Photos of sunken civilizations revealed by technology
Imagine ancient cities shrouded in mystery beneath the ocean’s waves, forgotten yet preserved in time. These sunken civilizations hold untold secrets of human history and ingenuity. For centuries, their stories have remained hidden, only whispered about in myths and legends.
However, with modern technology, we’re beginning to unveil these secrets, diving deeper into our past than ever before. Join us as we explore the fascinating world of underwater archaeology and the discoveries that challenge what we thought we knew about ancient societies.
The Rise of Deep-Sea Drones in Archaeology
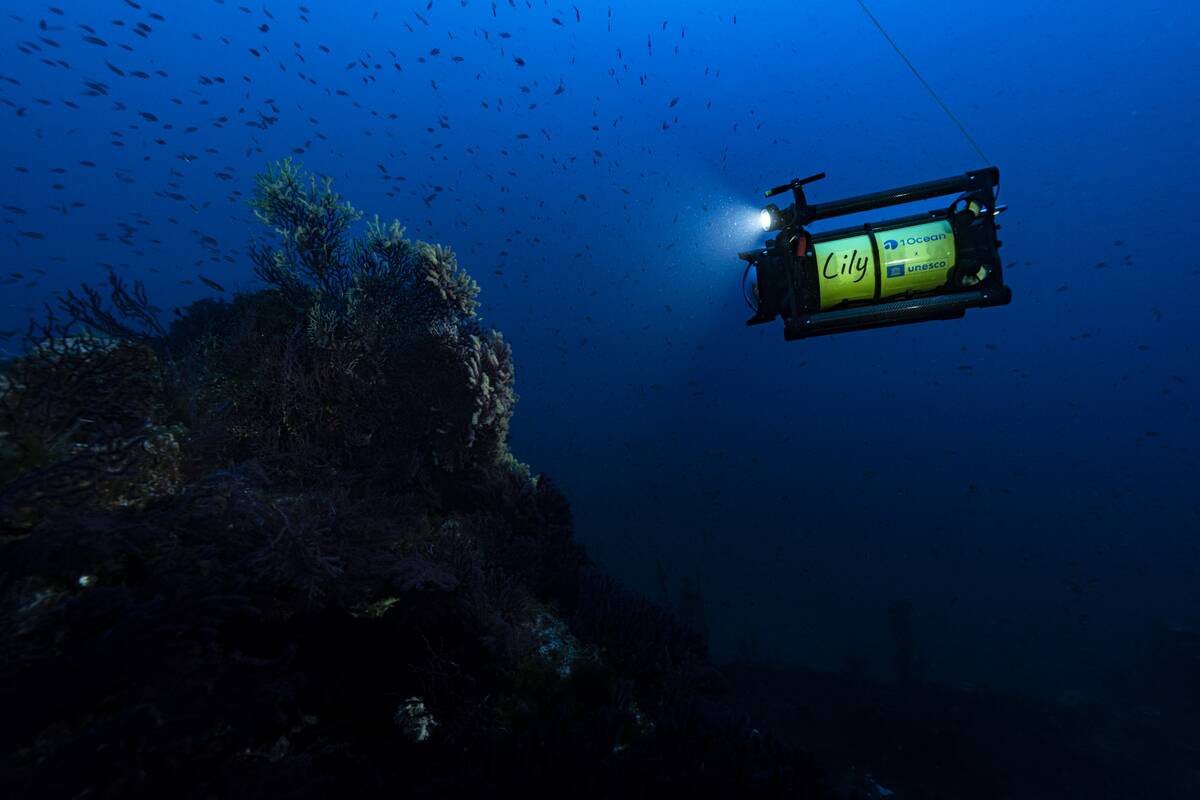

As the ocean’s depths remain one of the last unexplored frontiers, deep-sea drones have become indispensable tools for archaeologists. These autonomous robots can reach depths that are otherwise inaccessible to humans, capturing high-resolution images and collecting data.
Unlike traditional methods, drones provide a non-invasive way to explore underwater sites, preserving them for future generations. As technology advances, drones become more sophisticated, enabling researchers to uncover more about our submerged past with unprecedented accuracy.
What Exactly Are Sunken Civilizations?
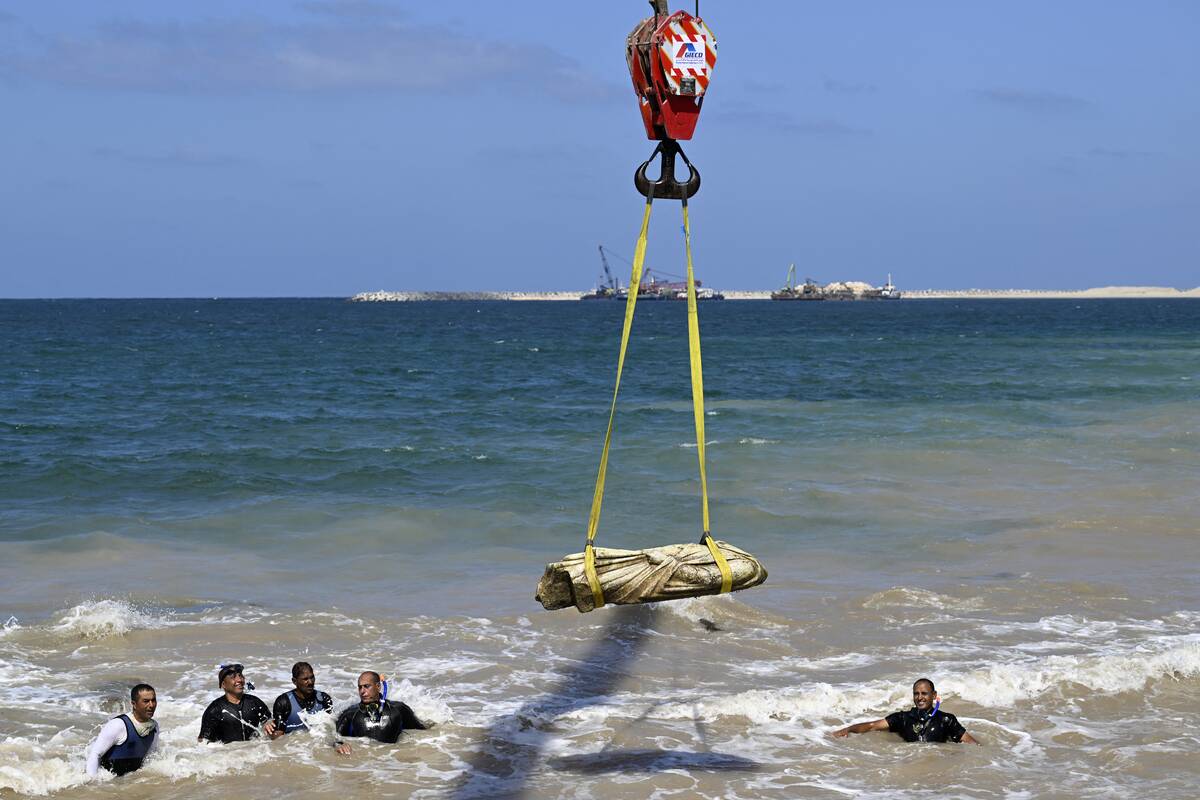

Sunken civilizations refer to communities that were once thriving on land but became submerged due to natural events like sea-level rise or tectonic shifts. These ancient societies, such as those around the Mediterranean and the Caribbean, offer a glimpse into human adaptation and resilience.
Discovering these sites helps historians piece together cultural practices and trade routes of bygone eras, offering a unique perspective on how ancient people interacted with their environment and each other.
A Brief History of Underwater Exploration
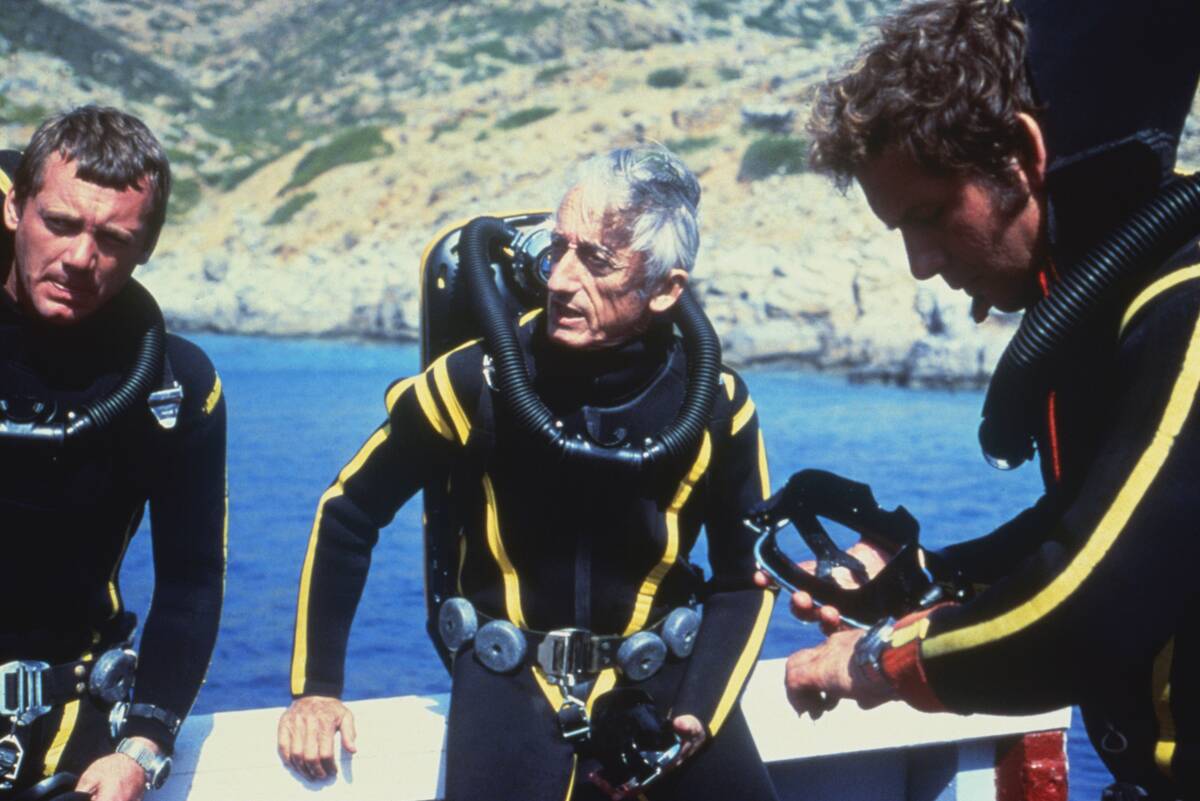

The allure of what lies beneath has captivated explorers for centuries. Early attempts at underwater exploration date back to ancient Greece with diving bells and simple breath-holding.
However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that technological advancements like scuba gear and submersibles allowed for more extensive underwater study. These innovations paved the way for significant discoveries, transforming underwater archaeology from a niche pursuit into a respected scientific discipline.
How Do Deep-Sea Drones Work?
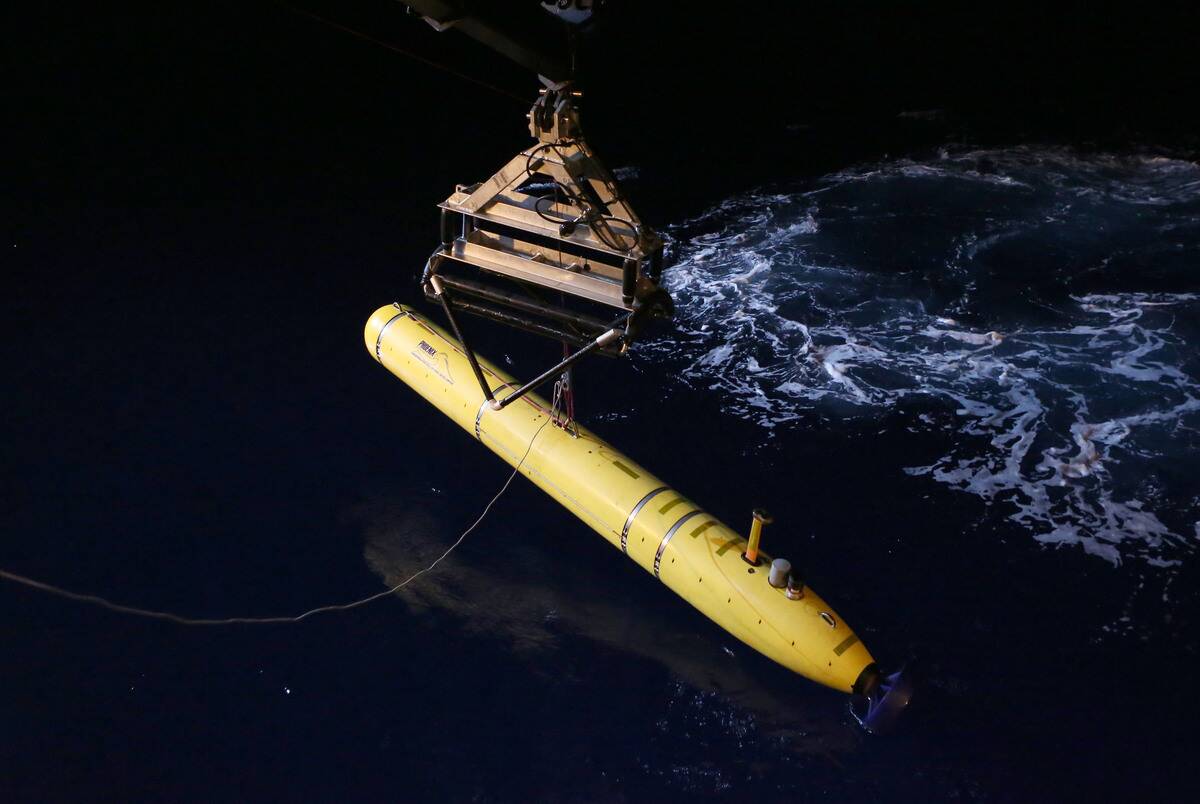

Deep-sea drones, or Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs), are equipped with advanced sonar systems, cameras, and sensors. These devices navigate the ocean floor using pre-programmed routes or real-time control from a research vessel.
With the ability to withstand extreme pressures and temperatures, drones can explore areas previously unreachable, providing valuable data about submerged sites. This technology has revolutionized how archaeologists study underwater environments, reducing risk and increasing efficiency.
Notable Discoveries Made by Deep-Sea Drones
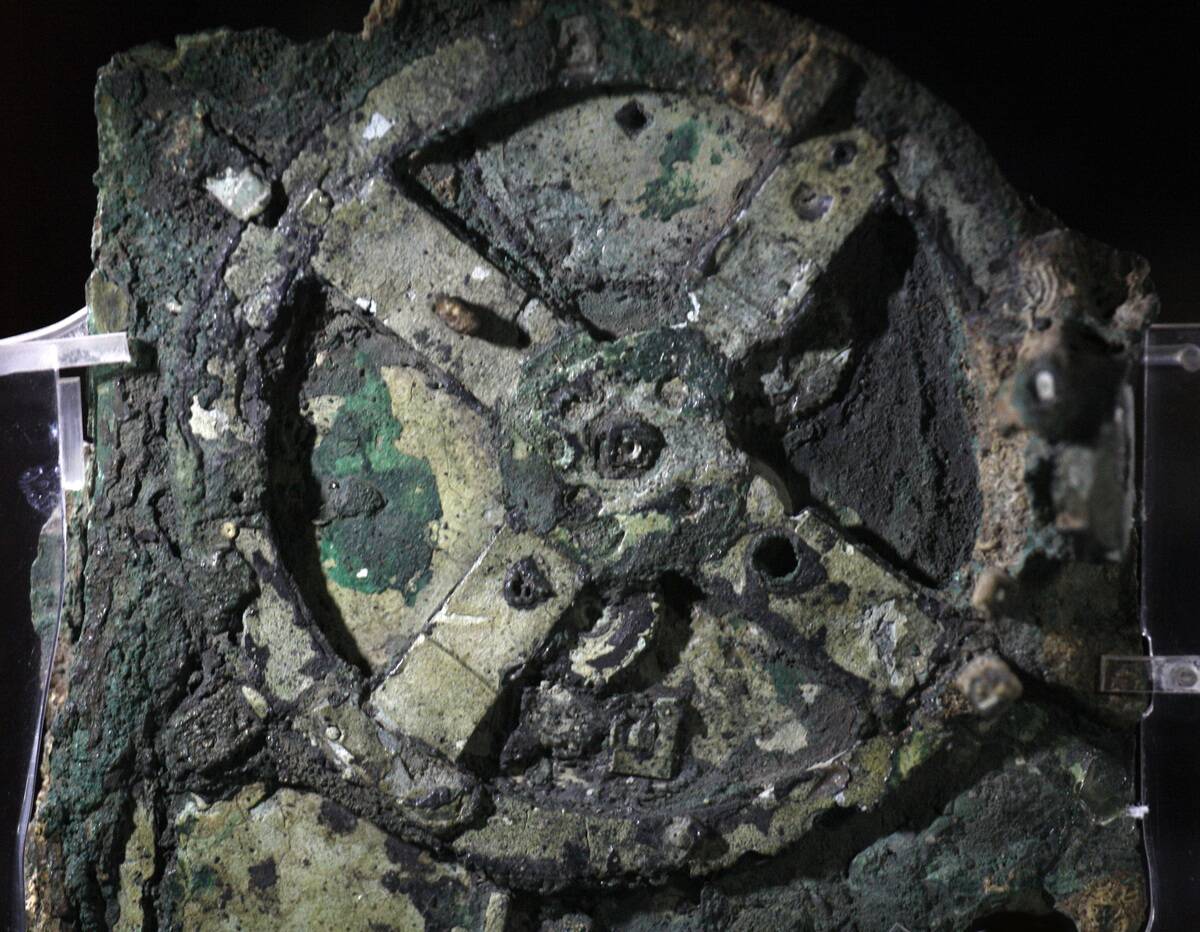

Deep-sea drones have uncovered remarkable finds, from ancient shipwrecks to submerged settlements. One notable discovery is the Antikythera shipwreck, where a complex mechanical device known as the Antikythera mechanism was found.
This discovery provided insights into ancient Greek technology and craftsmanship. Other significant finds include the remains of ancient trade routes in the Indian Ocean, offering clues about cultural exchanges and commerce thousands of years ago.
The Role of Technology in Modern Archaeology

Technology has become a cornerstone of modern archaeology, allowing researchers to delve deeper and unearth more than ever before. Techniques such as 3D mapping and virtual reality reconstructions bring ancient sites to life, offering immersive experiences for both scholars and the public.
These tools not only enhance research but also democratize knowledge, making distant civilizations accessible to a global audience. As technology continues to evolve, so too does our understanding of the past.
Atlantis: Myth or Reality?
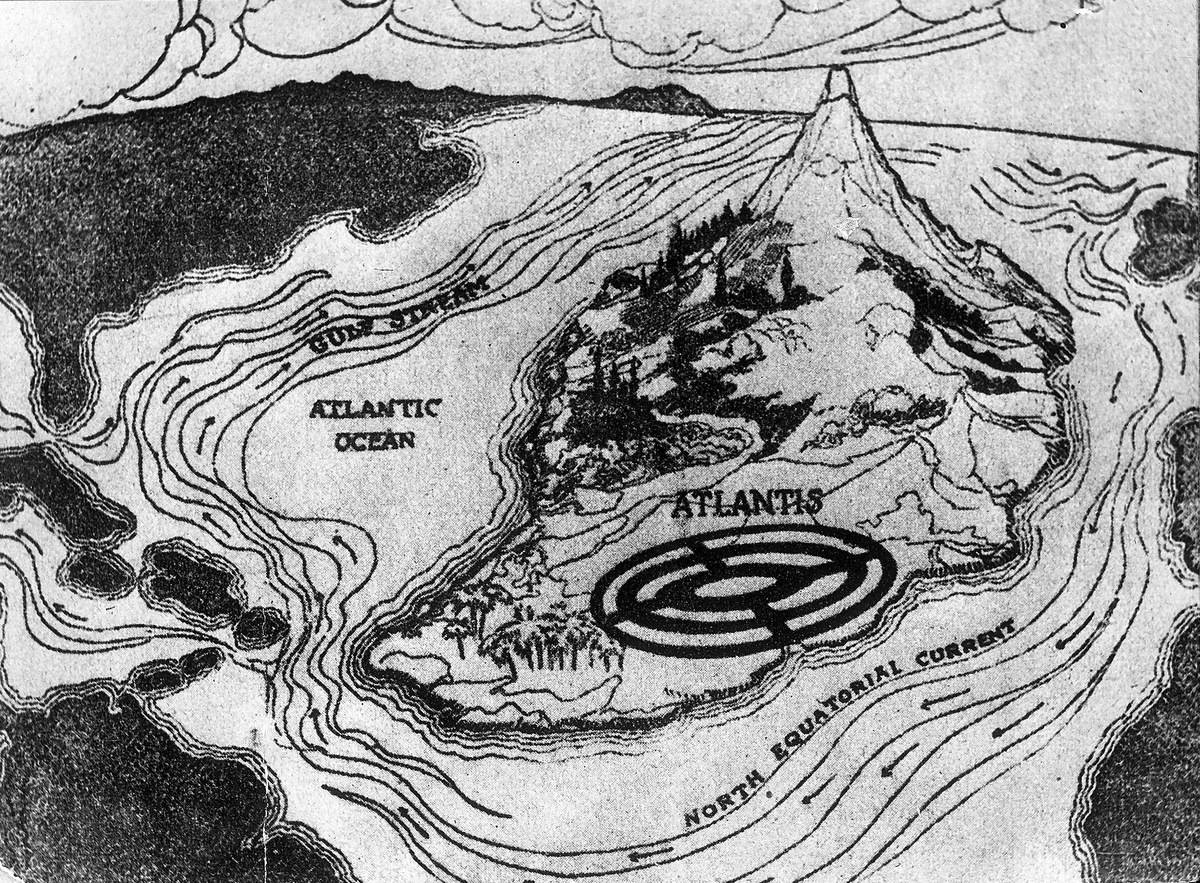
The legend of Atlantis has fascinated humanity for millennia. First mentioned by Plato, this mythical island civilization supposedly vanished beneath the waves in a single day and night. While many regard it as mere myth, some researchers continue to search for evidence of its existence.
Various theories propose locations from the Mediterranean to the Caribbean, fueling debates and inspiring countless expeditions. Whether Atlantis is fact or fiction, its story remains a captivating part of popular culture.
Exploring the Lost City of Dwarka

Dwarka, an ancient city mentioned in Hindu texts, is believed to have been submerged off the coast of India. Archaeological findings, including pottery and structural remains, suggest a city dating back to over 4,000 years ago.
These discoveries align with descriptions in ancient scriptures, sparking debate among historians about the historical accuracy of these texts. The exploration of Dwarka offers a rare intersection of archaeology and mythology, shedding light on India’s rich cultural heritage.
The Mysteries of Thonis-Heracleion
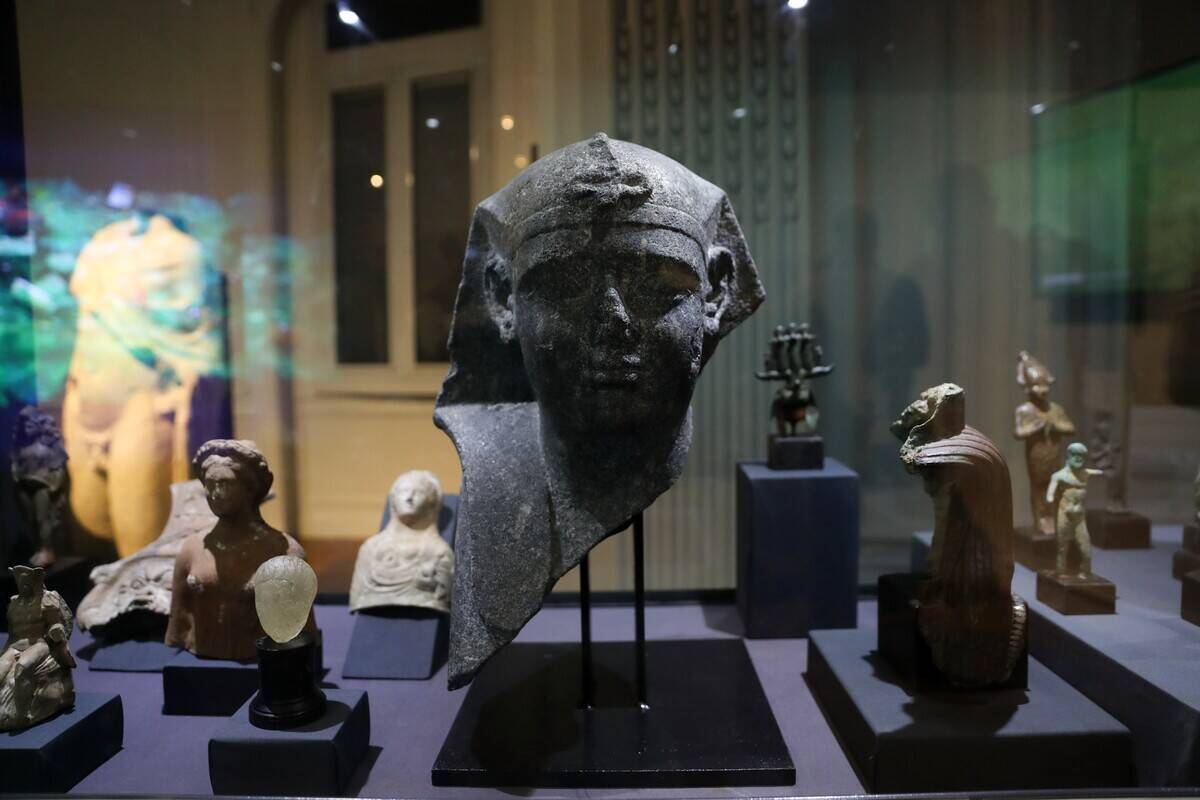

Thonis-Heracleion, once a bustling Egyptian port city, was lost beneath the Mediterranean Sea until its rediscovery in 2000. Artifacts such as colossal statues and religious relics have been unearthed, providing insights into the city’s prosperity and eventual decline.
The discovery of Thonis-Heracleion has reshaped our understanding of ancient Egyptian trade and politics, highlighting the significance of maritime networks. Its excavation continues to reveal the complexities of life in this forgotten city.
Yonaguni Monument: Nature or Nurture?
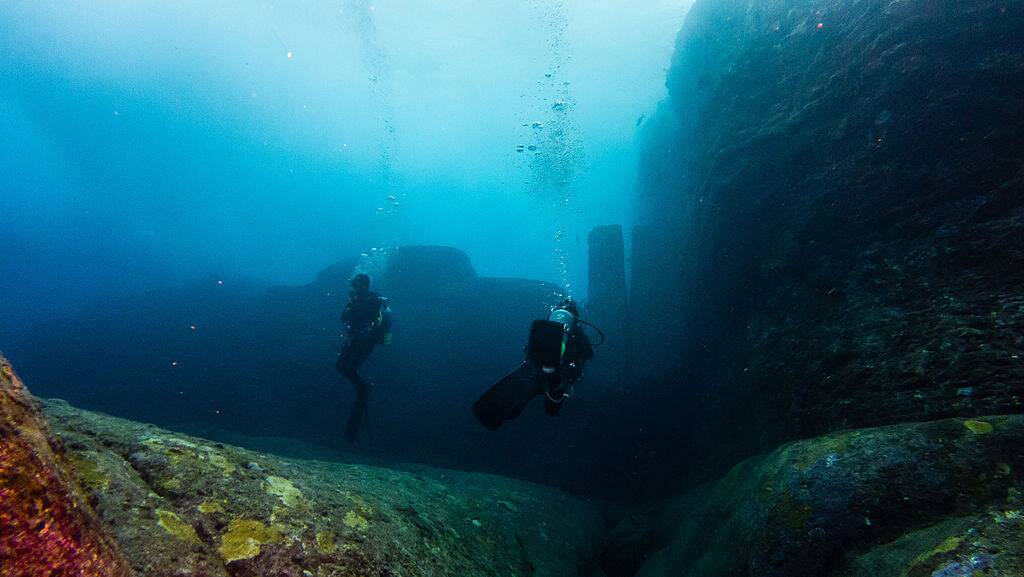

Off the coast of Japan lies the Yonaguni Monument, a massive underwater rock formation that has sparked debate among geologists and archaeologists. Some argue it is a natural formation sculpted by ocean currents, while others believe it to be the remnants of an ancient civilization.
The monument’s terraces and steps suggest human intervention, yet no definitive evidence has been found. This enigmatic site continues to intrigue researchers, blurring the lines between natural wonder and human creation.
The Significance of Pavlopetri: The World’s Oldest Submerged Town
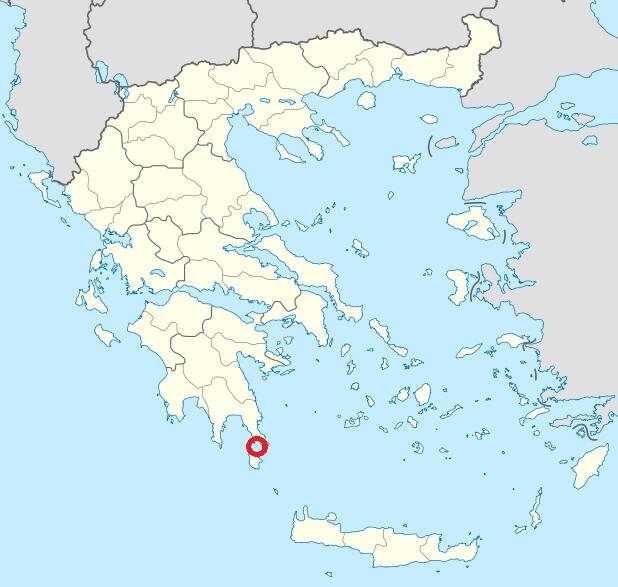
Pavlopetri, located off the coast of Greece, is the oldest known submerged town, dating back to around 5,000 years ago. Its well-preserved streets and buildings offer a unique glimpse into Bronze Age urban planning and daily life.
The town’s discovery has provided valuable information about ancient Greek society, trade, and architecture. Pavlopetri’s significance lies not only in its age but also in the insight it provides into the development of early urban environments.



