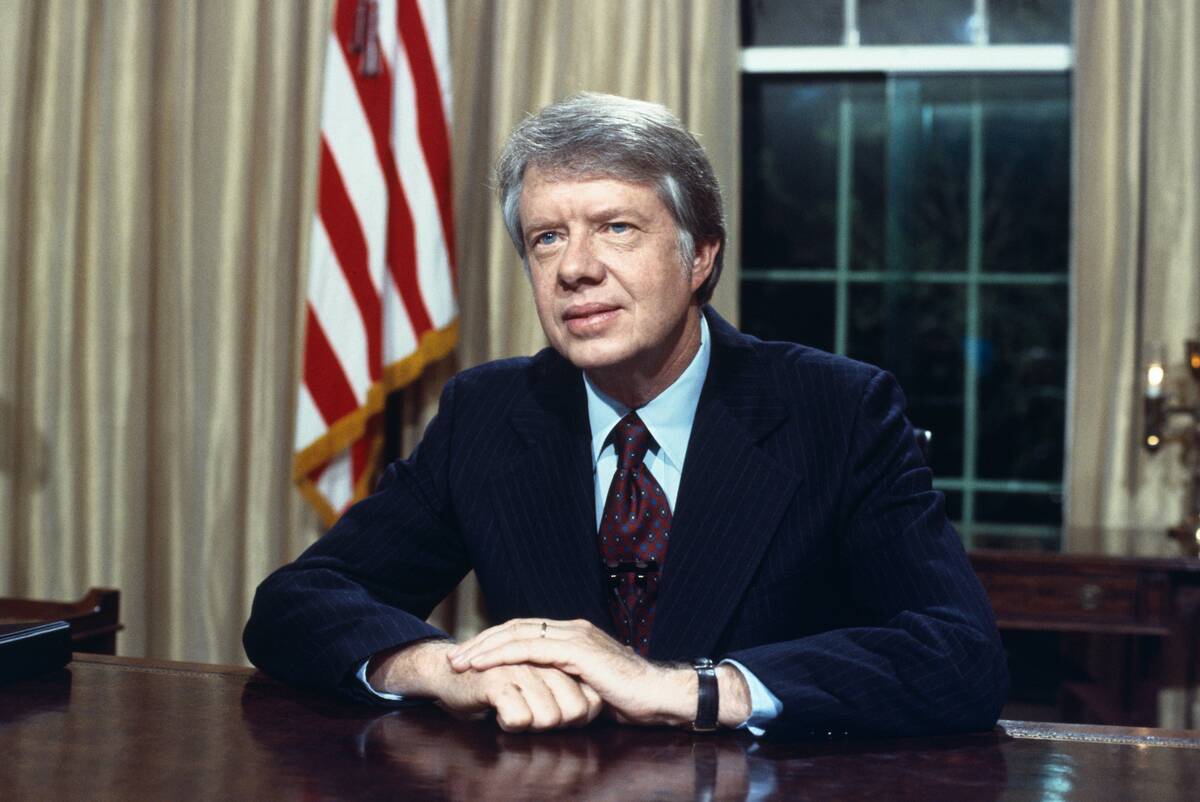

Although the term originates around 1912 between Germany and France, it is most often associated with the Cold War. President Carter was a major proponent of the policy, although Reagan reversed it during his presidency.
Which country started out allied with the Soviets but slowly began to grow closer to the United States?

A. China
B. Italy
C. Cuba
D. South Africa
Answer: China
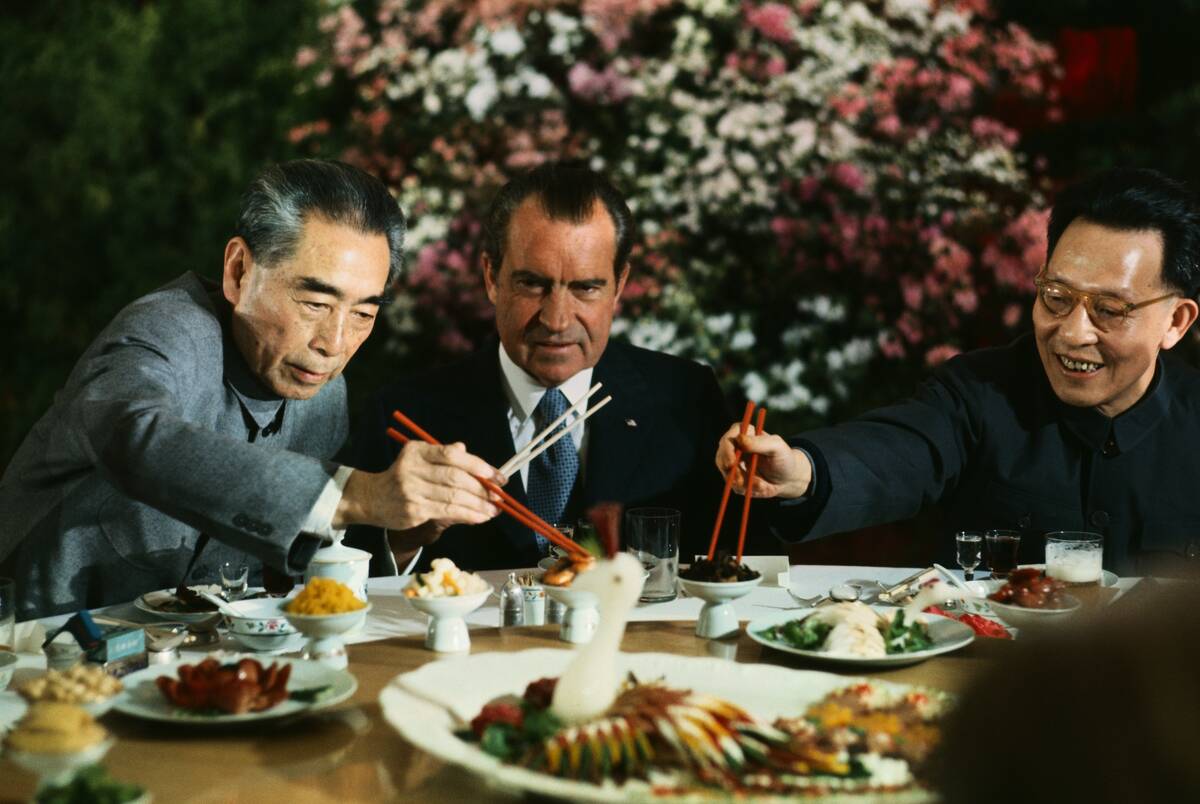

Although China started off in support of the Soviet Union and communism, as time went on, China began to feel threatened and cut ties with the Soviet Union. The United States was then quick to offer peace with the nation.
What was the name of the Polish group that resisted the Soviet Union?

A. Brotherhood
B. Solidarity
C. Freedom Fighters
D. Equality
Answer: Solidarity

Solidarity was one of the most active and vital civil resistance groups that fought against the spread of the Soviet Union. Its leader, Lech Walesa, was named the president of Poland after the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Who is credited with triggering the Cold War?

A. Igor Gouzenko
B. Joseph Stalin
C. Fidel Castro
D. Mikhail Gorbachev
Answer: Igor Gouzenko
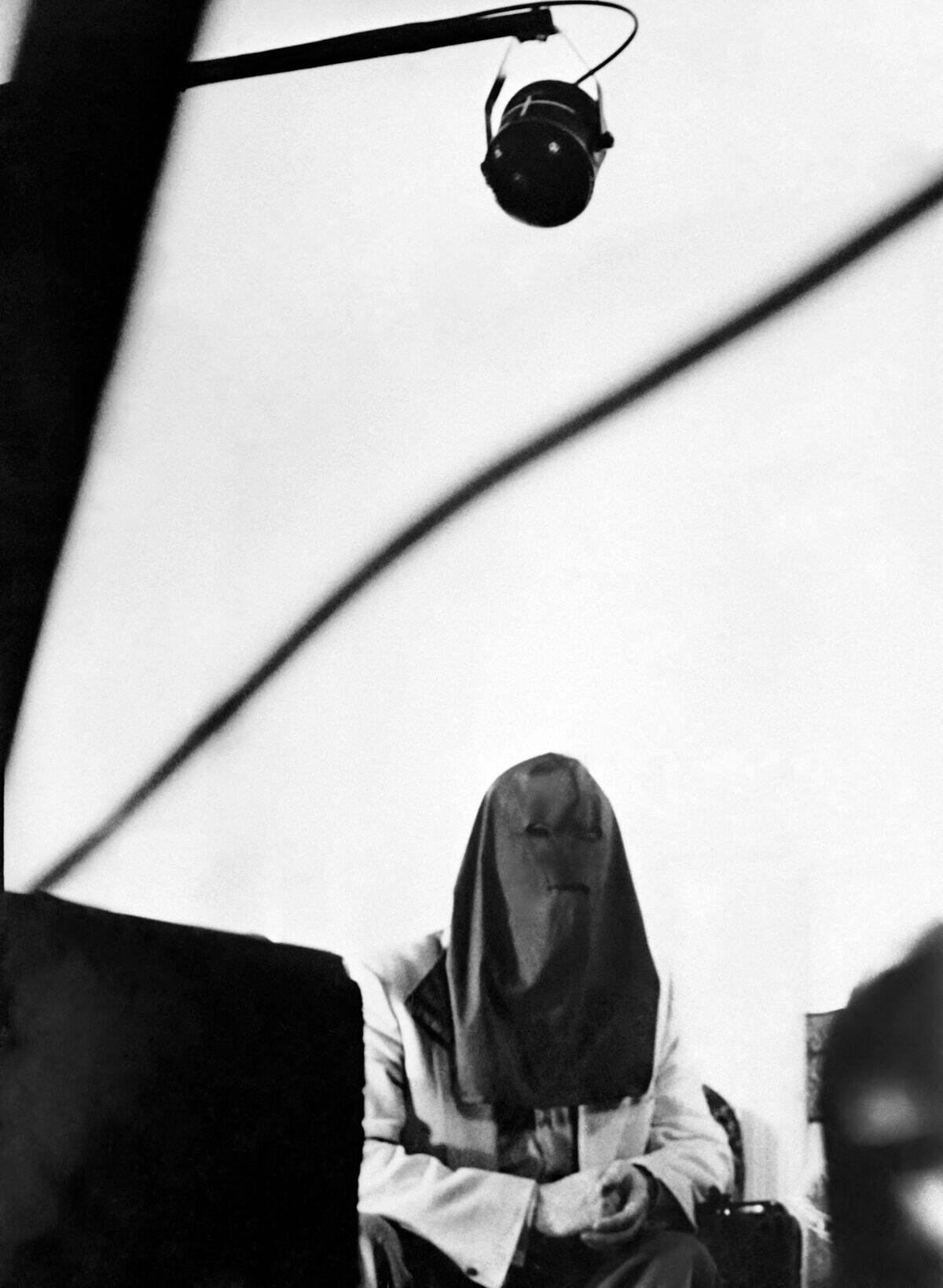

Igor Gouzenko was a cipher clerk for the Soviet embassy to Canada who defected just three days after the end of World War II with 109 documents on the USSR’s espionage activities in the West. The “Gouzenko Affair” is often credited as a triggering event of the Cold War.
Why is it called the Cold War?

A. It was a confrontation without any direct warfare
B. It occurred during the coldest years on record
C. It was named after a Russian diplomat
D. Militaries were working on technologies fueled by cold temperatures
Answer: It was a confrontation without any direct warfare

The Cold War was given its name because it took place over a series of decades in which the United States and the Soviet Union were at odds but never entered into an armed conflict with each other.
In the 1970s, Chinese and US relations were opened up by an exchange of sports teams. What was the sport?

A. Golf
B. Water polo
C. Table tennis
D. Basketball
Answer: Table tennis
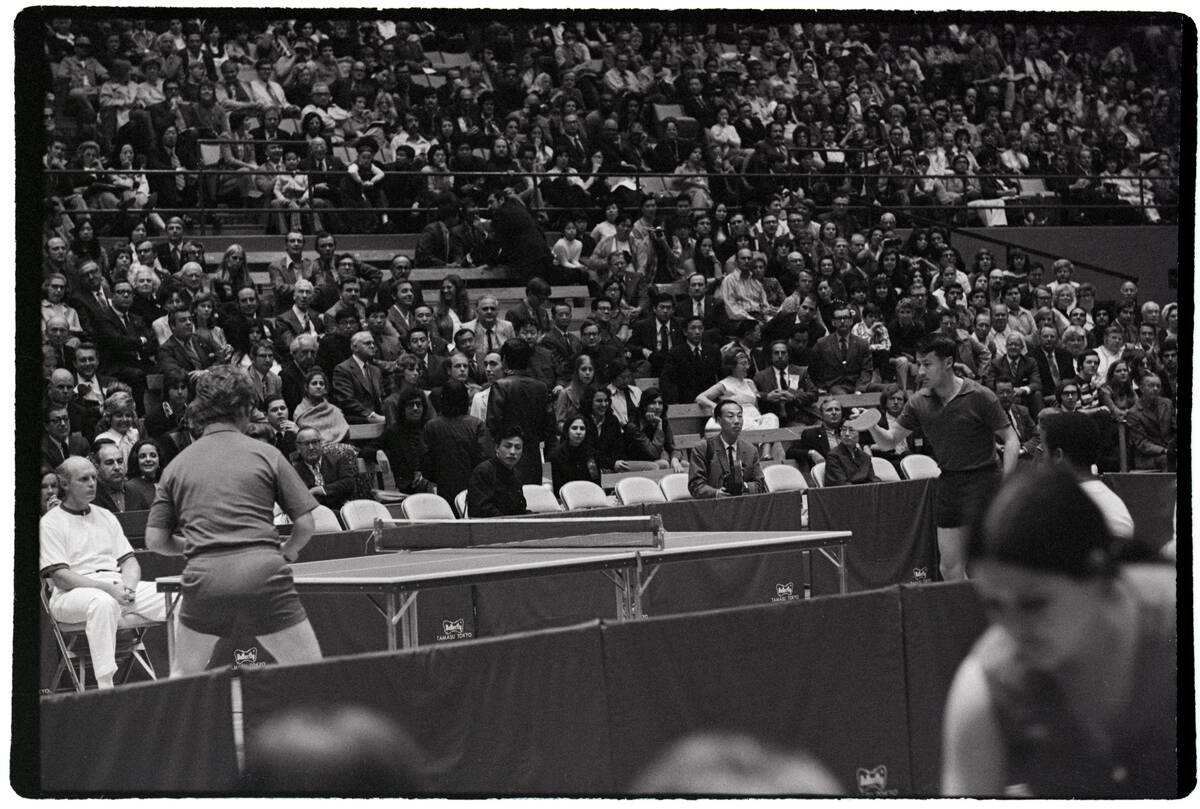

Ping-pong diplomacy refers to the exchange of table tennis players between the United States and the People’s Republic of China. The event helped to smooth over relations between the United States and China.
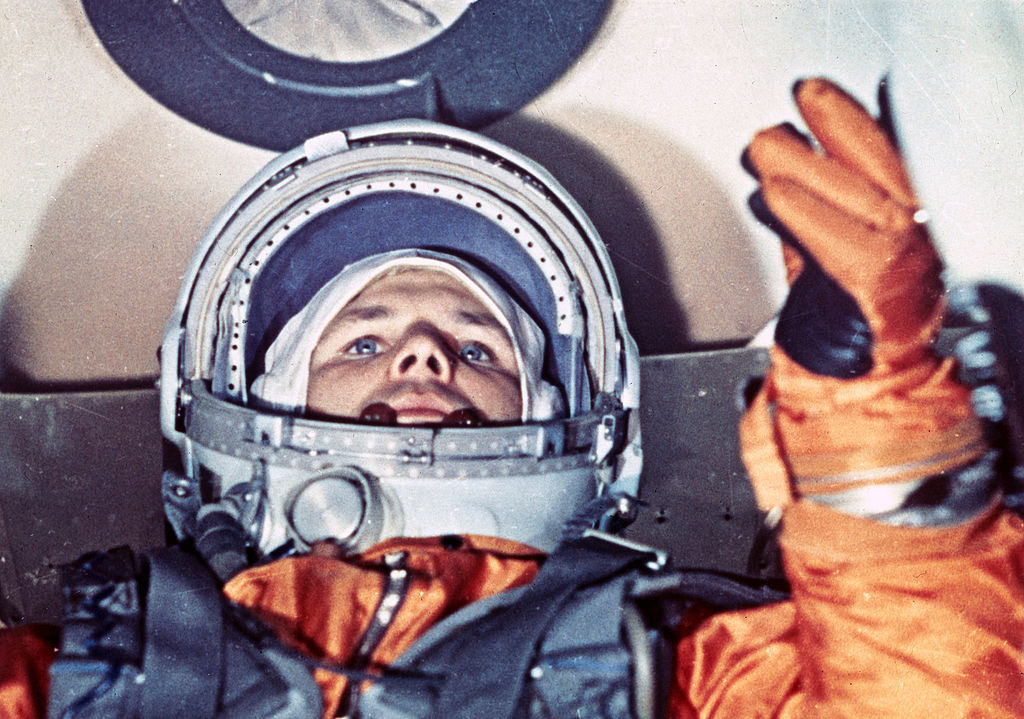
This Russian cosmonaut was the first man in space…

A. Yuri Gagarin
B. Alexei Leonov
C. Anton Shkaplerov
D. Sergey Volkov
Answer: Yuri Gagarin
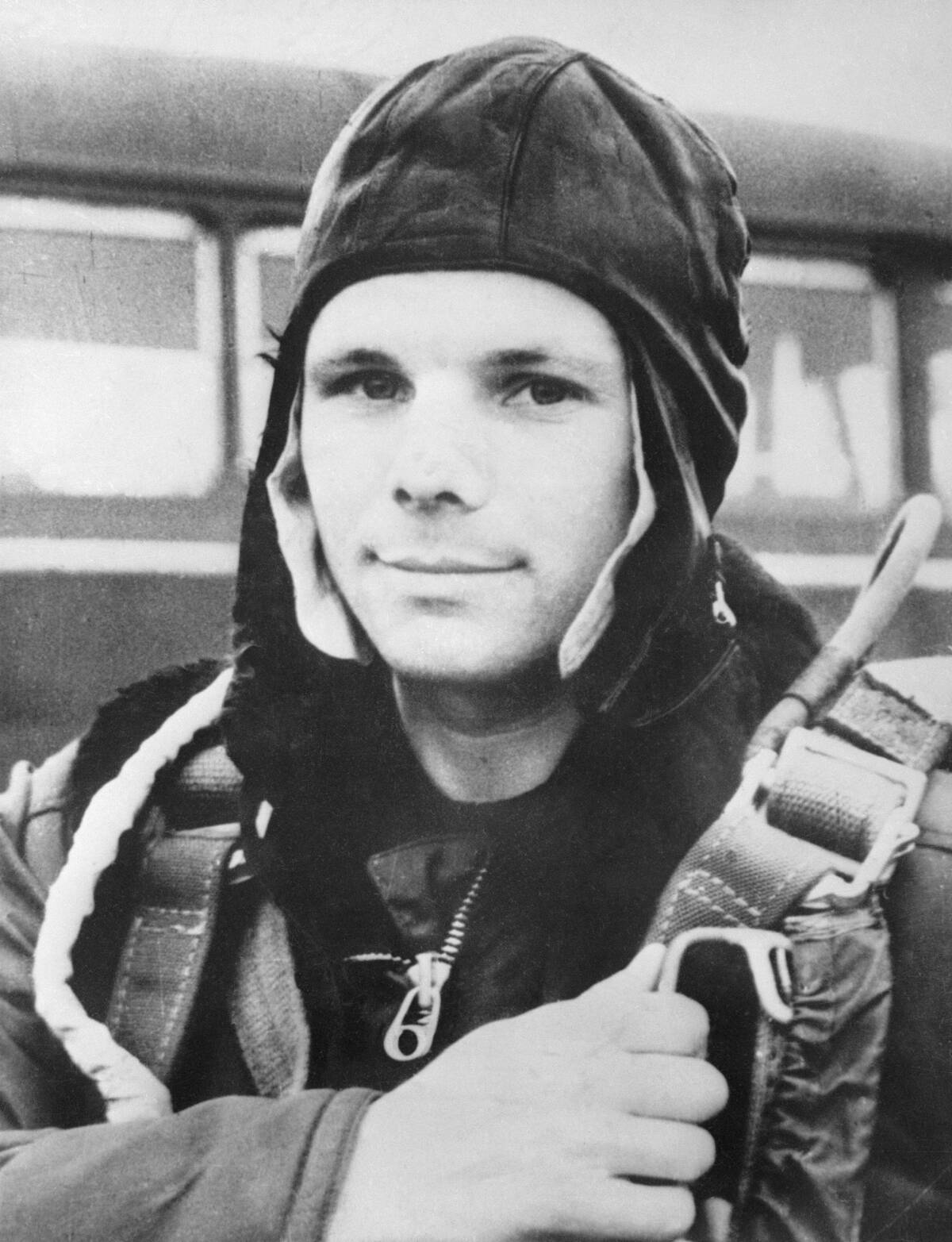

On April 12, 1961, Yuri Gagarin became the first human to journey into space, completing one orbit around the Earth. This was a major milestone in the Space Race and made Gagarin an international celebrity.
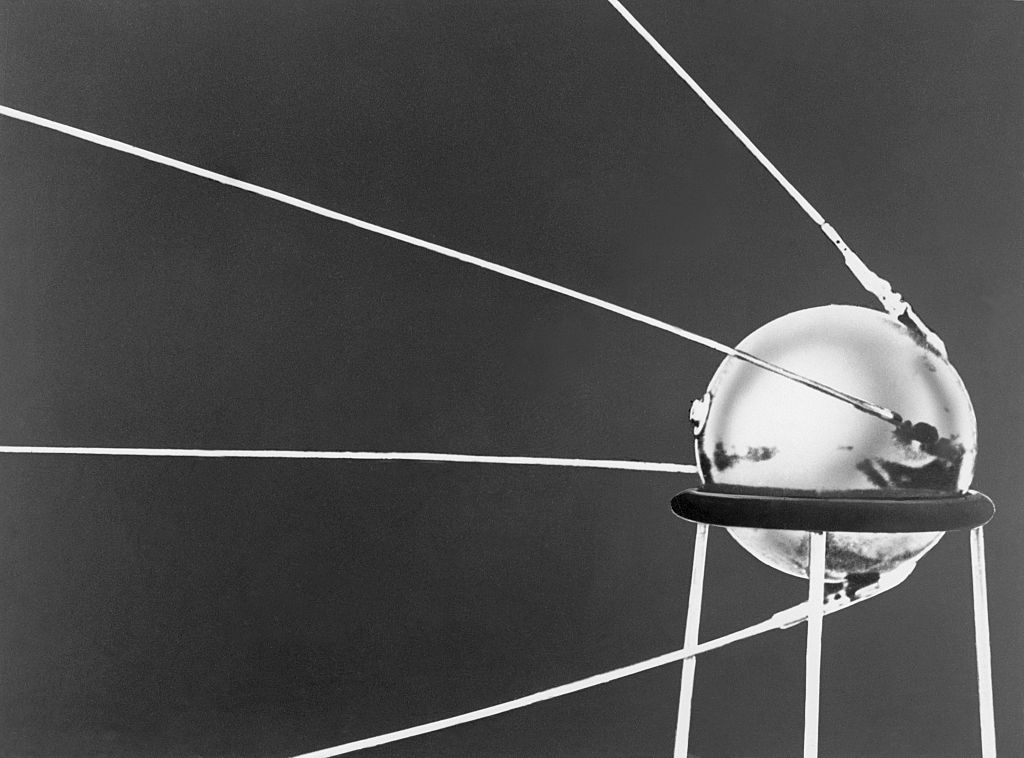
Why were Americans afraid of the Russian satellite Sputnik I?

A. They were going to launch nuclear international ballistic missiles
B. They were going to be the first on the moon
C. They were going to build an armored space station
D. They were going to spy on the United States
Answer: They were going to launch nuclear international ballistic missiles
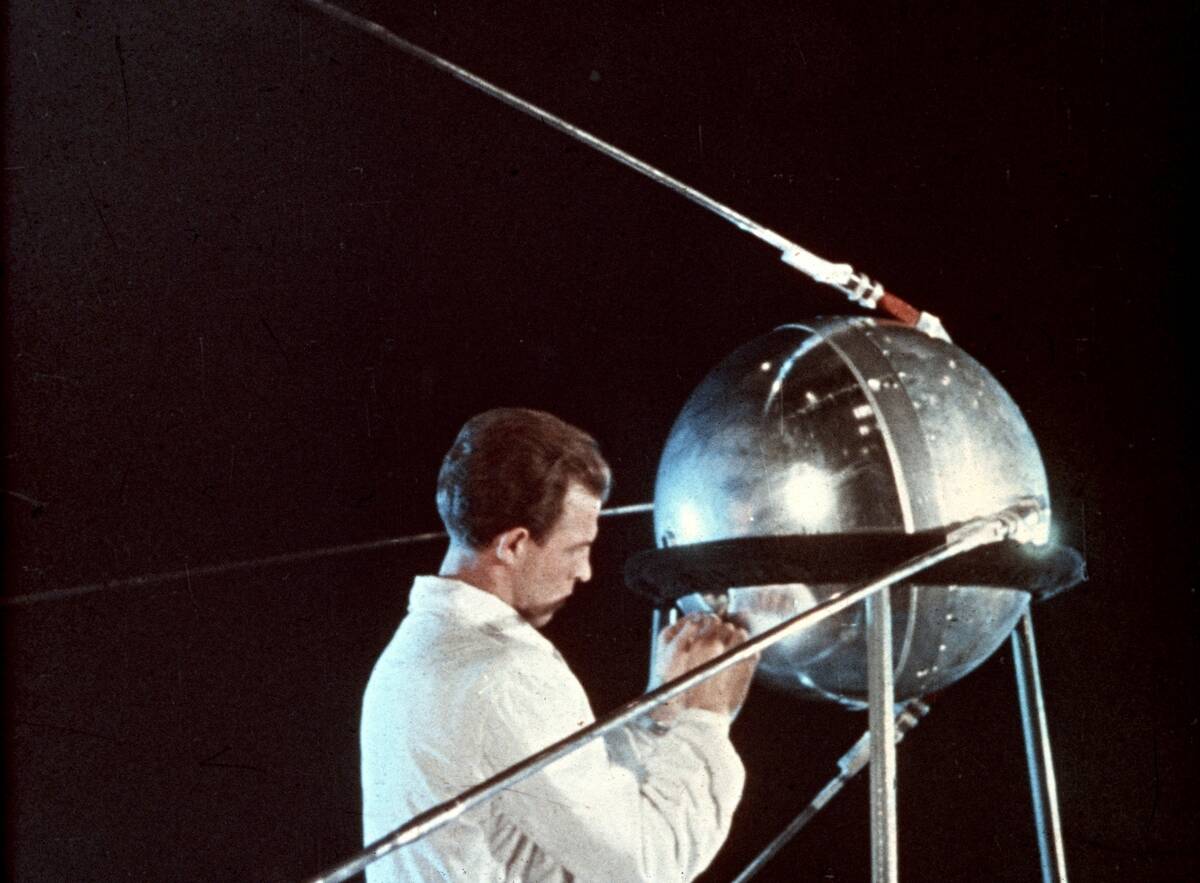

Sputnik I was the first artificial satellite that the Soviet Union launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit on October 4, 1957. Its launching triggered the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union.



