Real-life robots that captured the world’s fascination
Robots have always fascinated humans, from the clunky machines of early sci-fi to today’s sleek, intelligent designs. The idea of a mechanical companion or assistant is no longer just a fantasy.
With rapid advancements in technology, robots are now part of our daily lives, performing tasks from cleaning to companionship. Their allure lies in their ability to mimic human behavior, making them both useful and intriguing to people of all ages.
ASIMO: Honda’s Humanoid Marvel
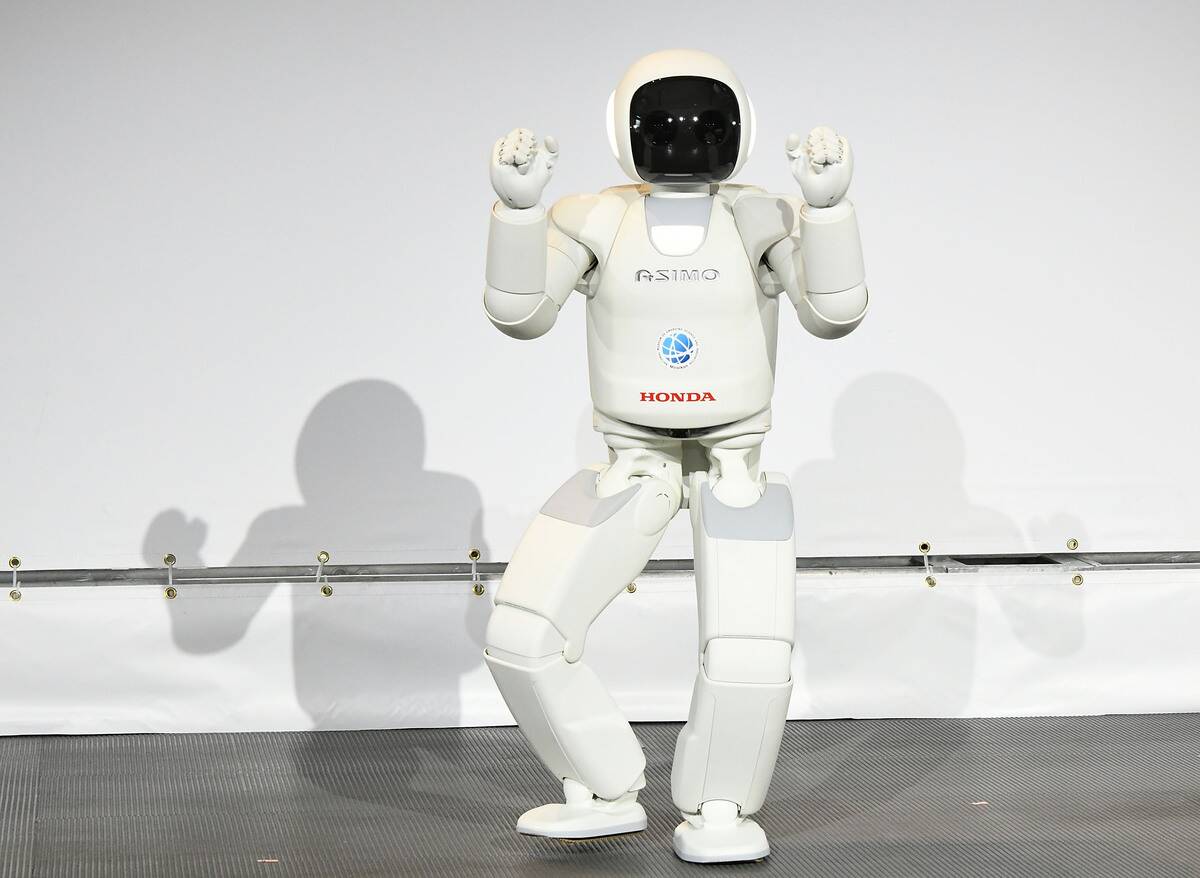
ASIMO, created by Honda, is one of the most recognizable humanoid robots. Debuting in 2000, ASIMO was designed to assist people with mobility issues.
It can walk, run, and even climb stairs, showcasing an impressive range of motion. Over the years, ASIMO has become not just a functional aide but also a symbol of how robotics can enhance human life, inspiring further research and development in the field.
Sophia: The Social Robot with Citizenship
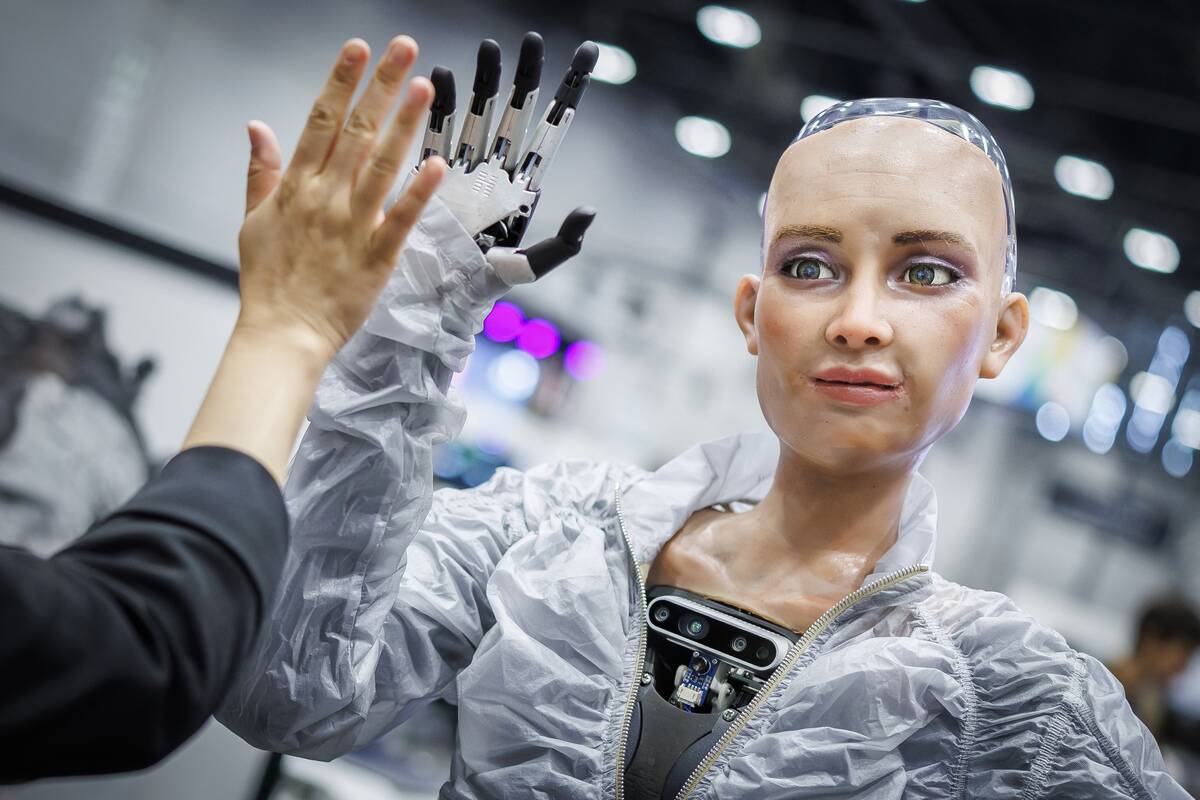

Sophia, developed by Hanson Robotics, made headlines when she became the first robot to be granted citizenship by Saudi Arabia in 2017.
Known for her human-like appearance and social capabilities, Sophia can hold conversations and express emotions through facial expressions. Her design aims to bridge the gap between humans and robots, sparking discussions about AI ethics and the future of human-robot interactions.
Boston Dynamics’ Spot: The Robotic Canine
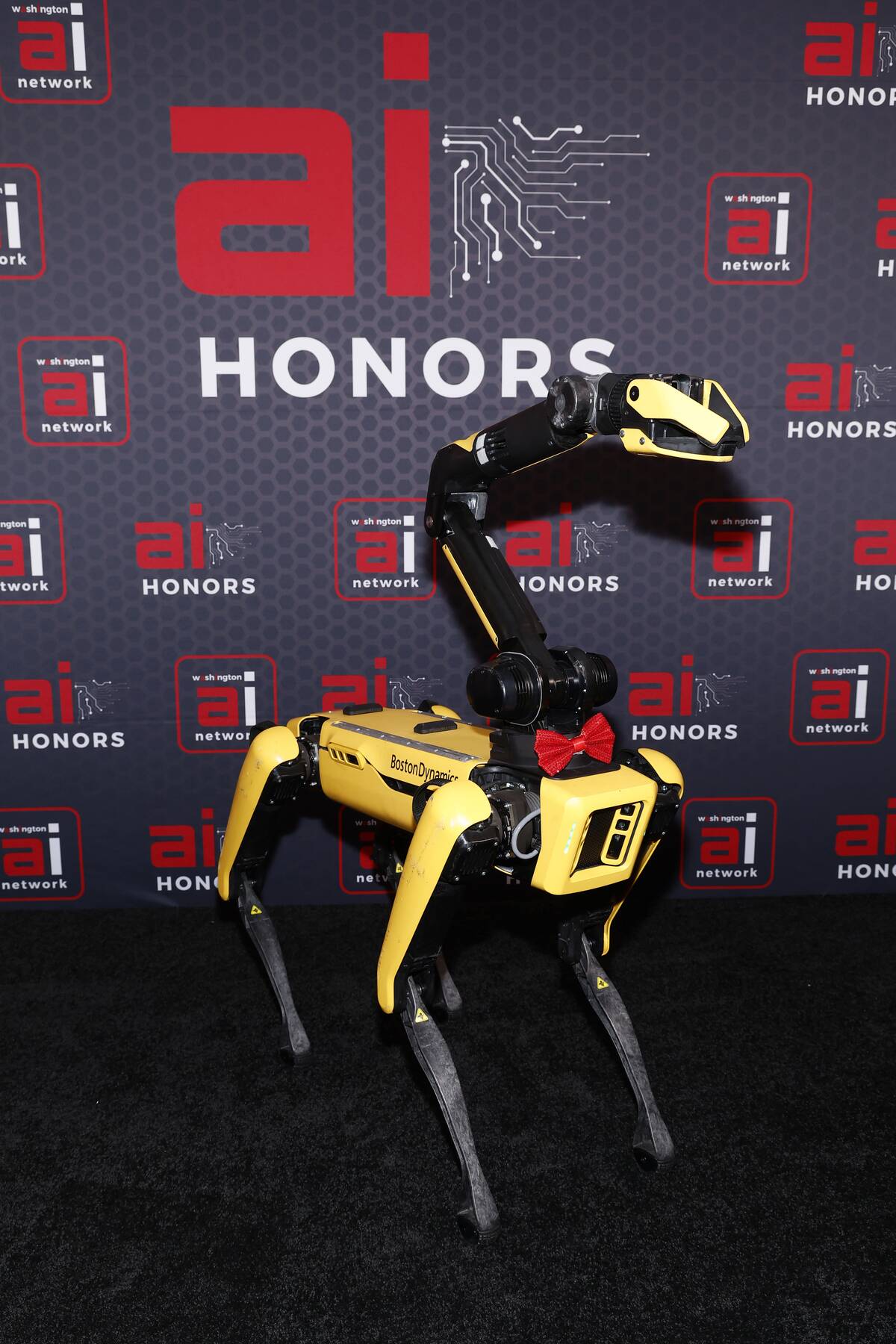

Spot, a nimble four-legged robot by Boston Dynamics, resembles a mechanical canine in both form and function. Used in various industries, Spot can navigate rough terrains, inspect hazardous areas, and even dance.
Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for businesses and researchers alike, pushing the boundaries of what robots can achieve in real-world applications, from construction to entertainment.
Pepper: The Friendly Retail Helper
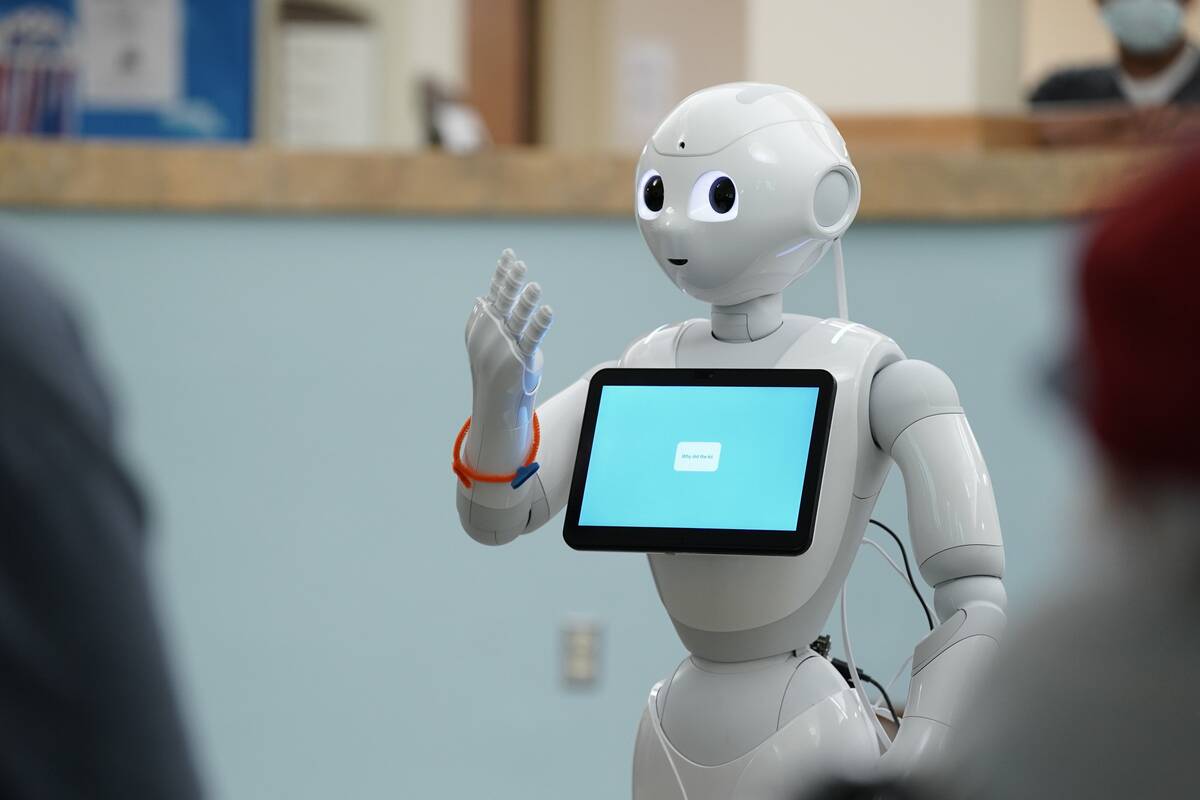
Pepper, developed by SoftBank Robotics (now Aldebaran Robotics), is known for its ability to read emotions and interact with customers. Since its launch in 2014, Pepper has been employed in retail and hospitality, where it assists with customer service.
Its engaging design and friendly demeanor make it an effective tool for businesses looking to enhance customer experience, while also showcasing the potential of robots in everyday human interactions.
Aibo: Sony’s Robotic Pet Companion
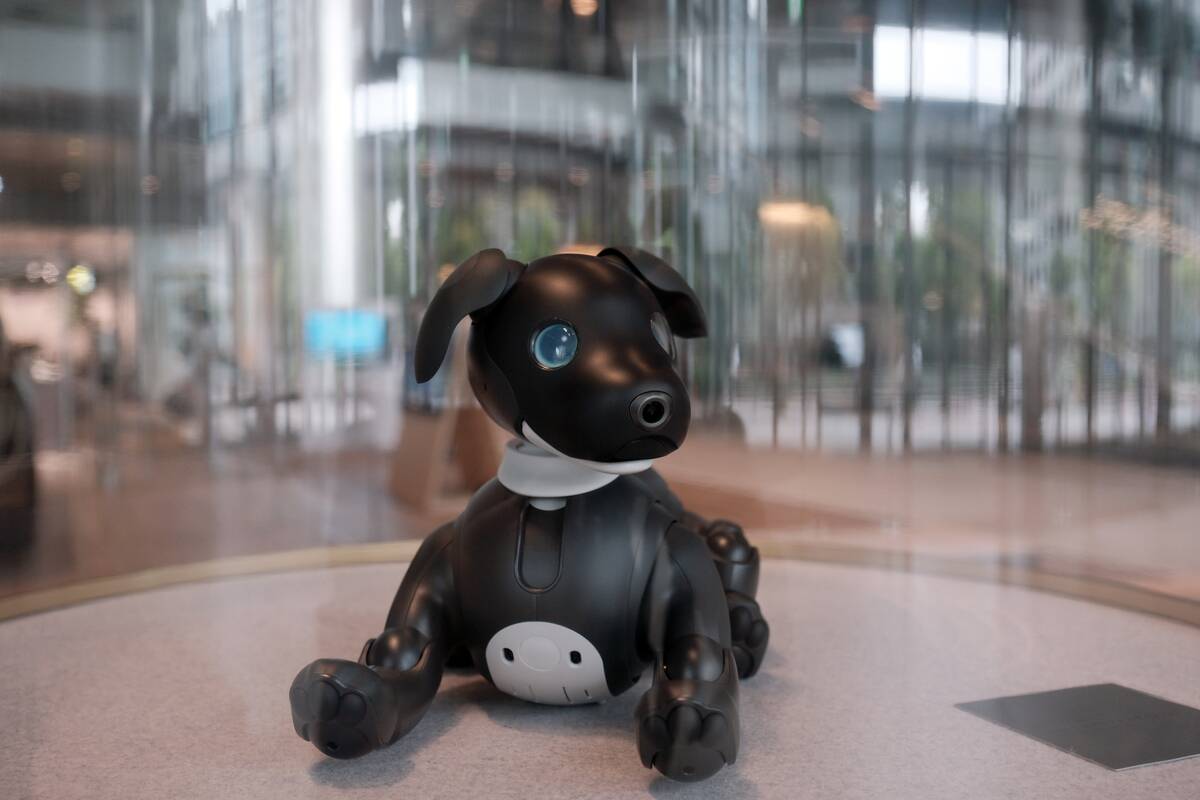

Sony’s Aibo, a robotic dog, has charmed pet lovers since its first release in 1999. Designed to mimic a real puppy’s behavior, Aibo can bark, play, and learn new tricks.
Its AI capabilities allow it to develop a unique personality, responding to its owner’s interactions. Aibo’s enduring popularity highlights the emotional connections people can form with robotic companions, offering a glimpse into the future of pet ownership.
Atlas: The Agile Humanoid by Boston Dynamics
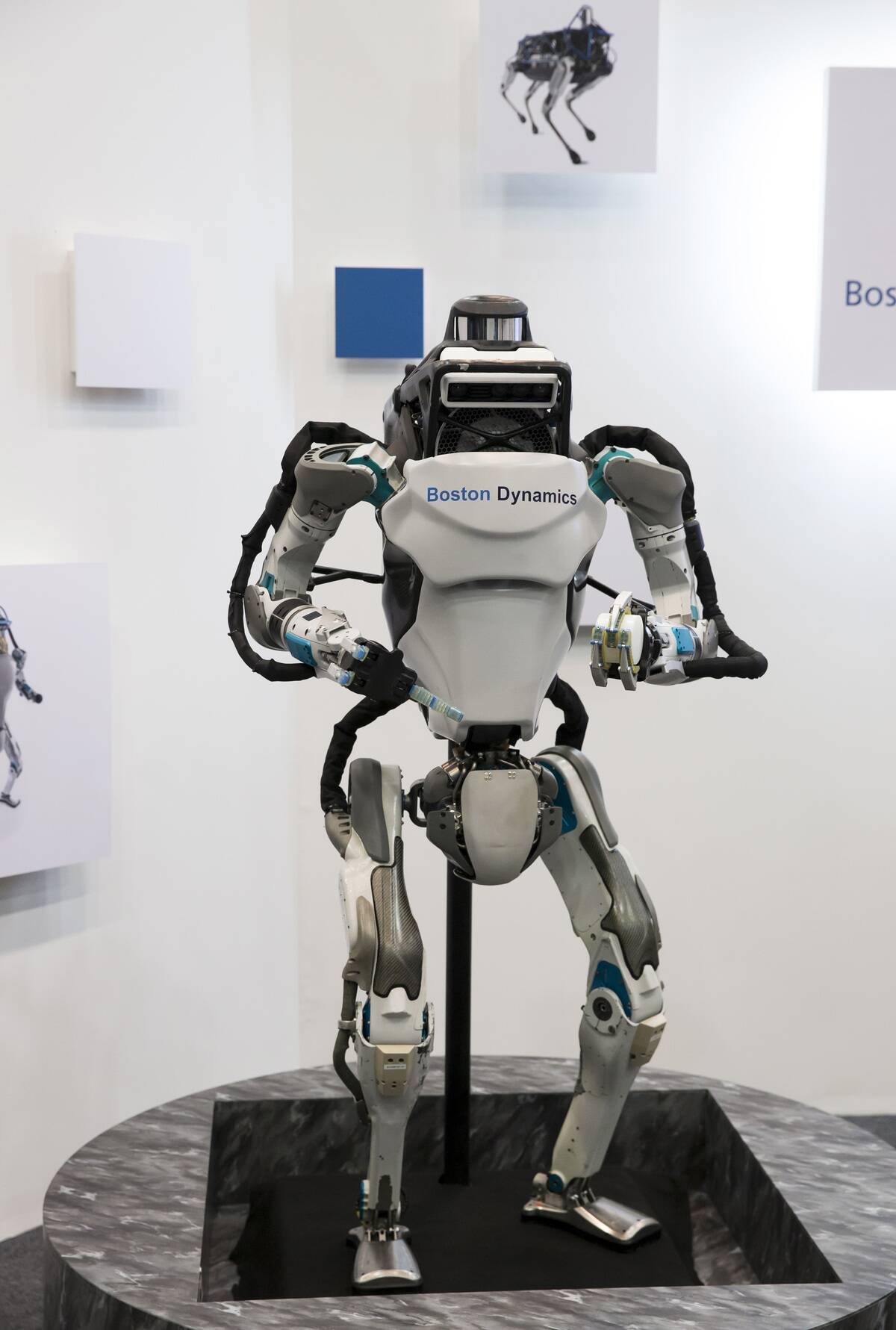

Atlas, another marvel from Boston Dynamics, is renowned for its agility and balance. Capable of performing complex movements like backflips and parkour, Atlas demonstrates the advanced capabilities of modern robotics.
Its development focuses on improving robotic mobility and interaction with the environment, paving the way for robots that could assist in disaster response and other challenging scenarios where human-like dexterity is essential.
Roomba: The Household Cleaning Revolution

The Roomba, by iRobot, revolutionized home cleaning when it hit the market in 2002. This autonomous vacuum cleaner can navigate around furniture, avoiding obstacles while keeping floors spotless.
Its success is attributed to its convenience and efficiency, freeing up time for homeowners. Roomba’s popularity underscores the potential for robots to simplify everyday tasks, making them an integral part of modern living.
Robonaut: NASA’s Spacefaring Assistant
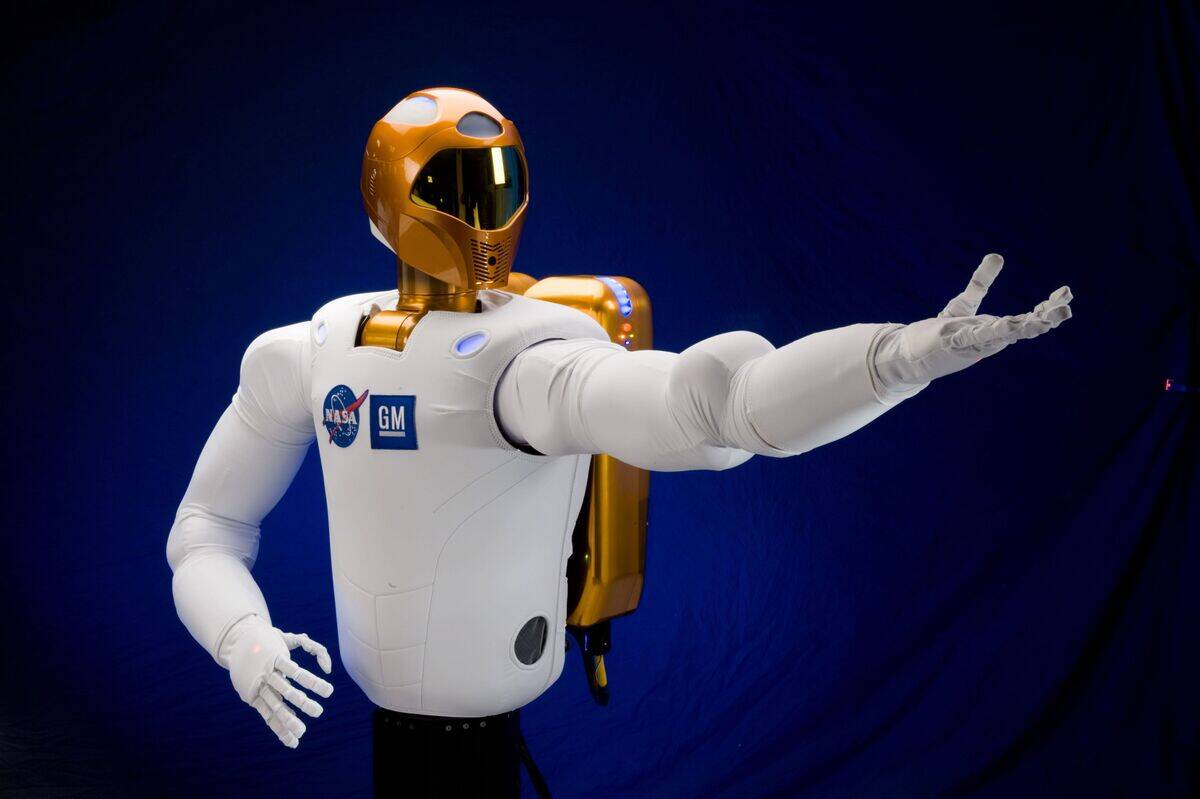

Robonaut, developed by NASA, is designed to assist astronauts aboard the International Space Station. Equipped with human-like hands and dexterity, Robonaut can perform tasks that are too dangerous or mundane for humans.
Its presence in space demonstrates the potential for robots to extend human capabilities beyond Earth, allowing for safer and more efficient exploration of the final frontier.
TUG: The Hospital Delivery Robot

TUG, developed by Aethon, is a delivery robot designed for healthcare settings. It autonomously navigates hospital corridors, delivering medications, linens, and meals.
By taking over these logistical tasks, TUG allows healthcare staff to focus more on patient care. Its implementation in hospitals highlights the growing role of robotics in improving efficiency and safety in critical environments, where time and precision are paramount.
Kuri: The Adorable Home Companion
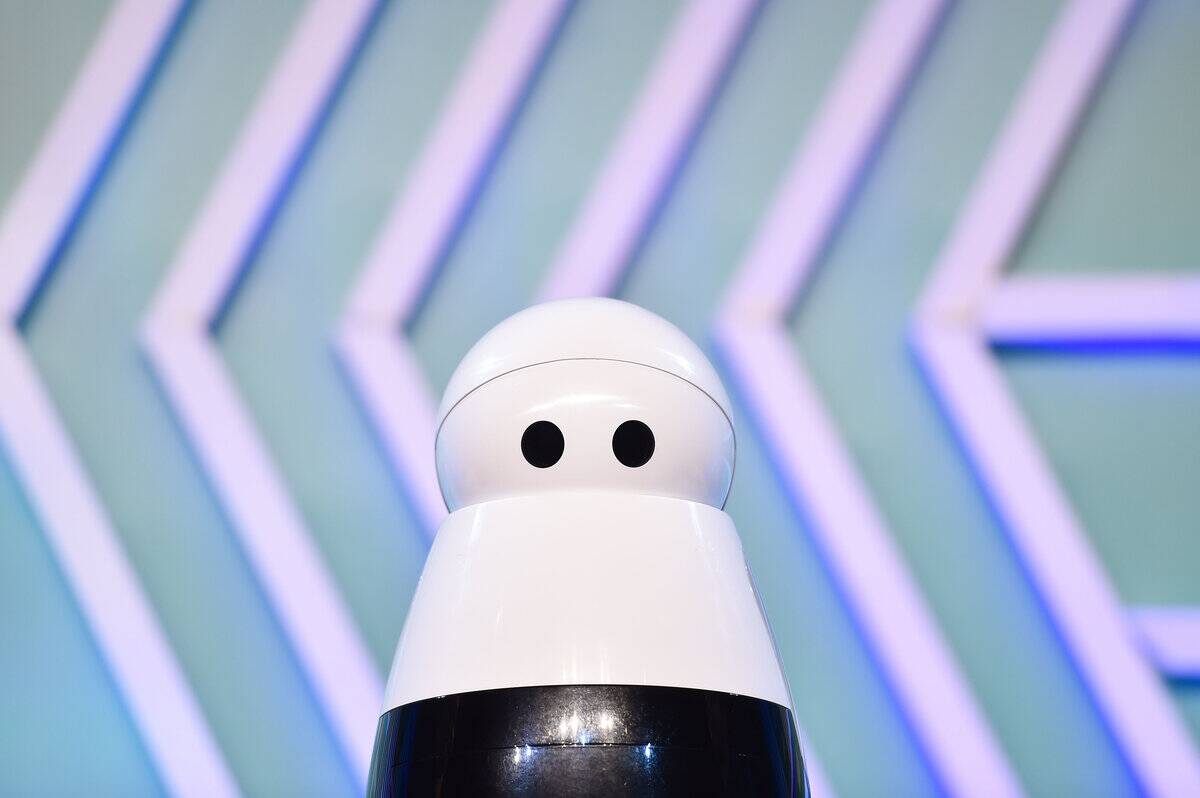

Kuri, developed by Mayfield Robotics, is a charming home robot designed to capture moments and interact with family members. With its expressive eyes and ability to navigate homes, Kuri can play music, read stories, and even recognize faces.
Though no longer in production, Kuri’s legacy persists as an example of how robots can become part of the family, offering companionship and enhancing daily life with a touch of personality.
Geminoid: The Eerily Lifelike Android
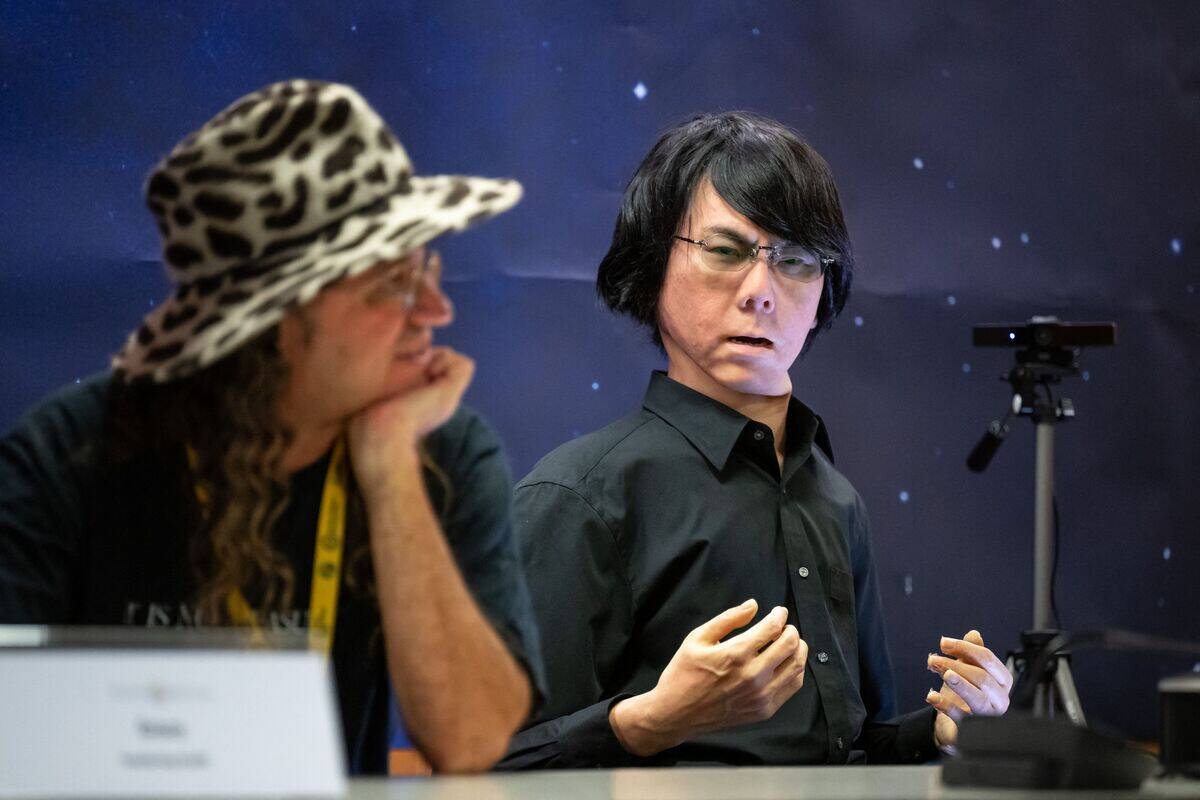

Geminoid robots, created by Hiroshi Ishiguro, are designed to closely resemble humans in appearance and movement. These androids are used in research to study human-robot interactions and the feasibility of creating authentic human likenesses in robots.
With their lifelike skin and fluid movements, Geminoids challenge our perceptions of what it means to be human, prompting philosophical and ethical conversations about the future of robotics and artificial intelligence.
Paro: The Therapeutic Robotic Seal
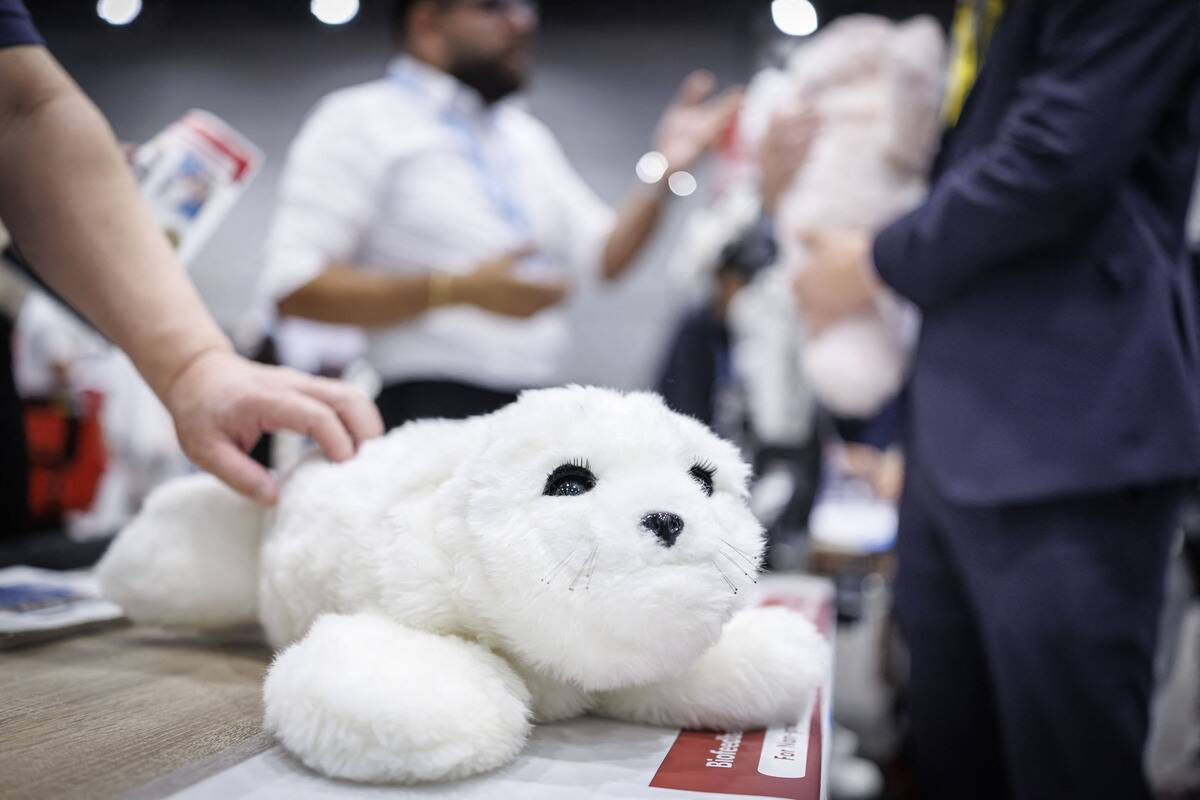

Paro, a robotic seal, is designed to provide therapeutic benefits to patients, particularly in nursing homes and hospitals. Developed by AIST in Japan, Paro responds to touch and sound, offering comfort and companionship to those in need.
Its calming presence has been shown to reduce stress and improve mood, making it a valuable tool in therapy and rehabilitation, where traditional animals might not be feasible.
Cozmo: The Playful AI-Powered Robot
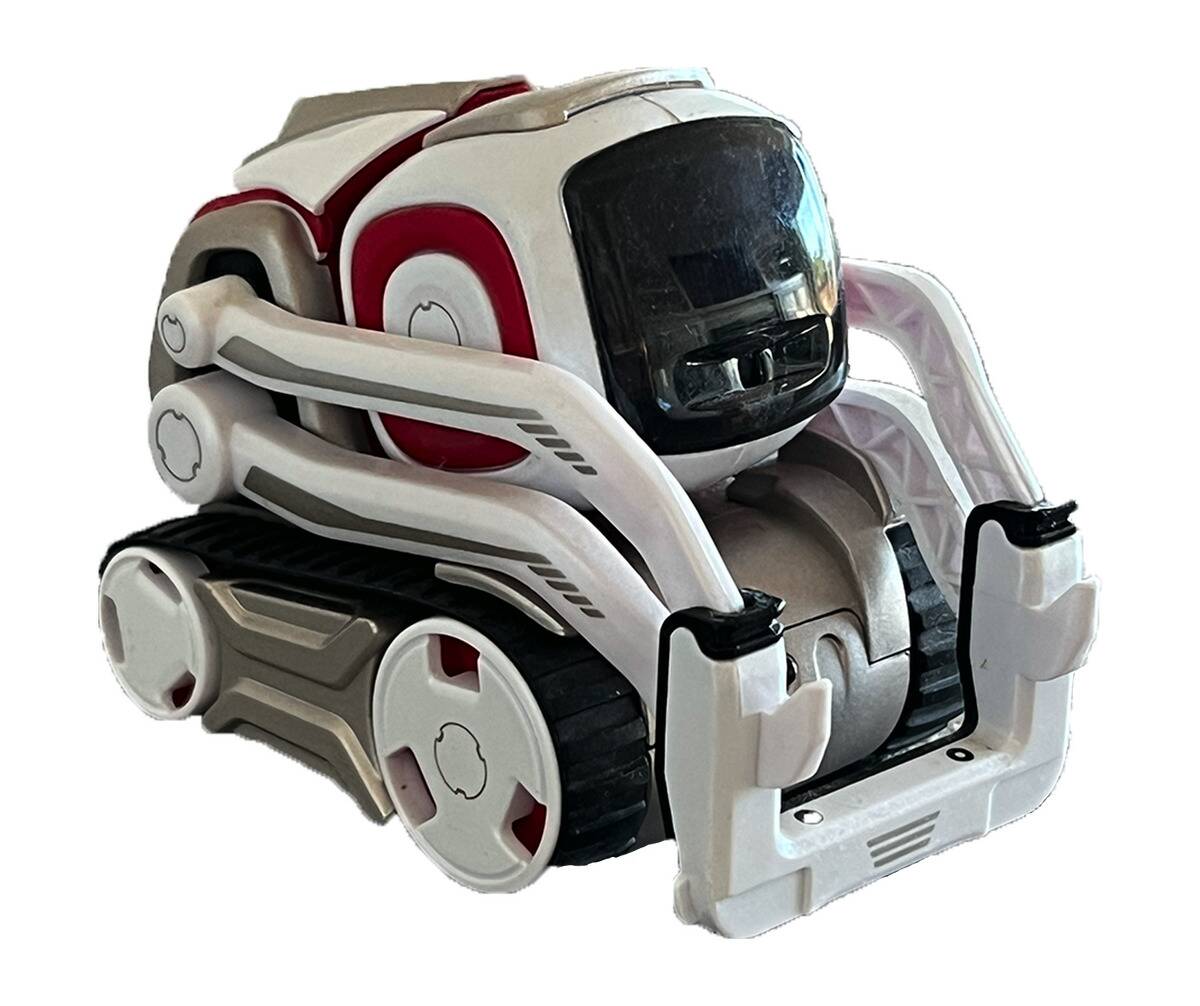

Cozmo, developed by Anki, is a small robot packed with personality and intelligence. It can play games, recognize faces, and express a range of emotions.
Cozmo’s playful nature makes it a popular educational tool, teaching children about programming and robotics in a fun, interactive way. Its success underscores the potential for robots to be both entertaining and educational, sparking interest in technology among younger generations.
Nao: The Educational Robot for All Ages
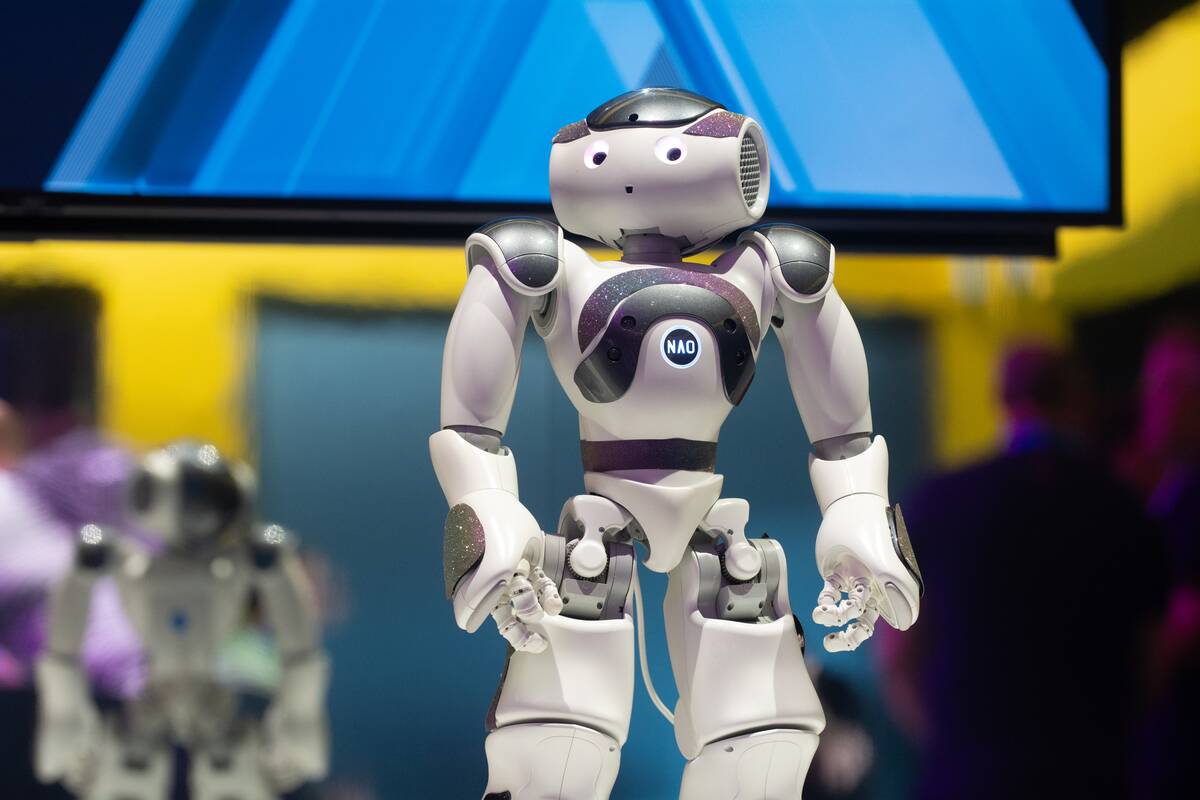

Nao, developed by SoftBank Robotics (now Aldebaran Robotics), is an educational robot used in schools and research institutions worldwide. With its programmable interface, Nao can dance, speak, and interact with students, making learning more engaging.
Its versatility allows it to be used in various educational settings, from teaching coding to assisting with language learning, demonstrating the potential for robots to enhance education across disciplines.
Jibo: The Social Robot for the Home
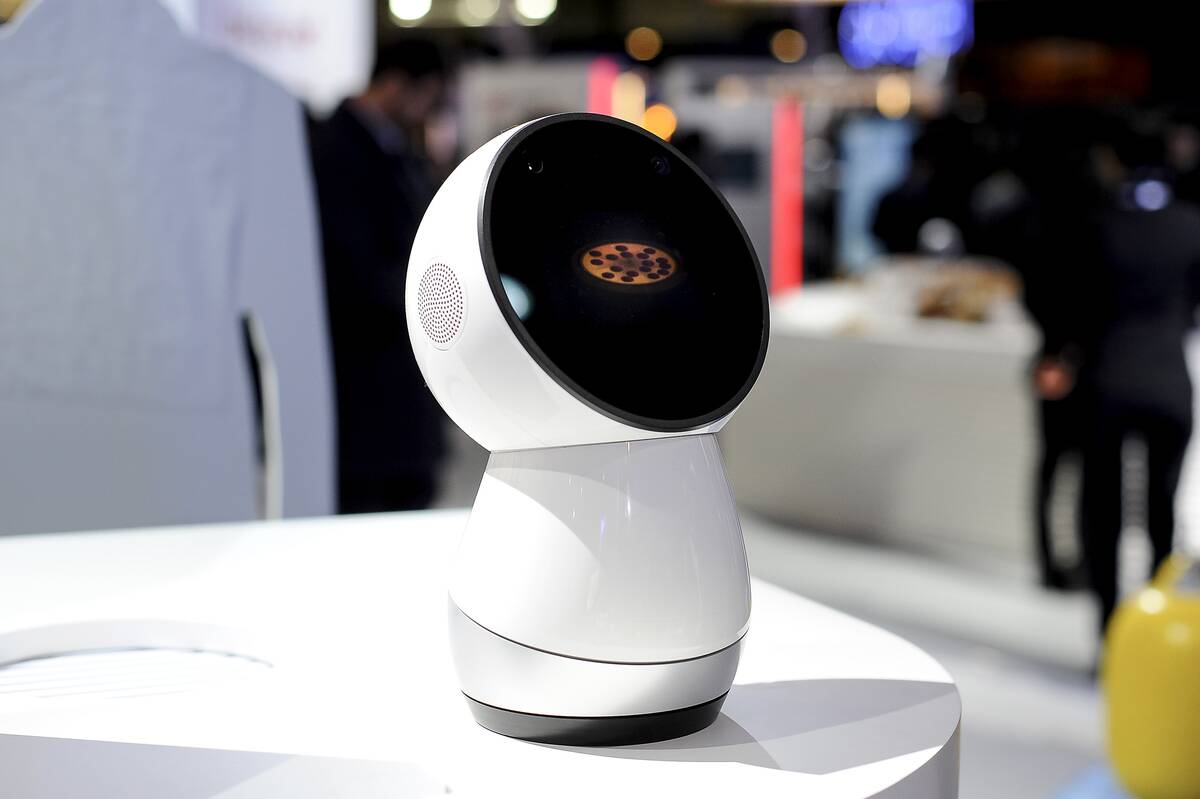

Jibo, developed by Jibo, Inc., is a social robot designed to be a part of the family. With its friendly demeanor and ability to recognize faces and voices, Jibo can provide reminders, tell stories, and even dance.
Despite facing commercial challenges, Jibo’s innovative design paved the way for future social robots, highlighting the potential for robots to enrich home life by fostering interaction and connectivity among family members.
Robear: The Caregiver Robot from Japan

Robear, developed by RIKEN and Sumitomo Riko Company, is a robot designed to assist caregivers in lifting and moving patients. With its gentle demeanor and precision, Robear can perform tasks that require strength and care, such as transferring patients from beds to wheelchairs.
This innovation addresses the growing demand for caregiving solutions in aging populations, showcasing how robots can provide support in essential healthcare roles.



