15 Cycles of innovation that shaped human history
Innovation is like a river, flowing continuously through time, carving new paths and shaping the world. From the first flickers of fire to the digital age, humans have always sought to push the boundaries of what’s possible.
The cycles of innovation have not only transformed our environment but also our societies and ways of living. Each era of discovery builds upon the last, creating a fascinating tapestry of human achievement that continues to evolve today.
The Dawn of Human Ingenuity: Fire and Tools
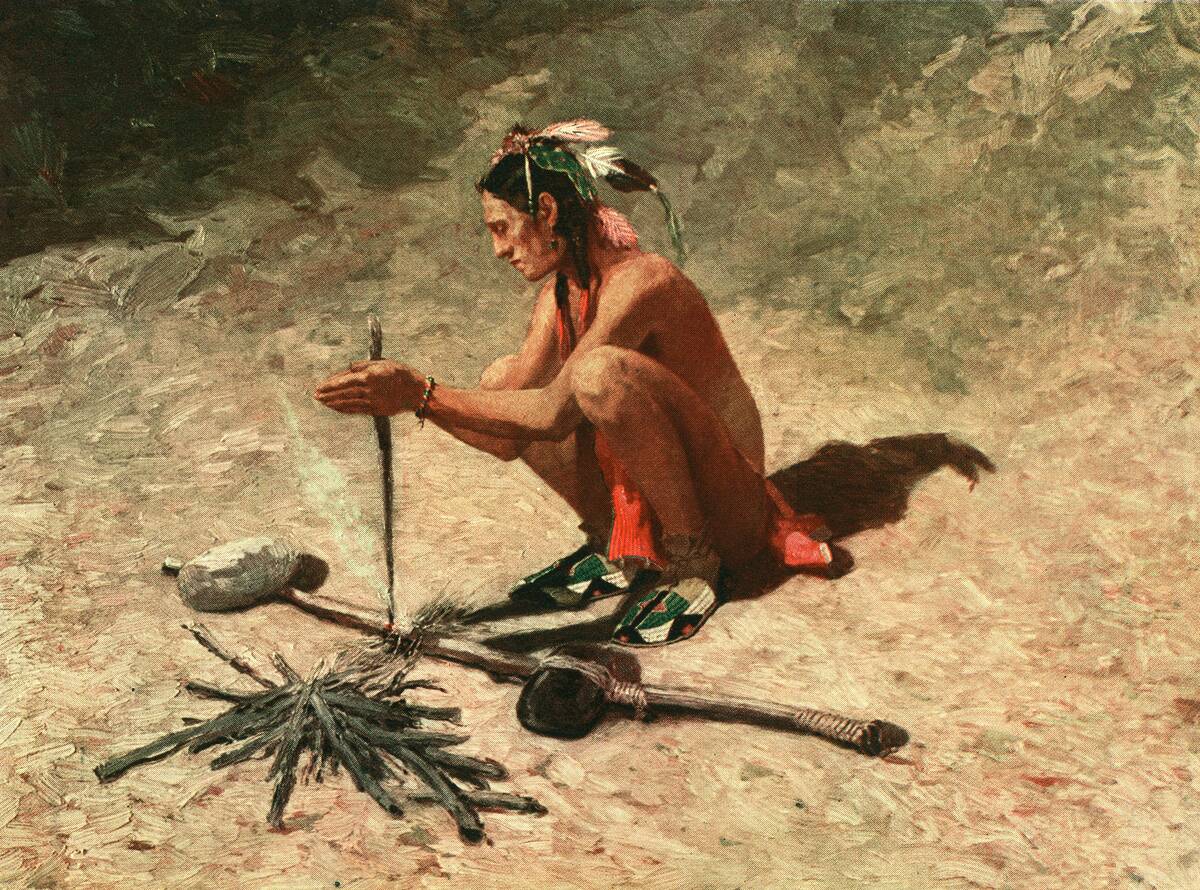

Imagine a world where the dark was truly dark until one day, a spark caught fire, and suddenly, the night was no longer an enemy. Fire, discovered over a million years ago, was a game-changer. It provided warmth, protection, and a new way to cook food.
Along with fire, early humans crafted simple tools from stone, bone, and wood. These tools were not just practical but ingenious, allowing our ancestors to hunt, build, and eventually thrive.
Agricultural Revolution: Sowing the Seeds of Change
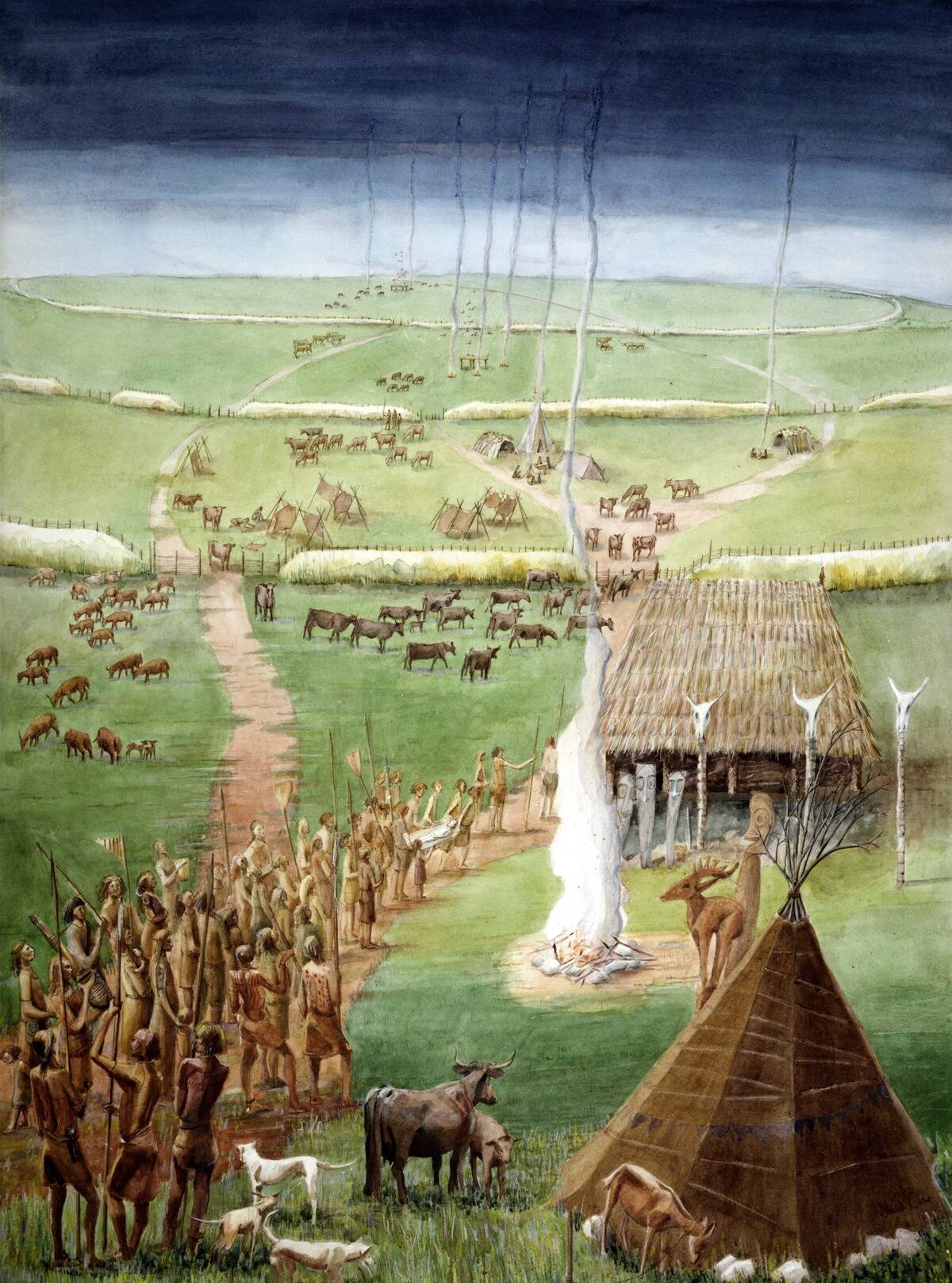

The Agricultural Revolution was the dawn of farming, fundamentally altering human existence and the landscape. About 10,000 years ago, humans began to cultivate crops and domesticate animals.
This shift from nomadic life to settled farming communities led to population growth and the rise of civilizations. Agriculture allowed for food surplus, which in turn enabled the development of cities, trade, and the specialization of labor. It was a period of profound transformation, setting the stage for future advancements.
The Wheel: Rolling Into a New Era
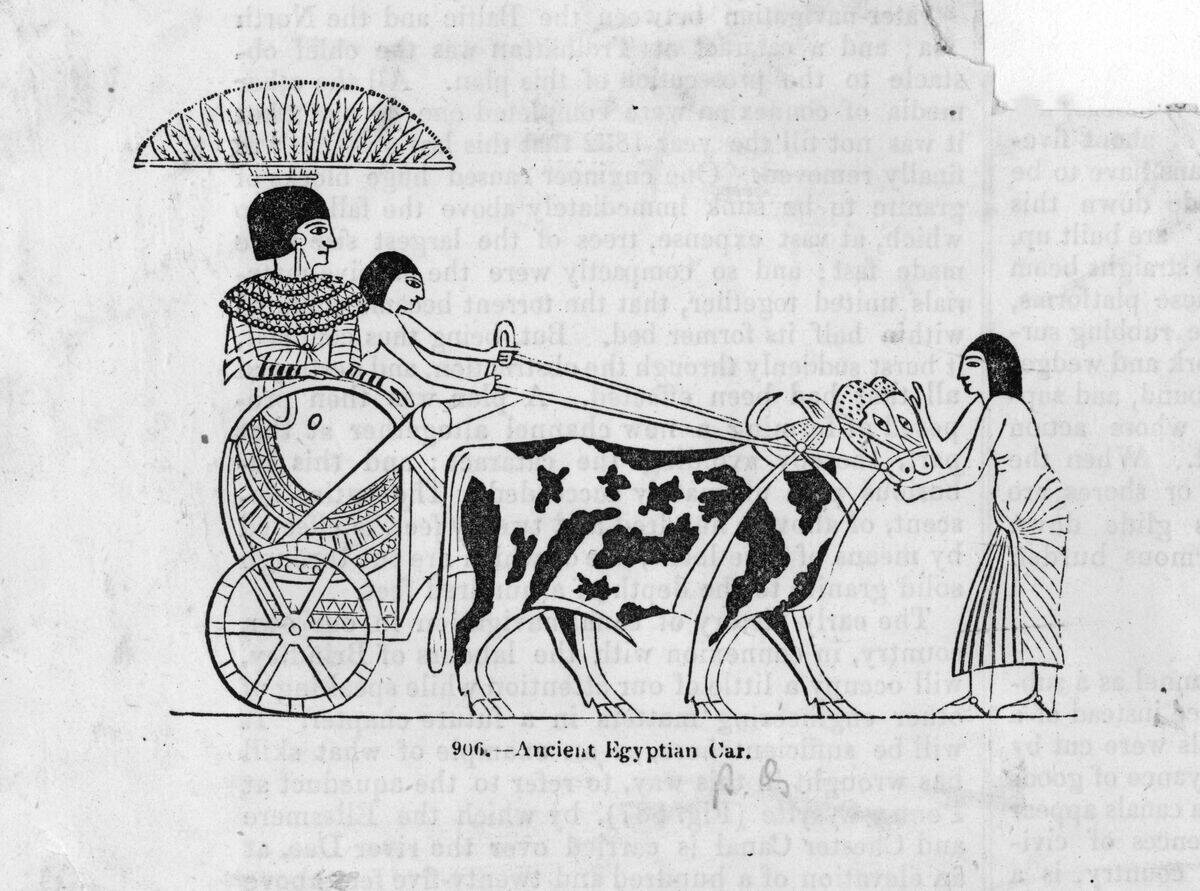

The invention of the wheel, around 3500 BCE, was a pivotal moment in history, symbolizing movement and progress. Initially used in pottery, the wheel soon found its place in transportation, transforming how goods and people traveled.
This simple yet revolutionary invention made it easier to move heavy objects, paving the way for the development of roads and trade routes. The wheel’s impact was felt across cultures, influencing everything from farming to warfare and beyond.
Written Language: The Birth of Communication

Written language was like opening a door to a new dimension of communication. Emerging around 3200 BCE, it allowed humans to record history, laws, and stories, preserving knowledge across generations.
The first known writing systems, like cuneiform and hieroglyphics, were complex, but they laid the groundwork for alphabets. Writing enabled the administration of large empires and facilitated trade across great distances. It was a cornerstone of civilization, influencing everything from education to governance.
The Iron Age: Stronger Tools, Stronger Societies
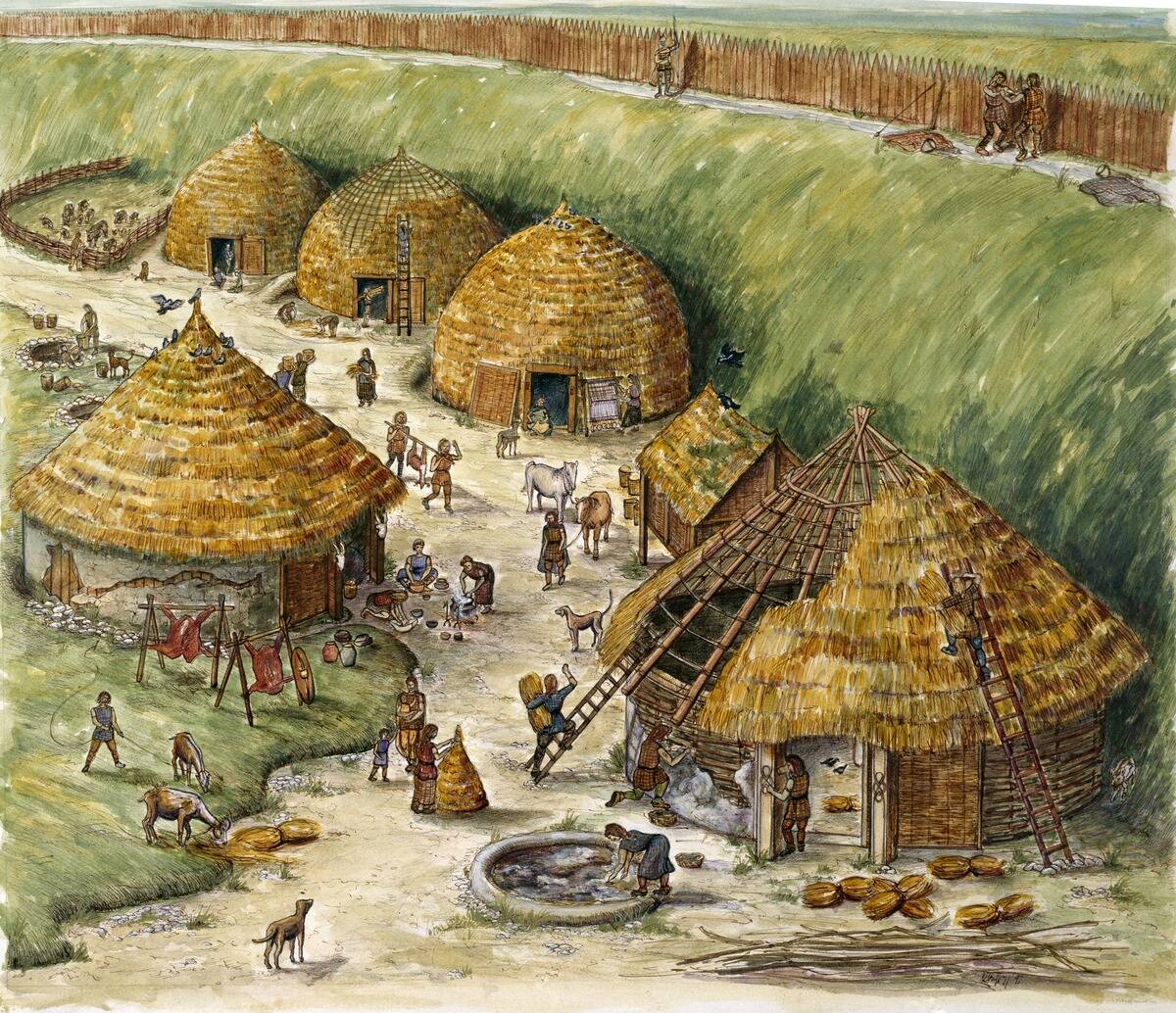

The Iron Age was a period of technological advancement, starting around 1200 BCE. Iron, stronger and more abundant than bronze, revolutionized tool and weapon making. Societies that mastered iron working gained military and agricultural advantages, leading to expansions and conquests.
The ability to clear land for farming and defend territories transformed social structures and economies. This era marked the rise of powerful empires and a shift in the balance of power across the ancient world.
The Renaissance: A Flourish of Artistic and Scientific Ideas
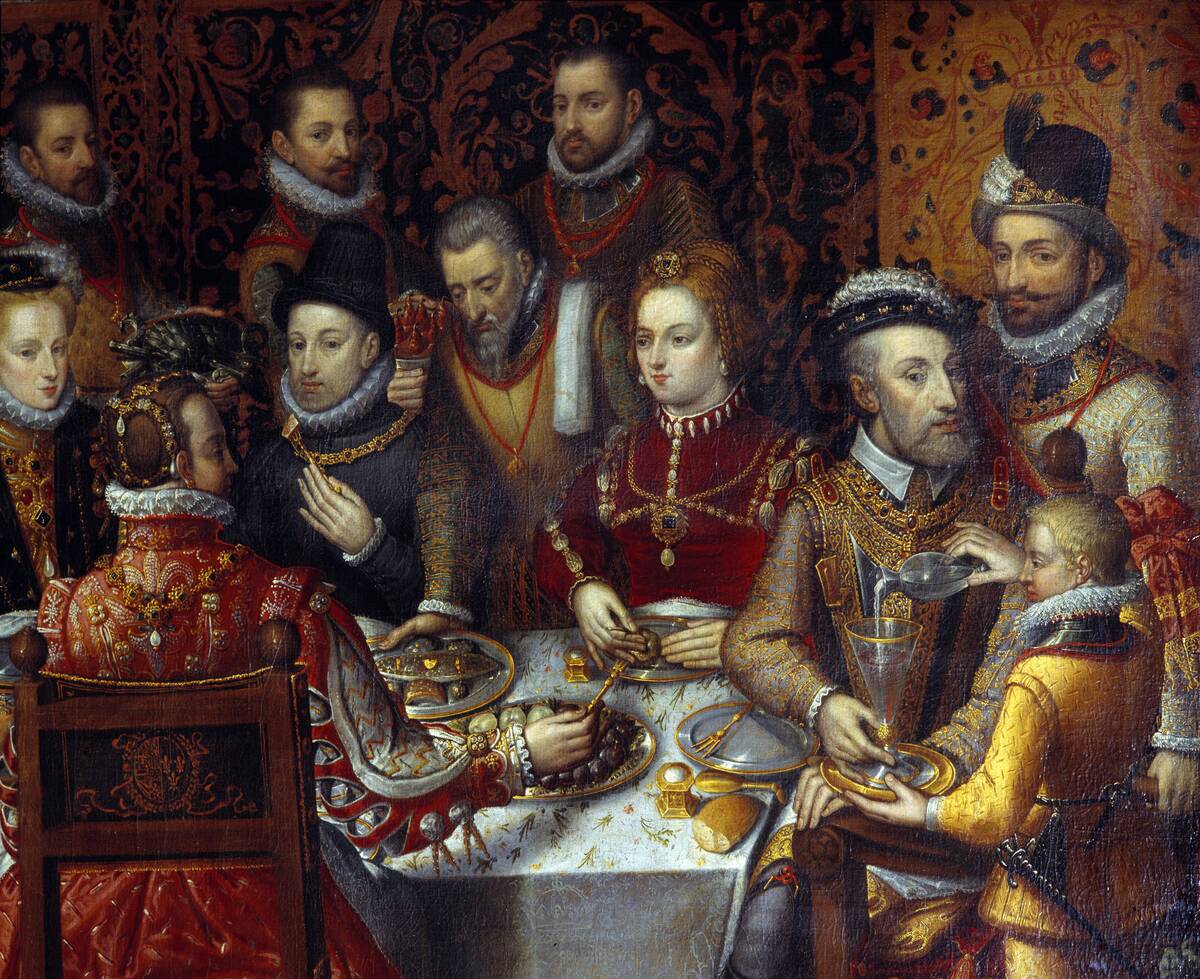

The Renaissance, spanning the 14th to 17th centuries, was a vibrant period of rebirth in art, science, and culture. Driven by a renewed interest in classical learning, it saw the emergence of figures like Leonardo da Vinci and Galileo Galilei.
This era celebrated human potential and individual achievement, leading to significant advances in anatomy, astronomy, and physics. The Renaissance laid the groundwork for the modern world, heralding a shift from religious to secular perspectives in education and thought.
The Printing Press: Spreading Knowledge Far and Wide
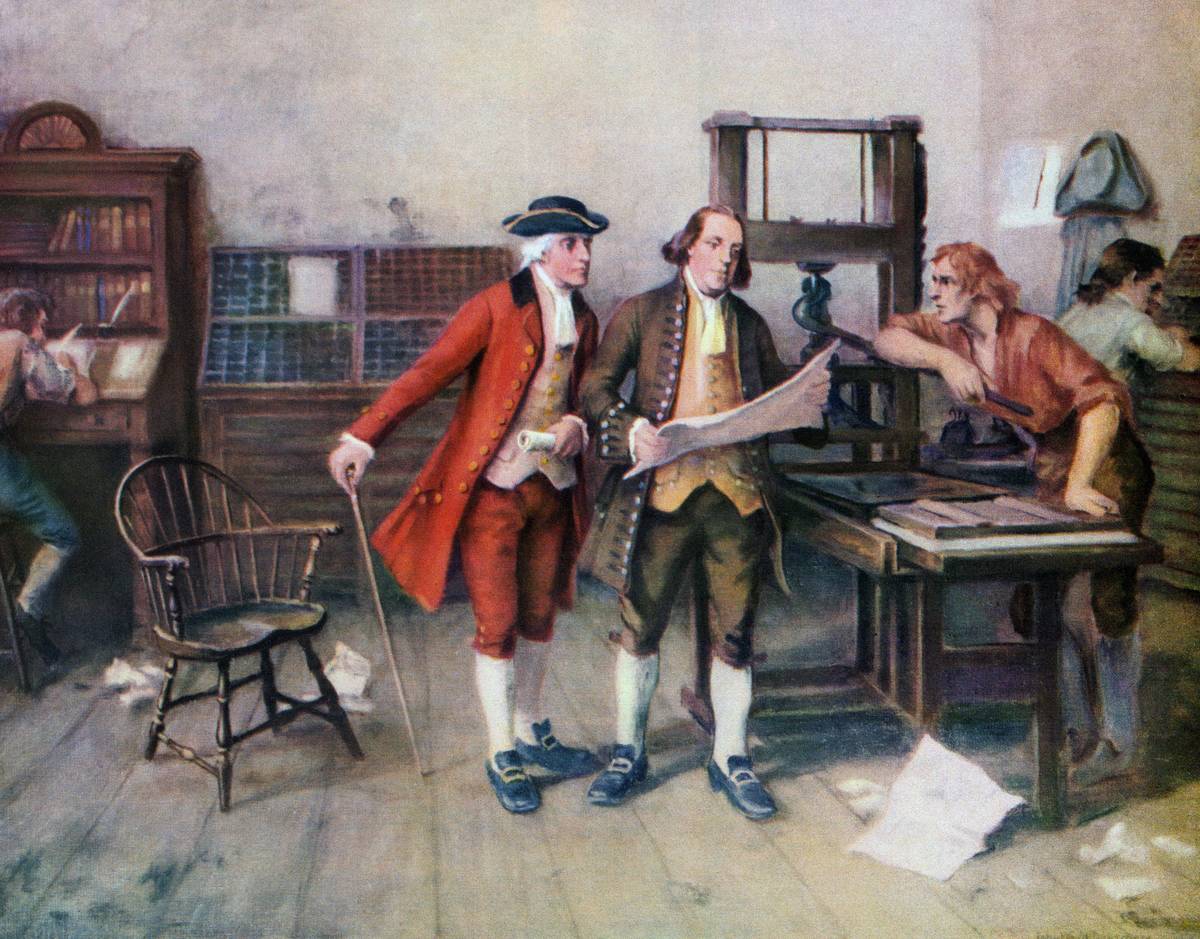

The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century was a catalyst for mass communication. It democratized knowledge by making books more accessible and affordable, fueling the spread of ideas and literacy.
The printing press played a crucial role in the Reformation and the Scientific Revolution, enabling thinkers to disseminate their work widely. It marked a turning point in history, transforming how information was shared and helping to usher in the modern era of enlightenment.
The Industrial Revolution: Gears of Progress
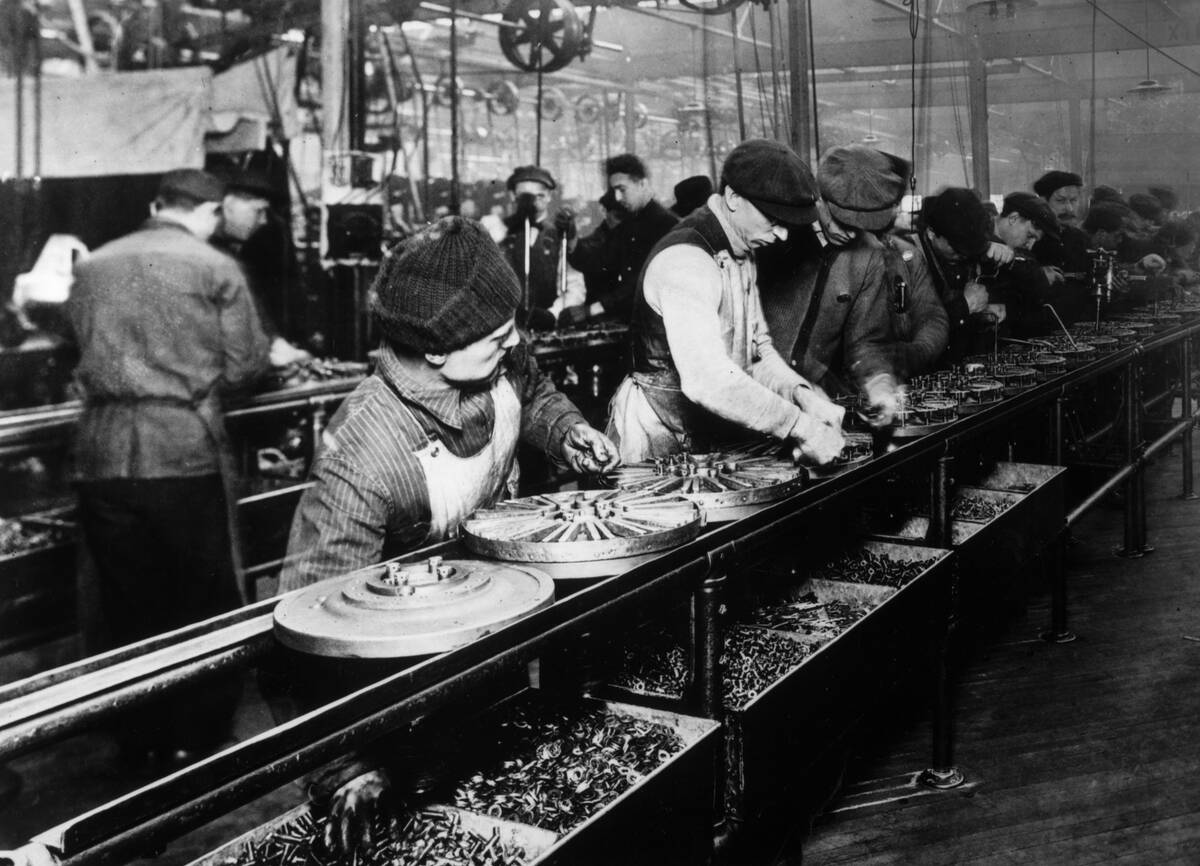

The Industrial Revolution, beginning in the late 18th century, transformed societies from agrarian to industrial powerhouses. Driven by innovations like the steam engine and mechanized looms, it changed how goods were produced and economies structured. Urbanization increased as people flocked to cities for factory jobs, shifting social dynamics.
This period also saw advancements in transportation and communication, such as railways and telegraphs, which connected the world in unprecedented ways, setting the stage for future technological leaps.
The Age of Electricity: Lighting Up the World

Electricity emerged as a transformative force in the late 19th century, illuminating homes and powering machinery. Thomas Edison’s invention of the practical lightbulb and Nikola Tesla’s work on alternating current paved the way for widespread electrification.
Electricity revolutionized industries, improved living standards, and created new forms of entertainment, like radio and cinema. This era marked a shift in how people lived and worked, with electricity becoming a fundamental part of modern life, driving innovation and connectivity.
The Automobile: Driving Forward
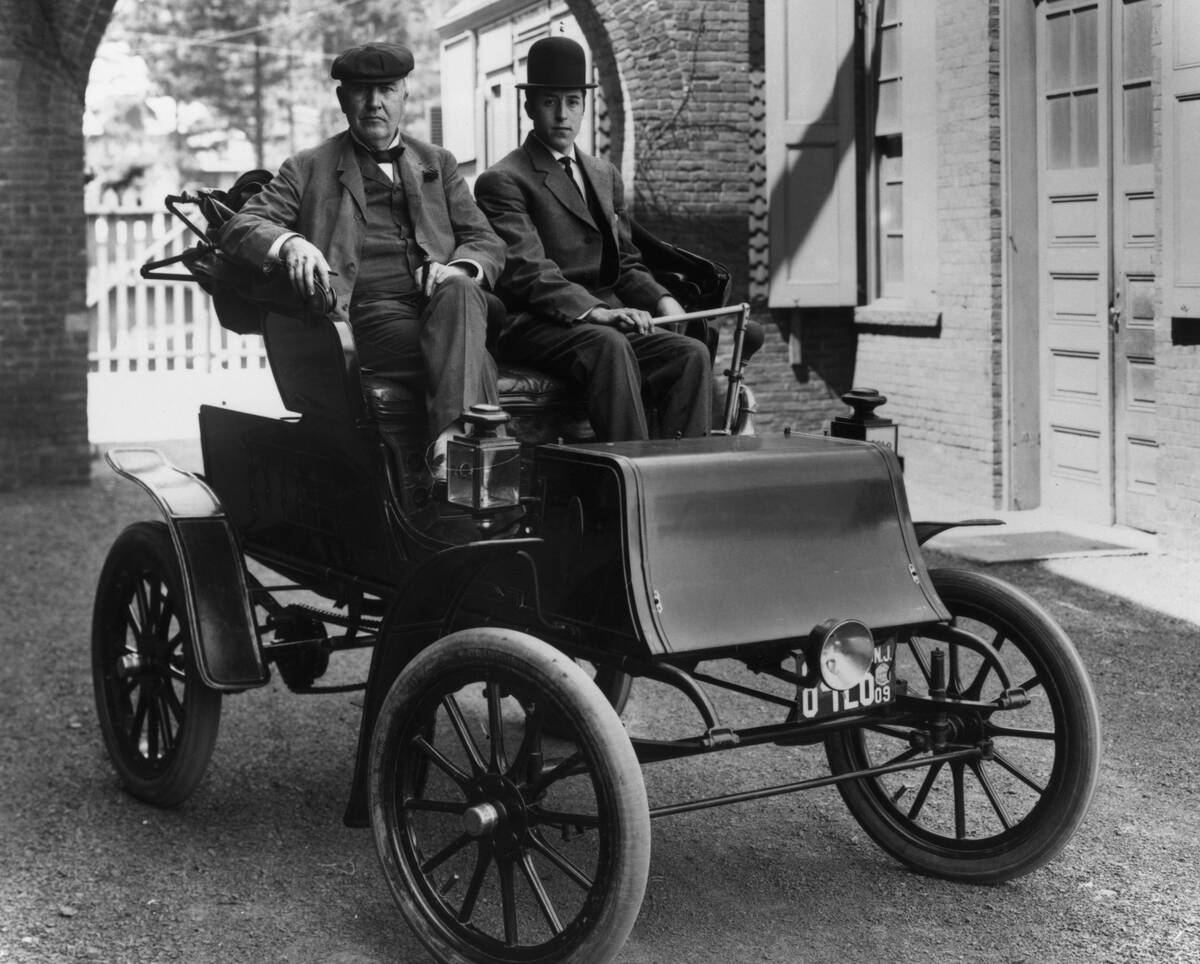

The automobile, a symbol of freedom and progress, began its journey in the late 19th century. Pioneers like Karl Benz and Henry Ford transformed transportation with innovations like the internal combustion engine and assembly line production. Cars revolutionized personal mobility, reshaping cities and economies.
They enabled the development of suburbs and the interstate highway system, changing how people traveled and lived. The automobile industry became a cornerstone of economic growth, influencing culture and society on a global scale.
The Digital Revolution: From Computers to the Internet
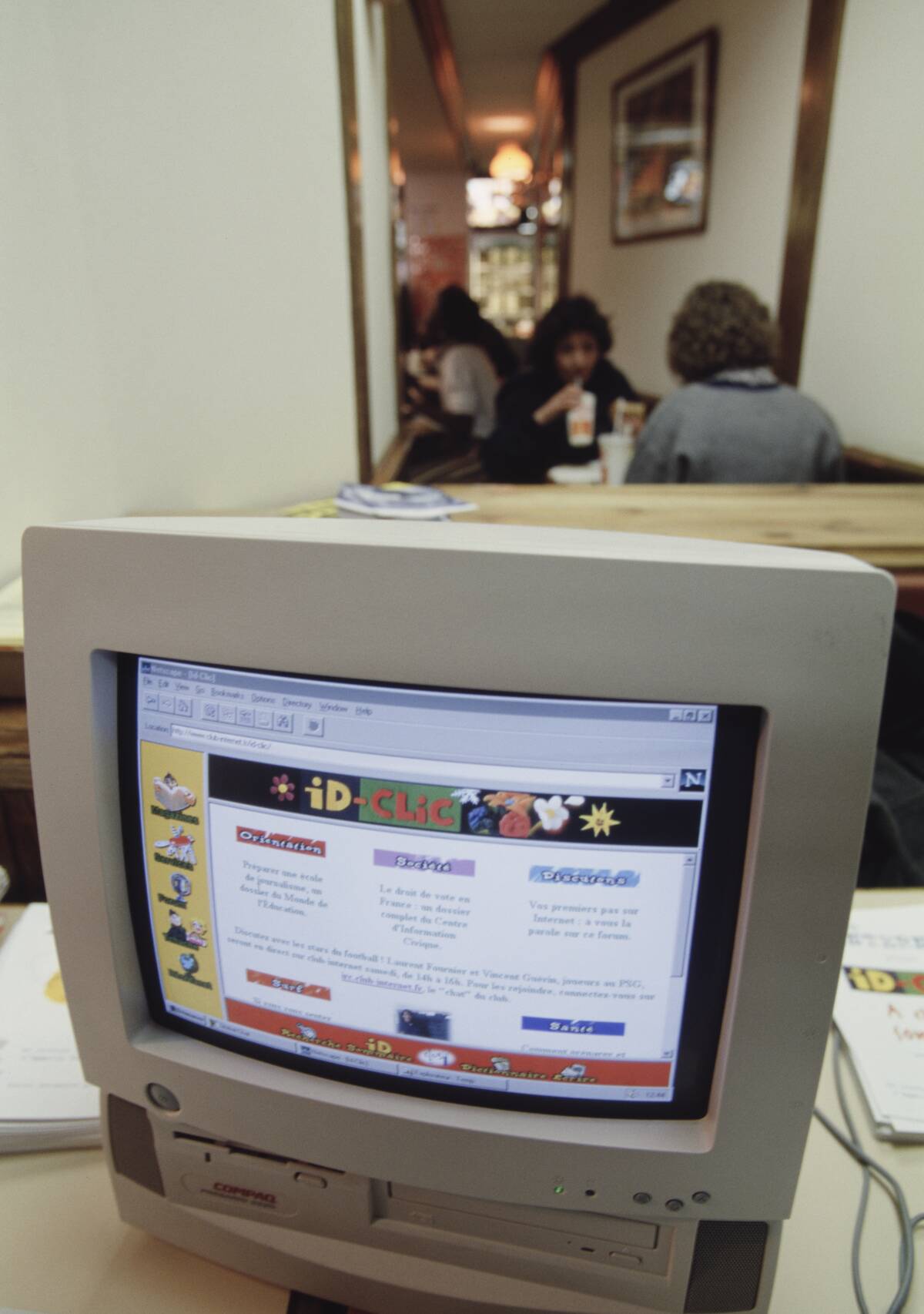

The Digital Revolution, spanning from the late 20th century to today, transformed how we communicate, work, and entertain ourselves. The invention of the microprocessor and personal computers made technology accessible to the masses.
The internet connected the world, creating a global village and democratizing information. This era saw the rise of social media, e-commerce, and digital communication, reshaping industries and daily life. The digital landscape continues to evolve, with innovations like cloud computing and artificial intelligence at the forefront.
The Rise of Biotechnology: Engineering Life

Biotechnology, a frontier of modern science, is unlocking the mysteries of life itself. Advances in genetic engineering and CRISPR technology have opened new possibilities for medicine, agriculture, and beyond.
Scientists can now edit genes with precision, leading to breakthroughs in treating genetic disorders and developing disease-resistant crops. Biotechnology promises to address global challenges like food security and health, offering innovative solutions that could redefine our relationship with the natural world and improve quality of life.
Renewable Energy: Powering a Sustainable Future
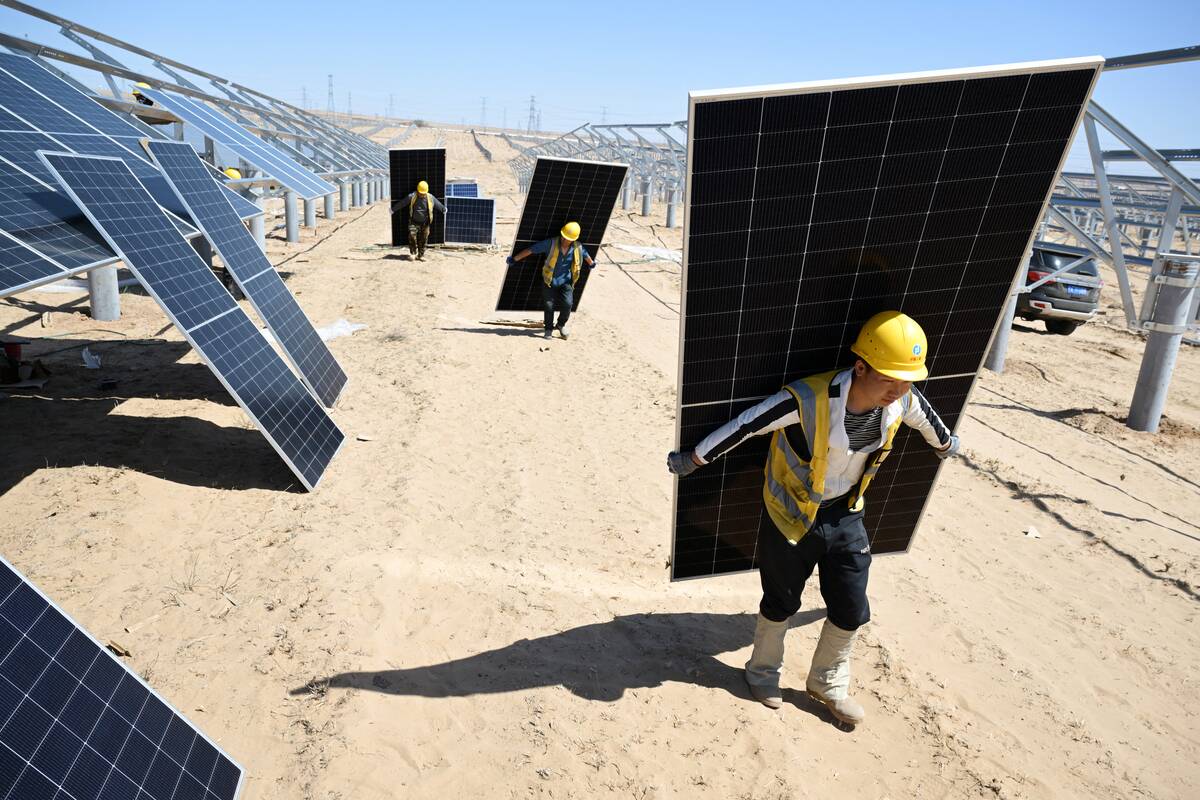

Renewable energy is driving a shift towards sustainability, harnessing natural resources like wind, solar, and hydro power. As concerns about climate change and fossil fuel depletion grow, renewables offer a cleaner, more sustainable energy solution.
Technological advancements have made renewable energy more efficient and cost-effective, enabling its integration into power grids worldwide. This transition is crucial for reducing carbon emissions and combating global warming, paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient future.
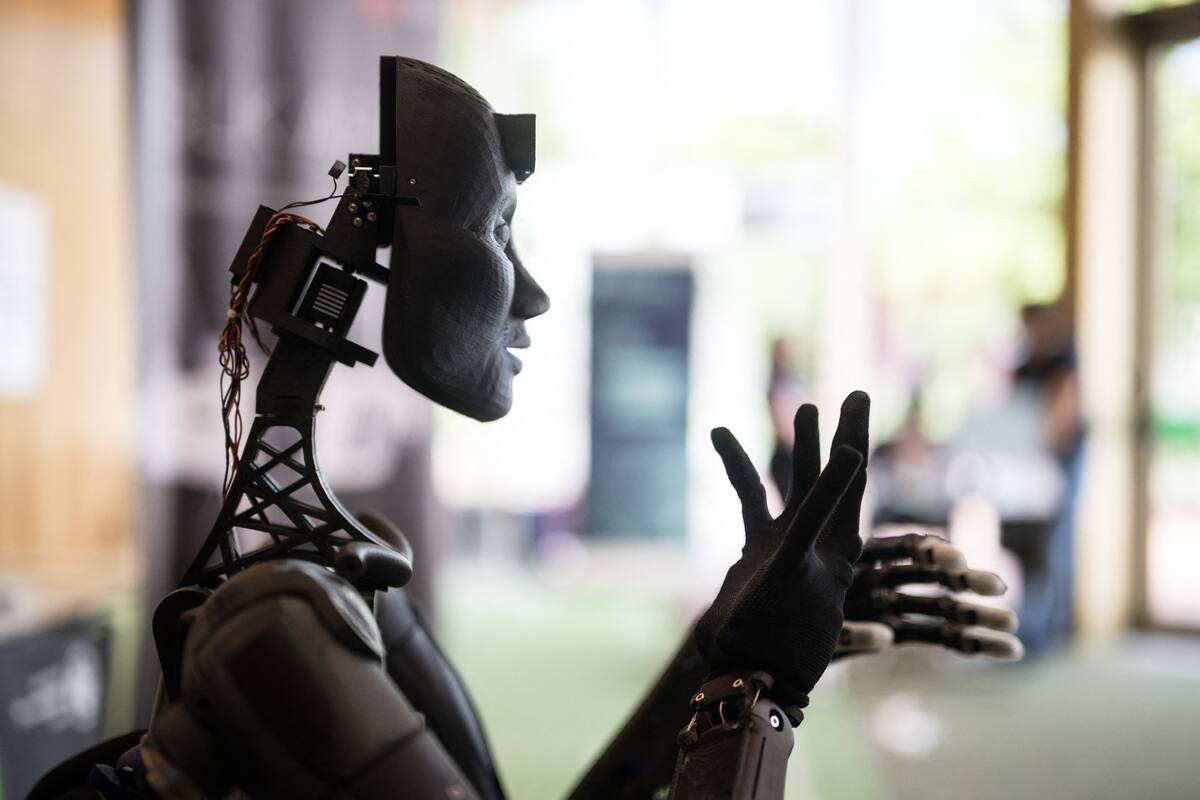
The AI Revolution: Machines That Think
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing industries by enabling machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. From voice assistants to autonomous vehicles, AI is transforming how we interact with technology and each other.
Machine learning and neural networks allow computers to learn from data, improving efficiency and decision-making. While AI offers immense potential for innovation and economic growth, it also raises ethical and societal questions about privacy, employment, and the nature of intelligence itself.
Reflecting on Patterns: How History Shapes Innovation

Looking back at the cycles of innovation, we see a pattern of human ingenuity responding to challenges and opportunities. Each era builds on the past, with technology and ideas evolving in response to societal needs.
Understanding these patterns helps us anticipate future trends and navigate the complexities of modern life. As we continue to innovate, reflecting on history reminds us of the power of creativity and collaboration in shaping a better future for all.




