Safety lessons learned from engineering failures
Engineering disasters, while tragic, have played a crucial role in shaping modern safety protocols. They serve as sobering reminders of the potential consequences when standards are overlooked.
Through examining historical incidents, we uncover a pattern of progress in safety regulations. Each disaster reveals lessons that have led to advancements in engineering practices. This narrative is not just about the past; it’s an ongoing journey toward safer futures in various industries.
The Collapse of the Tacoma Narrows Bridge: Lessons in Aerodynamics
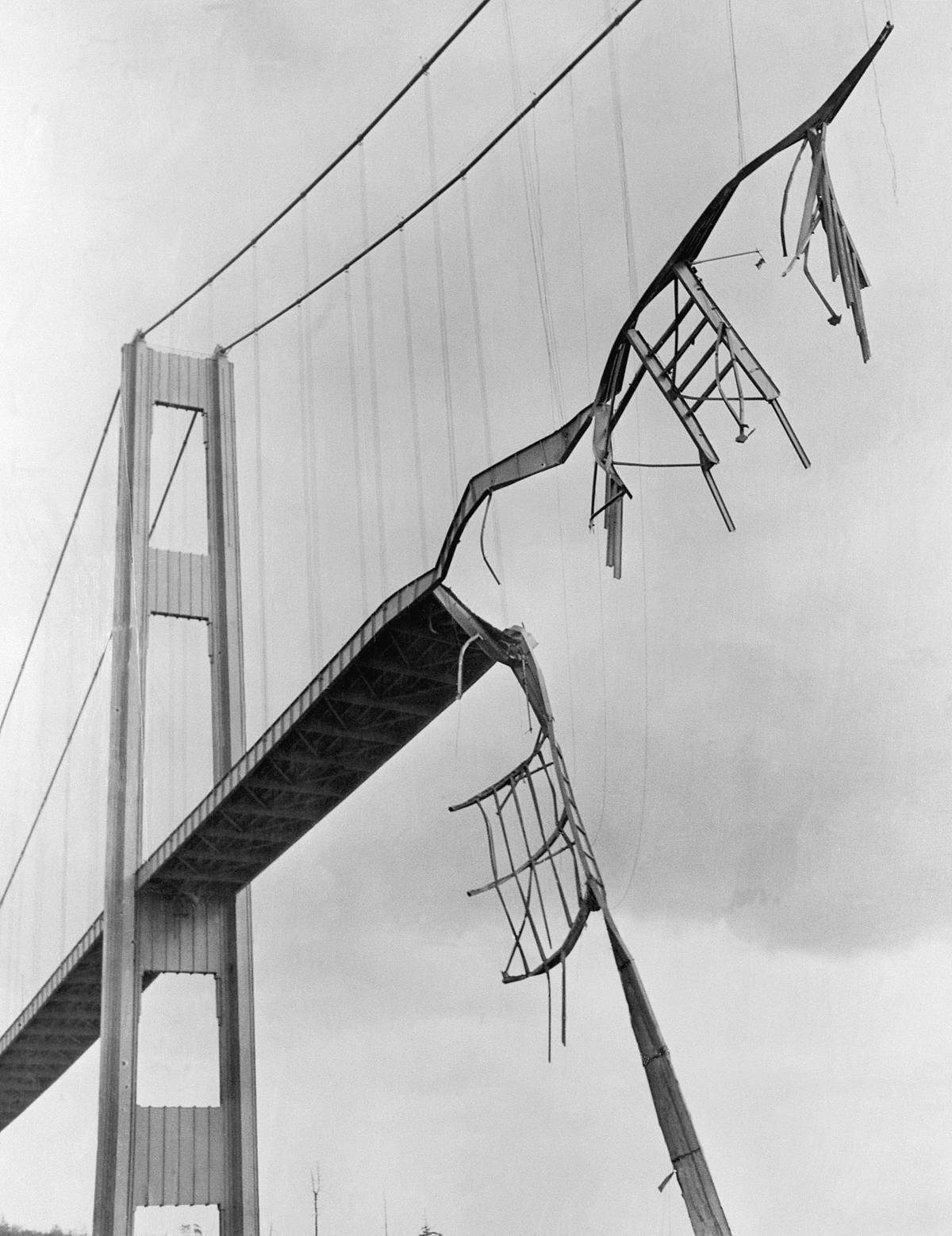

The Tacoma Narrows Bridge, nicknamed “Galloping Gertie,” collapsed in 1940 due to aeroelastic flutter. This failure highlighted the need for understanding aerodynamics in bridge design.
Engineers learned that bridges must be designed to withstand wind forces and oscillations. The collapse led to innovations in bridge construction, such as aerodynamic deck designs and the inclusion of wind-tunnel testing in the design phase. This disaster transformed how engineers approached large-scale projects.
The Chernobyl Disaster: A Wake-Up Call for Nuclear Safety
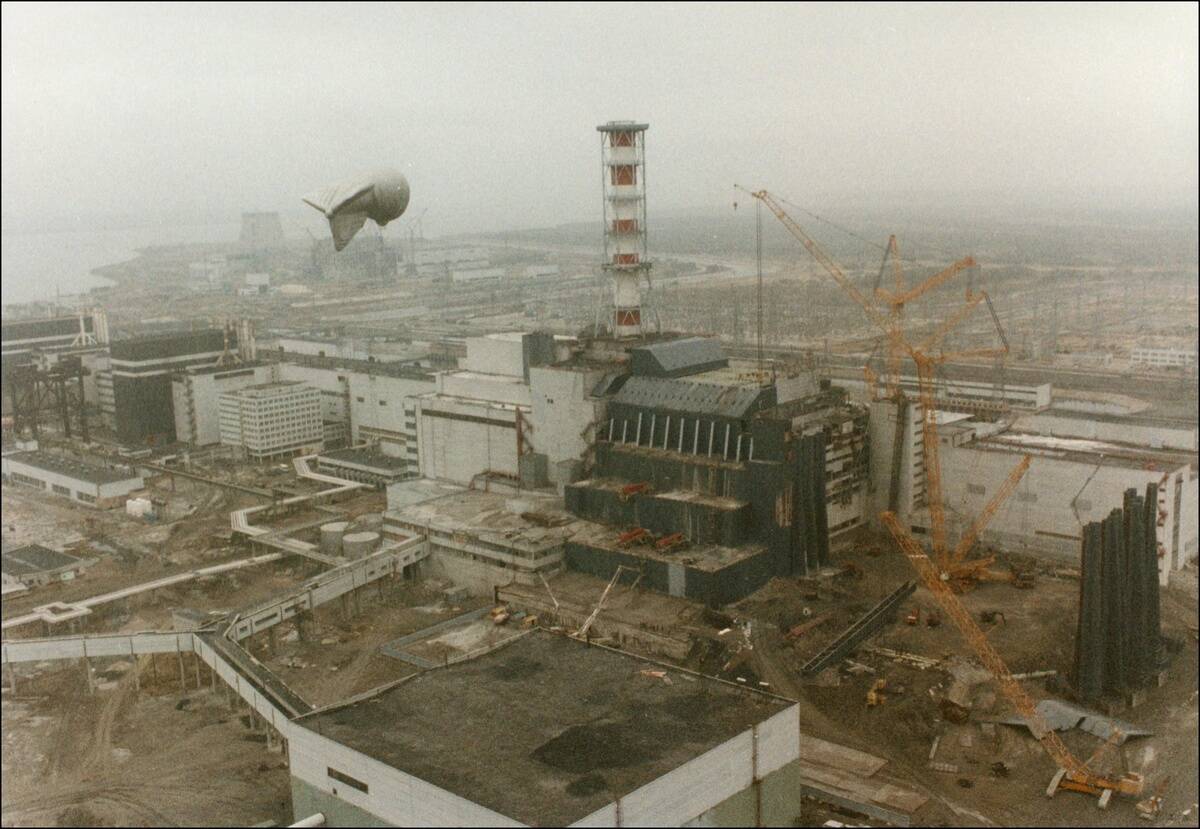

The Chernobyl disaster in 1986 was a pivotal moment in nuclear safety history. It exposed critical flaws in Soviet reactor design and emergency protocols.
The incident resulted in the establishment of the International Atomic Energy Agency’s safety standards, promoting global cooperation in nuclear safety. The disaster also prompted the implementation of more robust containment structures and emergency response plans, fundamentally changing how nuclear facilities operate worldwide.
The Sinking of the Titanic: Revolutionizing Maritime Safety Standards
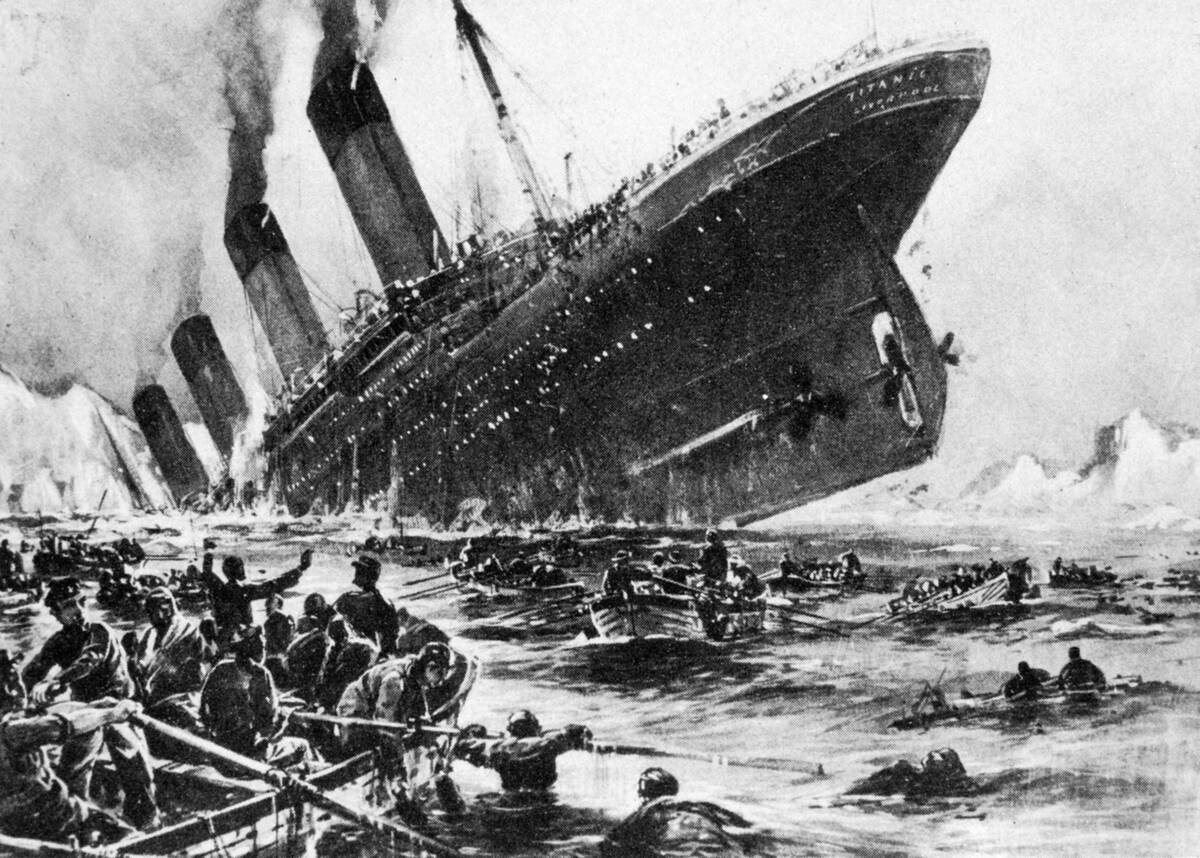

The Titanic’s tragic sinking in 1912 brought about sweeping changes in maritime safety. The ship’s inadequate lifeboat capacity and inefficient evacuation protocols were starkly highlighted.
In response, the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) was established in 1914. This set of international maritime safety standards mandated sufficient lifeboats, life vests, and improved ship design and crew training, ensuring that such a disaster would never happen again.
The Space Shuttle Challenger Explosion: Redefining Space Mission Protocols
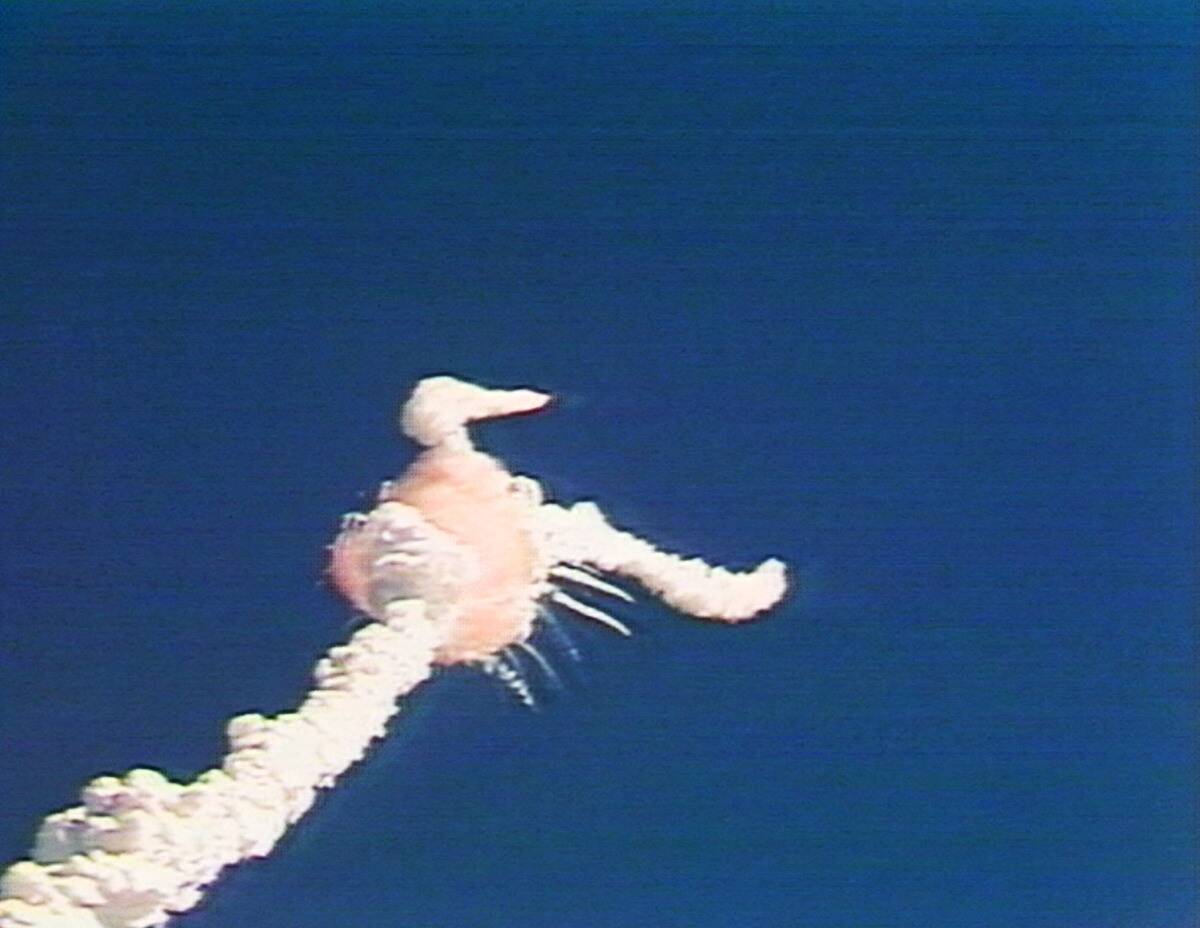
The Challenger explosion in 1986 was a devastating setback for NASA and space exploration. It was caused by the failure of an O-ring seal in the shuttle’s right solid rocket booster. This tragedy led to the Rogers Commission Report, which criticized NASA’s safety culture and decision-making processes.
As a result, NASA implemented significant changes, including improved risk assessment, enhanced communication channels, and the redesign of shuttle components, all contributing to safer space missions. However, progress on this was slower than it seems in retrospect, as the Columbia disaster of 2003 had similar systemic issues underlying it.
The Hyatt Regency Walkway Collapse: Structural Engineering Under Scrutiny
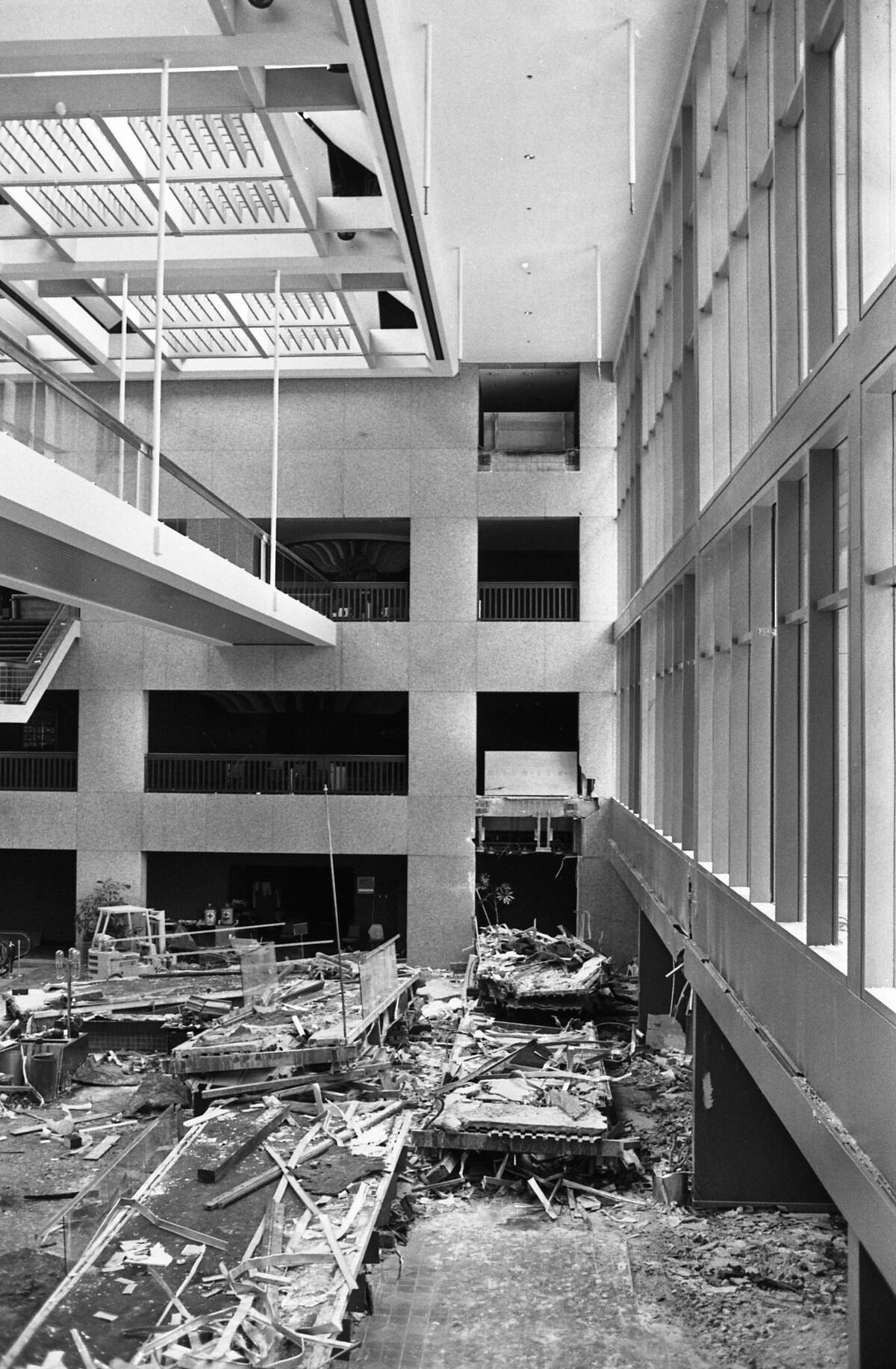

In 1981, a tragic structural failure occurred at the Hyatt Regency hotel in Kansas City. Two walkways collapsed, killing 114 people and injuring over 200. The disaster was traced to design changes that compromised the walkways’ structural integrity.
This led to stricter building codes and more rigorous peer reviews in engineering designs. The incident underscored the importance of thorough oversight and accountability in construction projects, highlighting the need for stringent engineering ethics.
The Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill: Environmental and Engineering Oversights
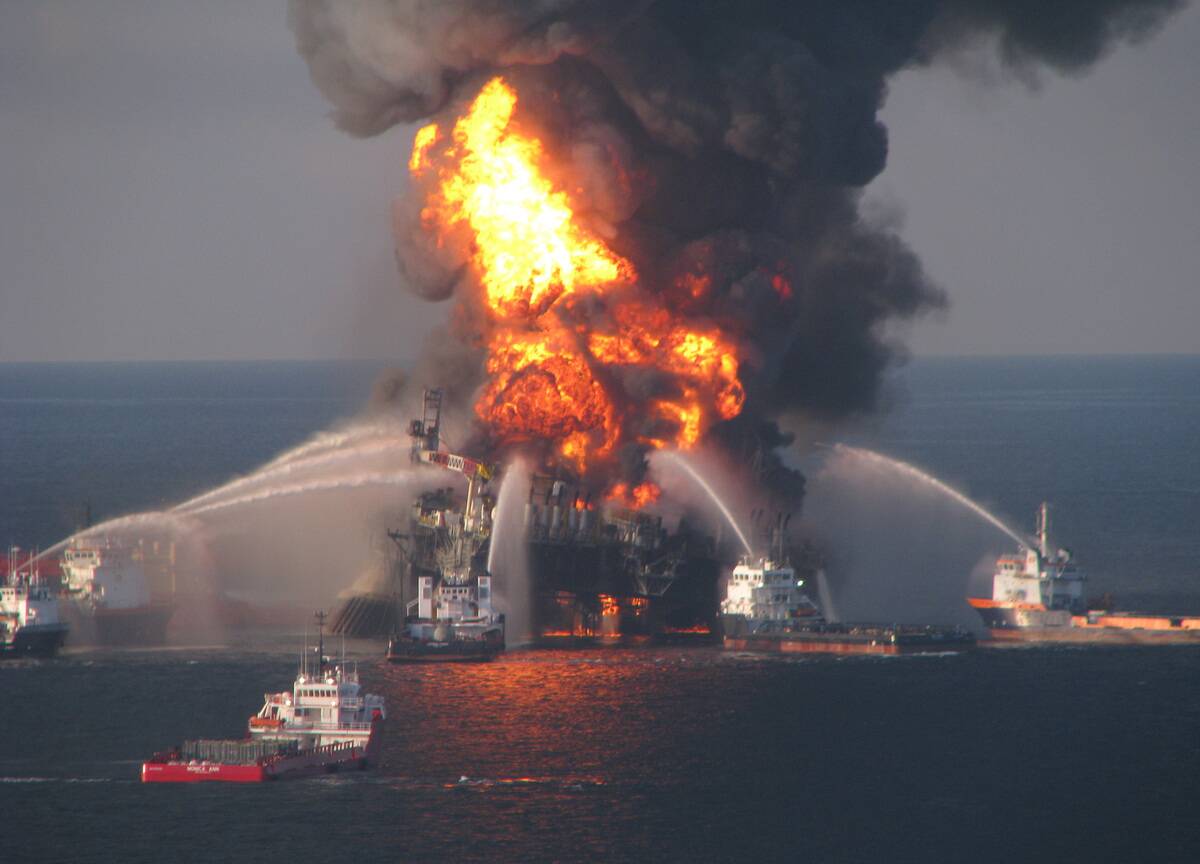

The 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill was a stark reminder of the environmental risks associated with deep-sea drilling. It highlighted significant engineering oversights and regulatory failures.
The disaster prompted the overhaul of offshore drilling regulations and the creation of the Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement. This incident emphasized the need for rigorous safety protocols and contingency planning, transforming how oil companies approach environmental risk management.
The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster: The Importance of Disaster Preparedness
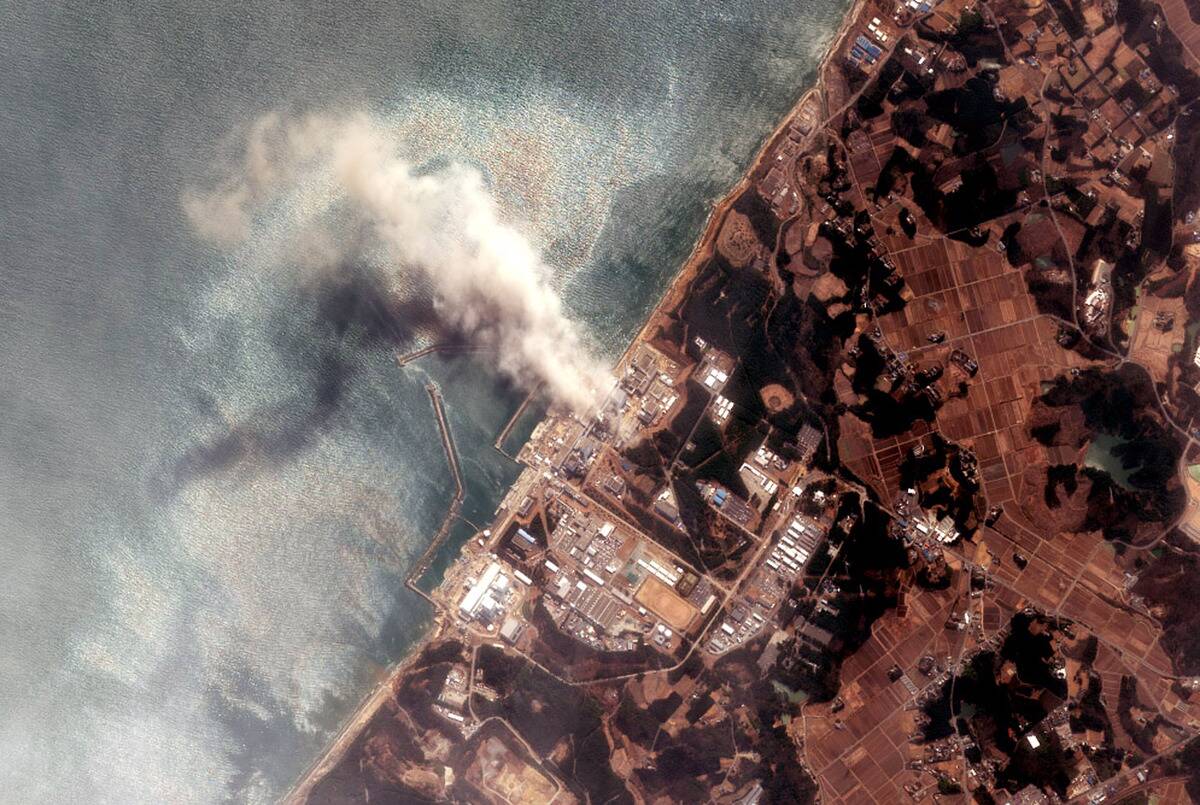

The 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster was triggered by a massive earthquake and tsunami. It exposed vulnerabilities in the plant’s design and emergency systems. In response, nuclear plants worldwide have enhanced their safety protocols, focusing on disaster preparedness and response.
This includes higher tsunami walls, additional backup power supplies, and improved evacuation planning. The disaster underscored the necessity of robust safety measures to protect against natural and man-made threats.
The St. Francis Dam Failure: Pioneering Modern Dam Safety Practices
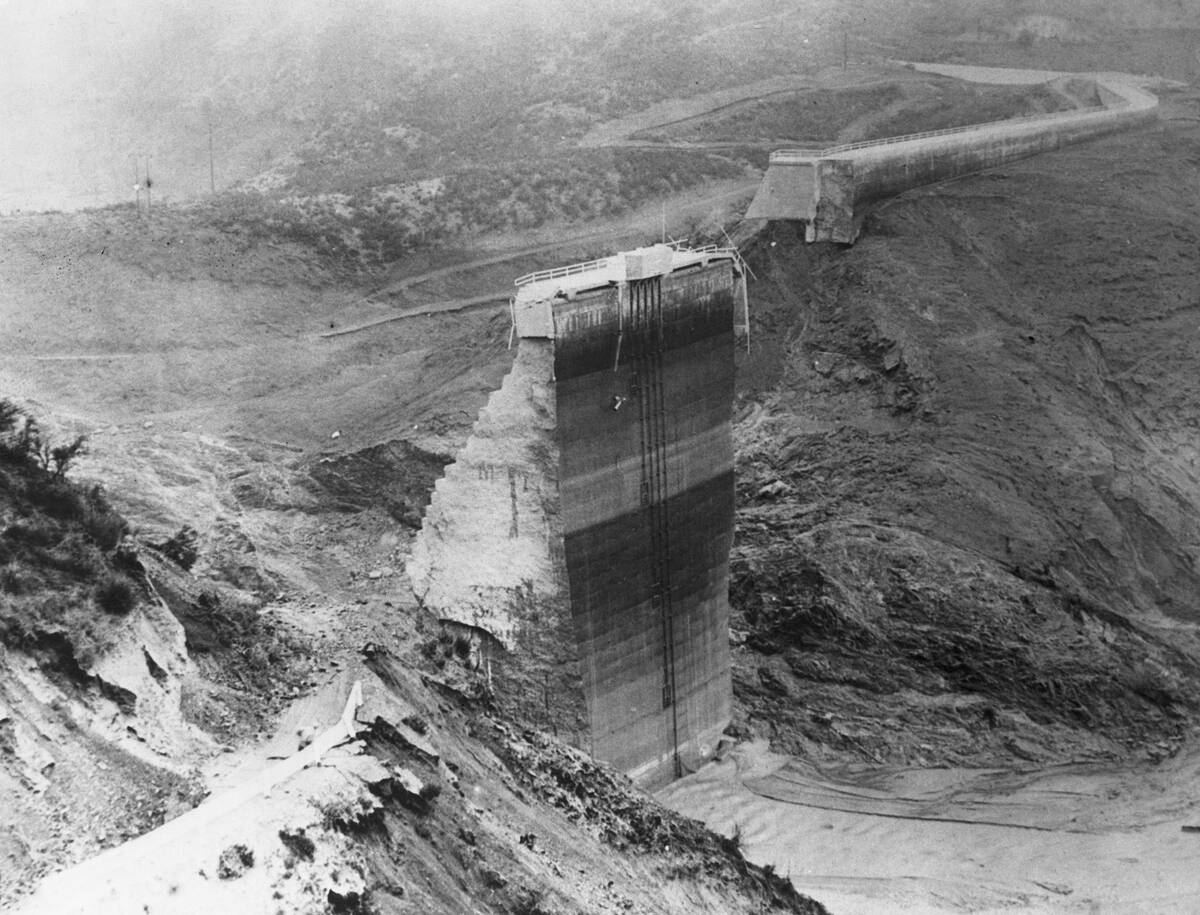

In 1928, the St. Francis Dam in California catastrophically failed, resulting in the deaths of over 400 people. This disaster revealed the dangers of inadequate safety oversight and poor construction practices.
It led to the establishment of more stringent dam safety regulations and the creation of the California Division of Safety of Dams. The incident served as a catalyst for modern dam engineering practices, emphasizing thorough site investigations and robust design standards.
The Love Canal Environmental Disaster: Birth of the Superfund Act

The Love Canal disaster in the late 1970s drew national attention to the dangers of toxic waste disposal. Residents of the Niagara Falls neighborhood were exposed to hazardous chemicals dumped by a local company.
This crisis led to the creation of the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA), also known as the Superfund Act. It provided a framework for cleaning up hazardous waste sites and holding polluters accountable, marking a turning point in environmental legislation.
The Hindenburg Disaster: Transforming Airship Safety Measures

The Hindenburg disaster in 1937 marked the end of the airship era. The German passenger airship caught fire while attempting to dock, resulting in 36 fatalities. Investigations revealed that static electricity ignited the hydrogen used for buoyancy.
This tragedy led to the abandonment of hydrogen in airships, with helium becoming the safer alternative. The disaster also pushed for stricter safety protocols and the development of more reliable air travel methods, ultimately paving the way for modern aviation.
The Silver Bridge Collapse: Inspiring Bridge Inspection and Maintenance
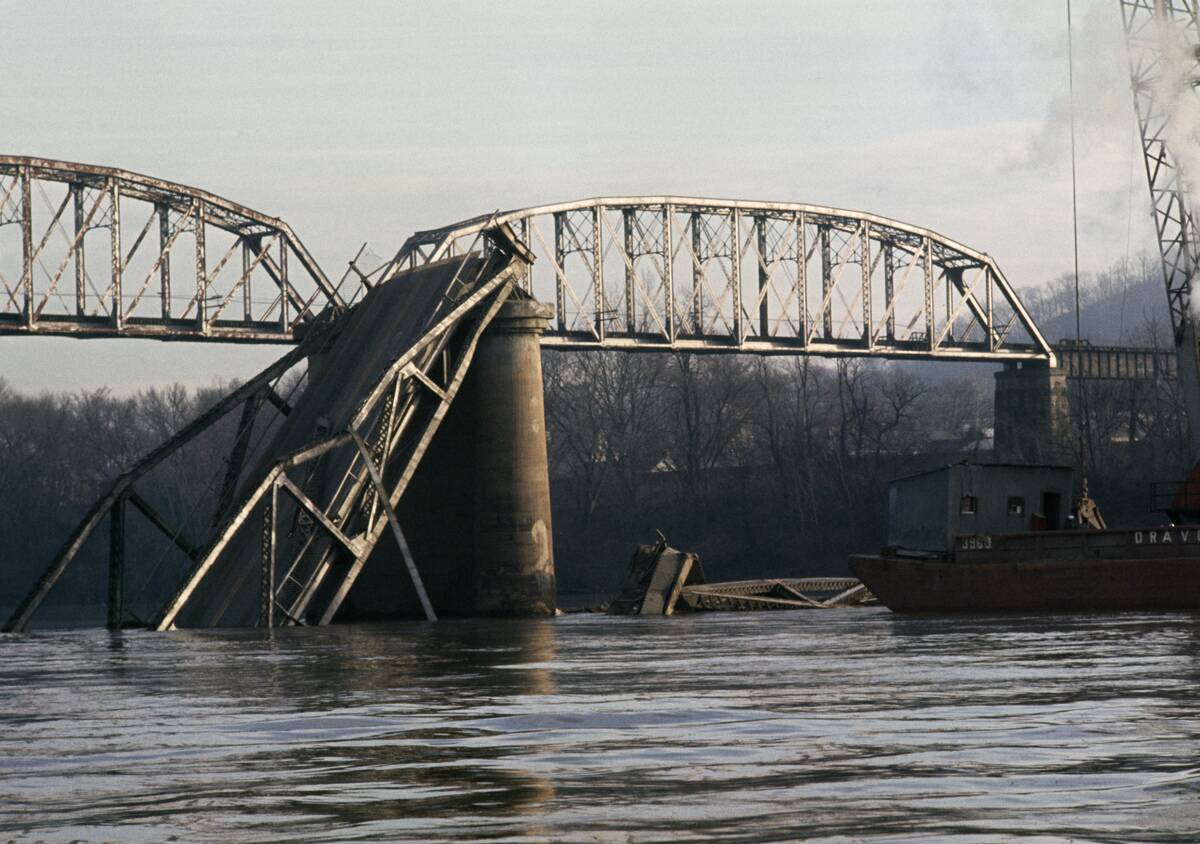

The collapse of the Silver Bridge in 1967 was a pivotal moment for infrastructure safety in the US. The failure of a single eyebar caused the bridge to collapse, leading to 46 deaths.
This tragedy prompted the establishment of the National Bridge Inspection Standards, requiring regular inspections of all bridges. It highlighted the importance of maintenance and the need for rigorous inspection protocols to ensure the safety and longevity of critical infrastructure.
The Grenfell Tower Fire: A Catalyst for Fire Safety Reforms

The Grenfell Tower fire in London in 2017 was a devastating event that exposed severe shortcomings in building safety regulations. The fire spread rapidly due to flammable cladding, resulting in 72 deaths.
This tragedy led to a comprehensive review of fire safety regulations in the UK, including revised building inspection processes, as the cladding materials involved were already banned in the U.K.. The disaster underscored the critical need for stringent fire safety standards and effective emergency response strategies.
The Morandi Bridge Collapse: Reevaluating Infrastructure Integrity
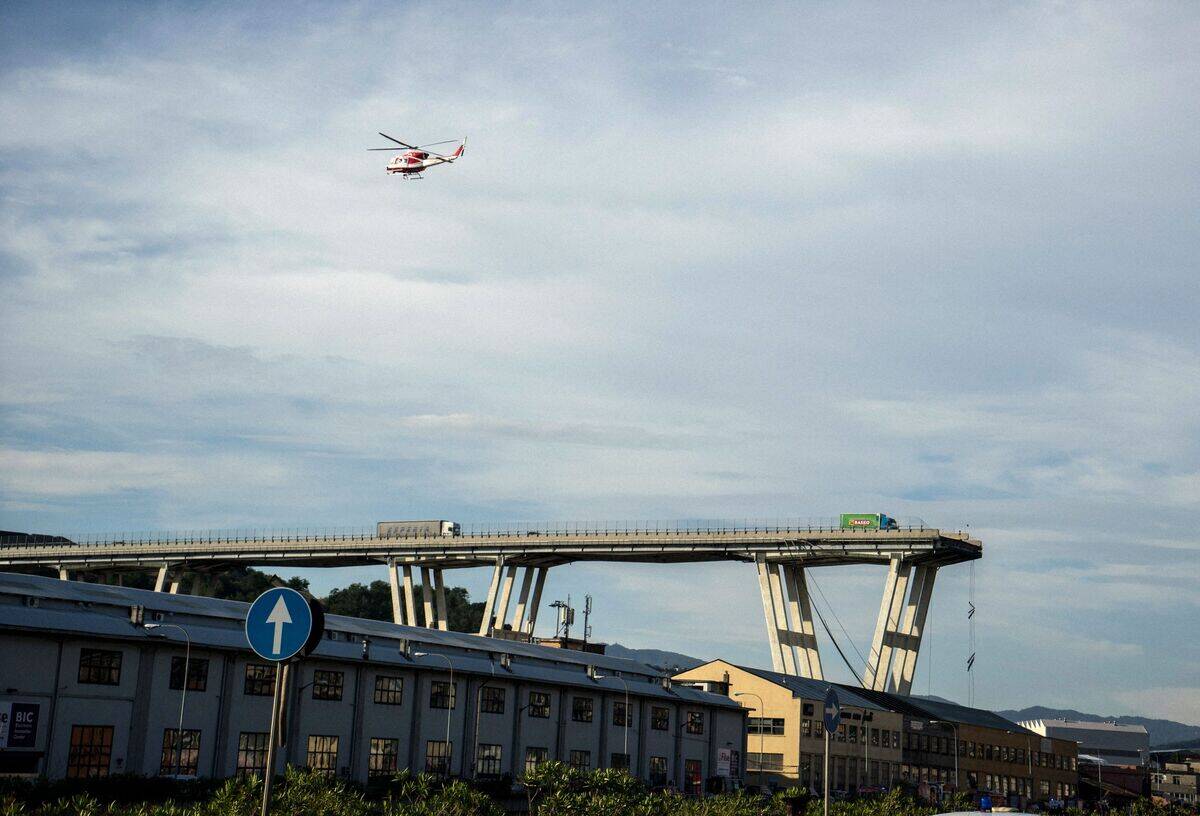

The Morandi Bridge collapse in 2018 in Genoa, Italy, resulted in 43 fatalities and raised serious concerns about infrastructure integrity. The collapse was attributed to corrosion and poor maintenance.
This disaster prompted Italy to reassess its national infrastructure policies, emphasizing the need for regular inspections and the use of advanced monitoring technologies. It highlighted the importance of proactive maintenance and investment in infrastructure to prevent similar tragedies.
The Piper Alpha Oil Rig Disaster: Offshore Safety Regulations Enhanced
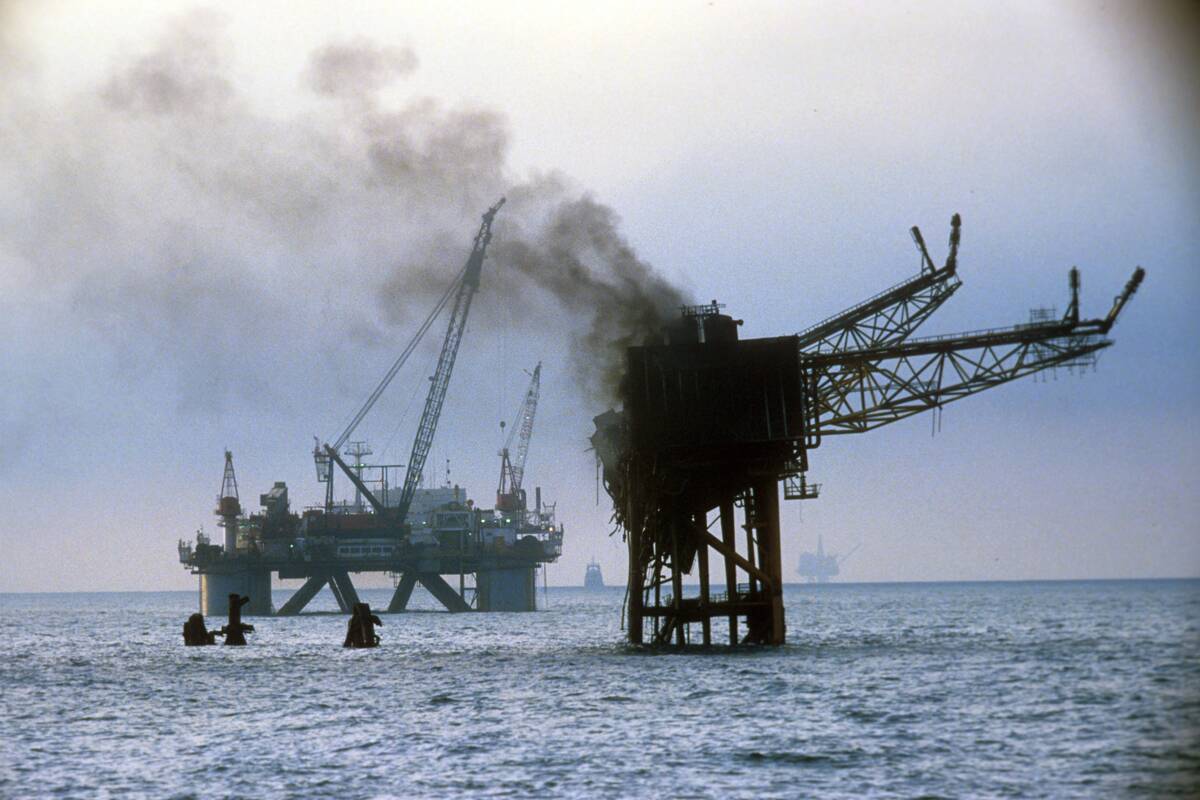

The Piper Alpha disaster in 1988 remains the deadliest offshore oil rig accident, with 167 fatalities. A gas leak led to a series of explosions, revealing significant safety lapses in offshore operations.
This tragedy resulted in the Cullen Report, which recommended sweeping changes to offshore safety regulations. The disaster underscored the necessity for rigorous safety protocols, regular safety drills, and the implementation of a safety case regime to ensure the highest safety standards in offshore operations.
The Sampoong Department Store Collapse: Construction Safety Revisited
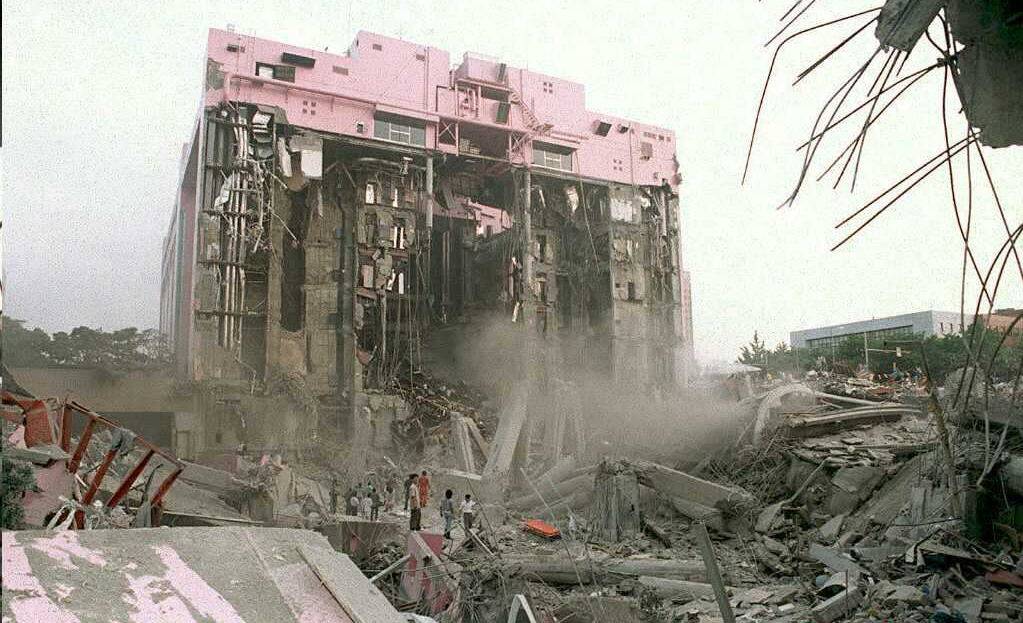

The collapse of the Sampoong Department Store in Seoul, South Korea, in 1995 was a stark reminder of the consequences of ignoring construction standards. The building’s design flaws and unauthorized modifications led to the collapse, killing 502 people.
This disaster prompted South Korea to overhaul its construction safety regulations, emphasizing stricter enforcement of building codes and better training for engineers and contractors. The incident highlighted the critical importance of adhering to safety protocols in construction projects.
The Rana Plaza Collapse: Factory Safety and Ethical Manufacturing Practices
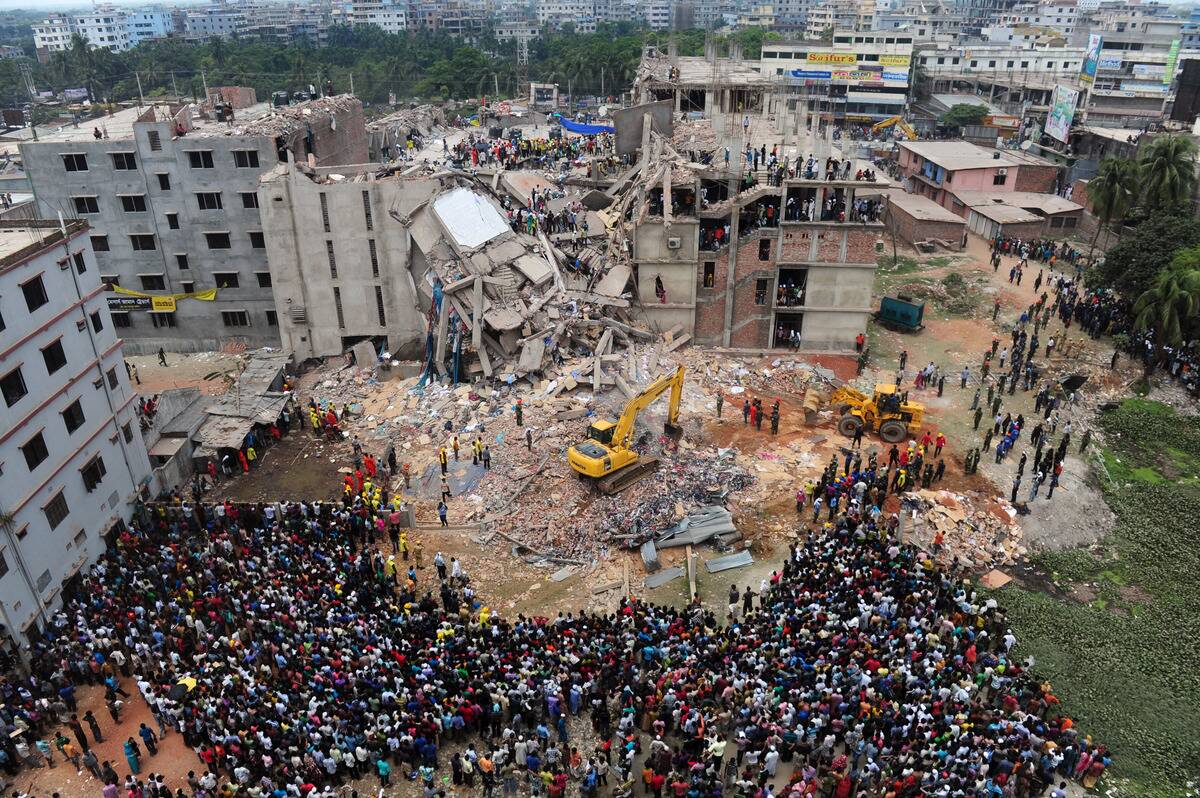

The Rana Plaza collapse in Bangladesh in 2013 was a devastating industrial disaster that killed over 1,100 people. The building housed garment factories and collapsed due to poor construction and lack of oversight.
This tragedy led to a global outcry for better factory safety standards and ethical manufacturing practices. Initiatives like the Accord on Fire and Building Safety in Bangladesh were established, aiming to improve working conditions and ensure the safety of workers in the garment industry.



