Ancient artifacts revealing early intercontinental trade
Trade has always been a crucial part of human history, acting as a bridge between diverse cultures. Ancient trade routes weren’t just about exchanging goods; they were avenues for cultural exchange and innovation.
From the sun-baked deserts of Africa to the frozen fjords of Scandinavia, artifacts have been unearthed that reveal the vast networks of trade our ancestors built. These items tell stories of journeys across vast distances, of lands and peoples connected in ways previously unimagined.
The Tale of the Egyptian Scarabs Found in Scandinavia
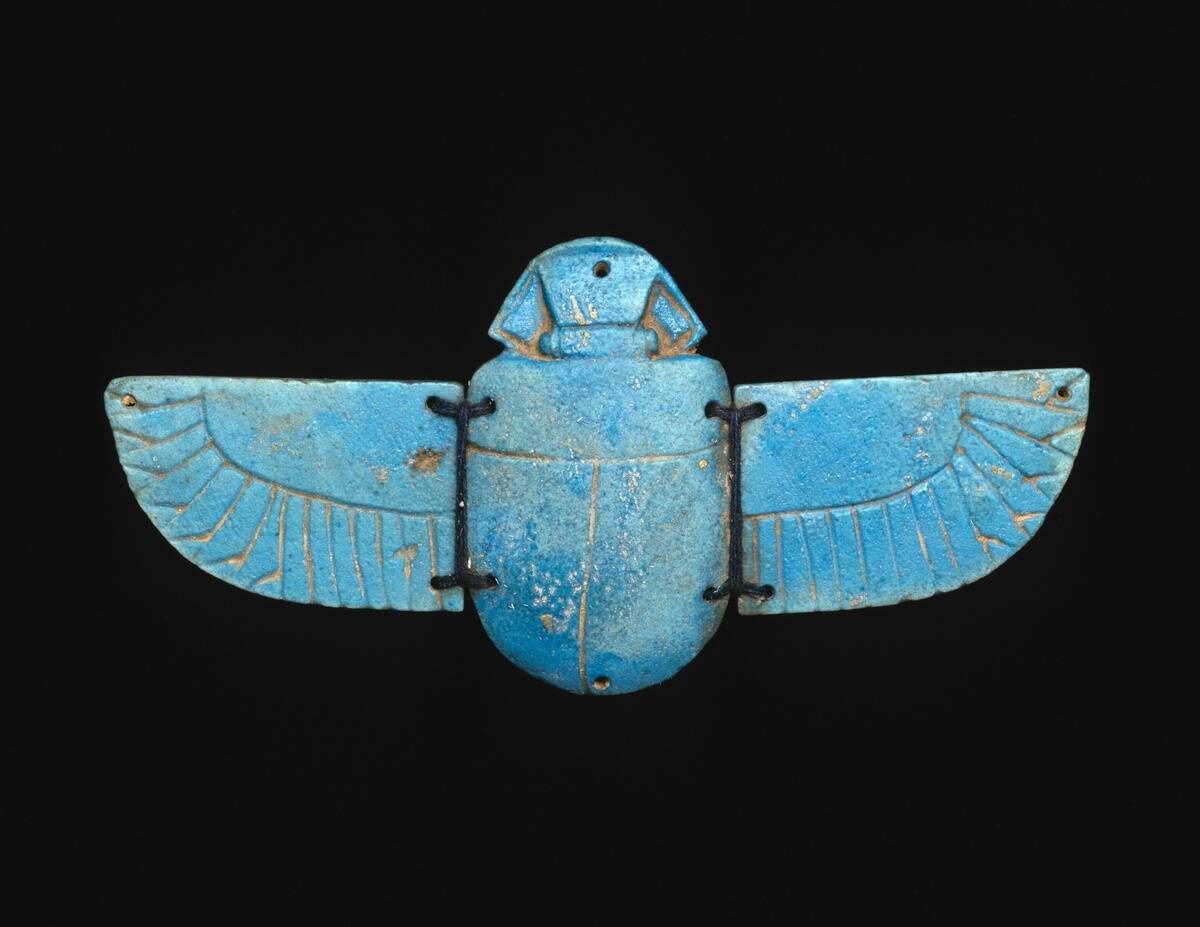

Imagine stumbling upon Egyptian scarabs in the chilly landscapes of Scandinavia! These tiny amulets made their way thousands of miles north, suggesting a far-reaching trade network. The scarabs, often used as seals or jewelry in ancient Egypt, were likely traded as high-value items.
Their presence in Scandinavia speaks volumes about the exchange of luxury goods and the interconnectedness of ancient societies. It’s fascinating to consider how these small objects became tokens of distant empires.
Roman Coins in the Faraway Lands of India
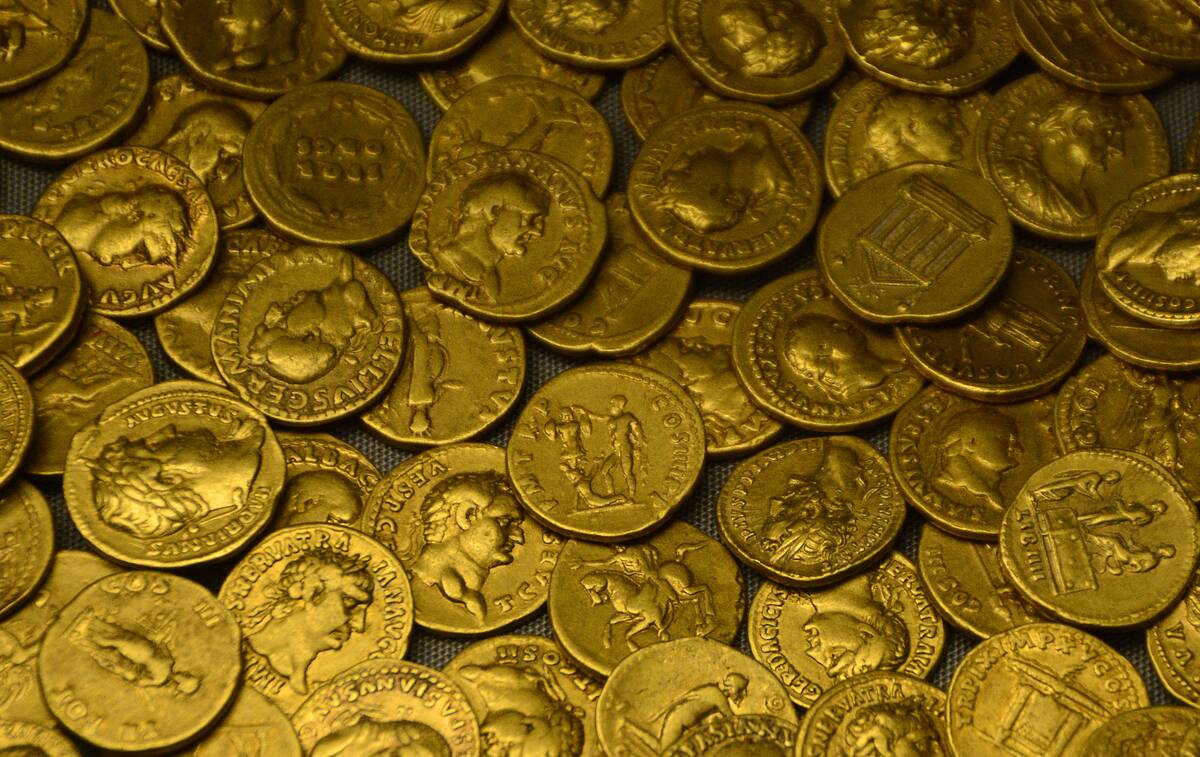

Roman coins have been discovered in India, sparking intrigue about the extent of ancient trade. These coins, often found in southern India, date back to the first few centuries AD, a testament to the bustling trade relations between the Roman Empire and the Indian subcontinent.
The coins were not just currency; they were symbols of the Roman world’s reach and influence. Such finds highlight how economic interests fostered connections between disparate cultures, facilitating the spread of ideas and commodities.
Silk Road Treasures: A Melting Pot of Cultures
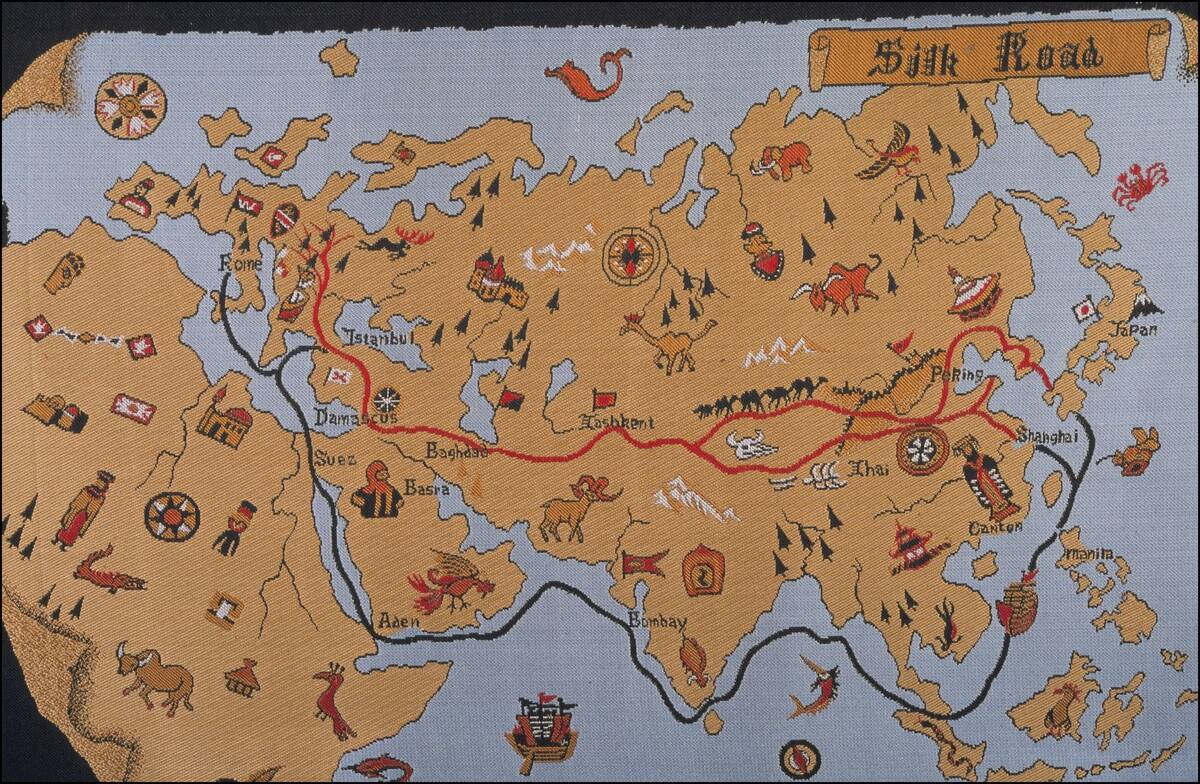
The Silk Road is perhaps the most famous ancient trade route, a network stretching from China to the Mediterranean. It was more than just a path for silk; it was a conduit for spices, textiles, and even religions.
The exchange along these routes brought about a melting pot of cultures, with merchants and travelers sharing stories, beliefs, and technologies. The treasures excavated from Silk Road sites reveal a world where East met West, creating a tapestry of shared human history.
The Olmec Civilization and African Influences
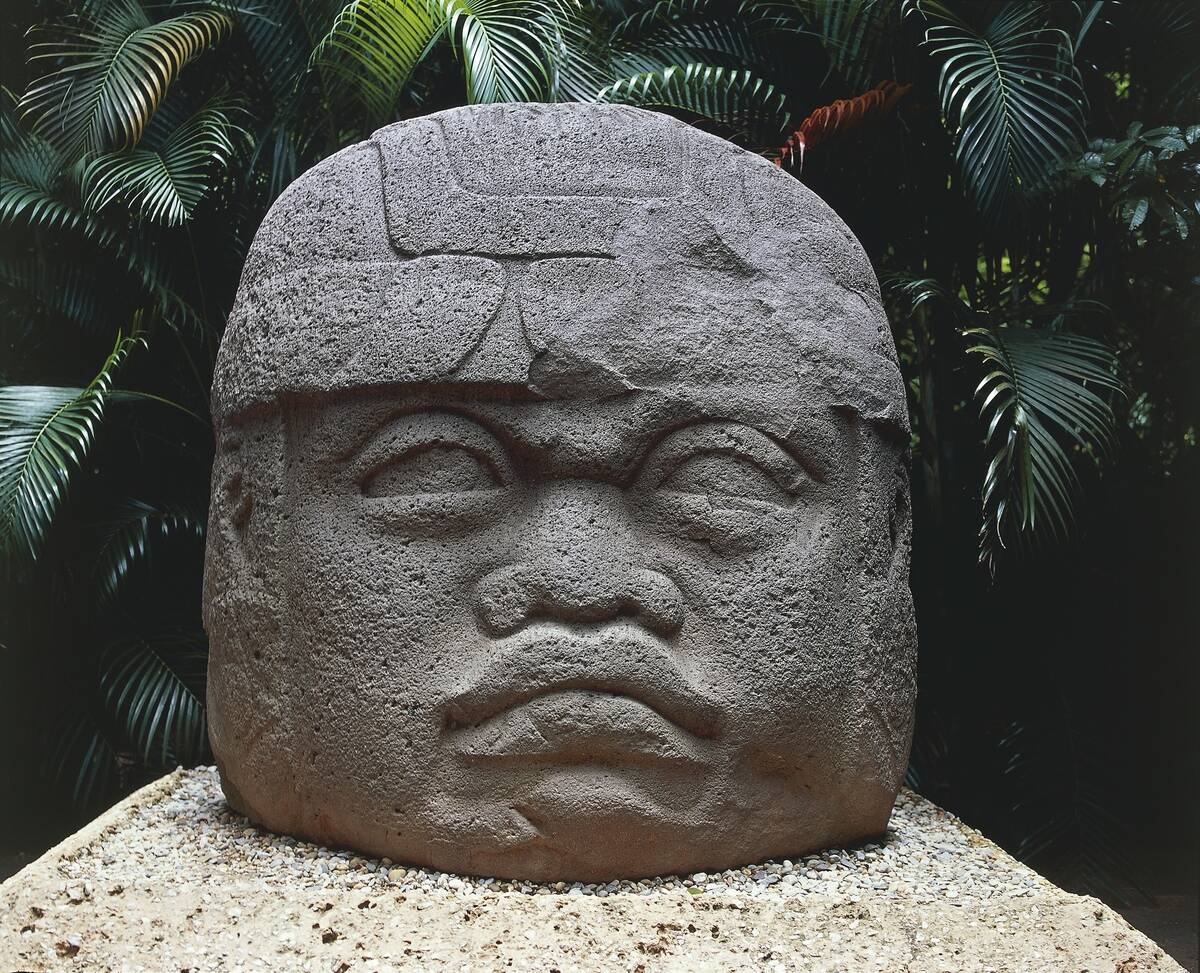

The Olmec civilization, known for its colossal stone heads, has fascinated historians and archaeologists for centuries. While some have proposed theories about possible influences from African cultures based on certain artistic similarities, these claims remain speculative and are not widely accepted by experts.
Most scholars attribute the Olmec’s unique art styles and motifs to indigenous developments within Mesoamerica. The civilization’s legacy continues to inspire research into the rich cultural exchanges of ancient America.
Greek Pottery Fragments in the Sands of Egypt
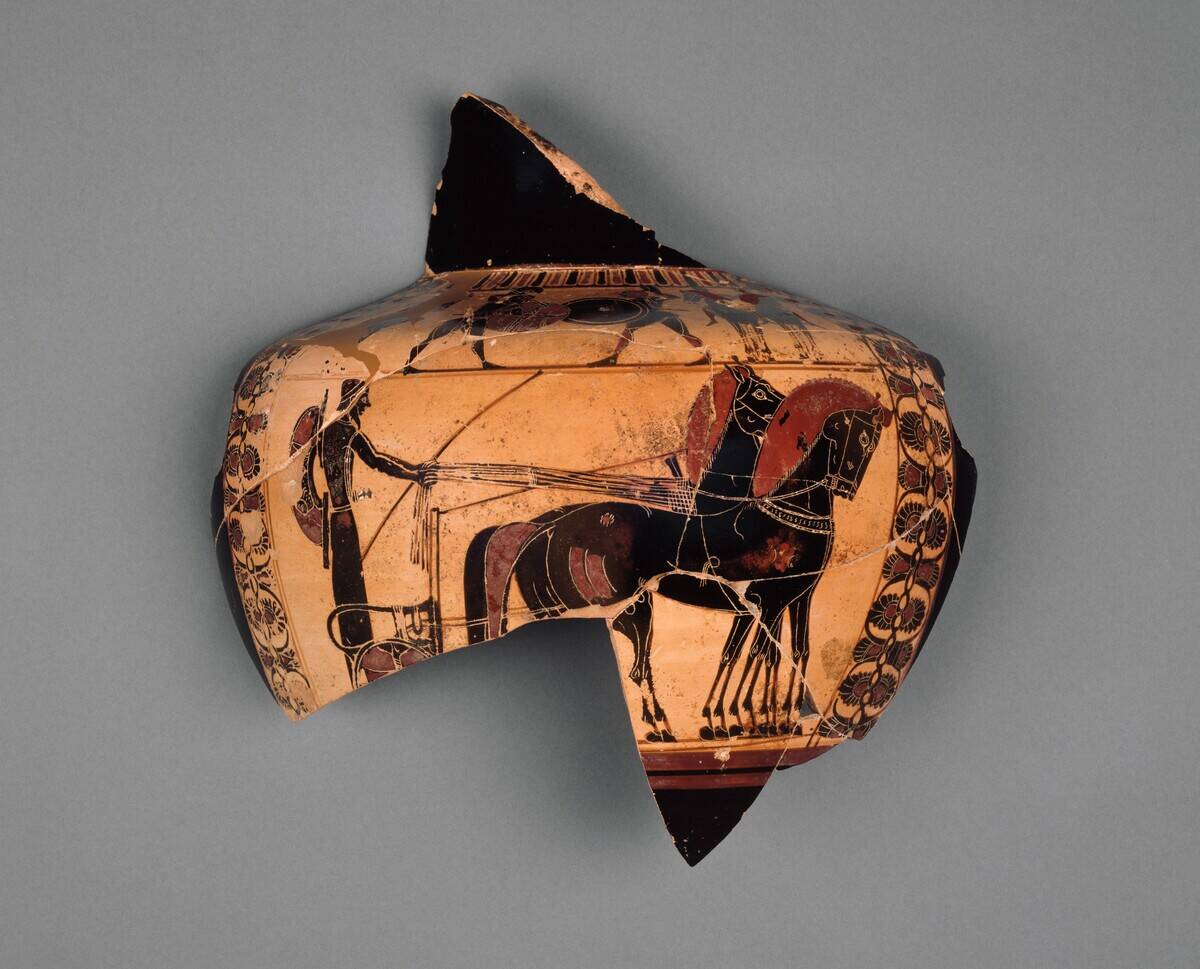

The discovery of Greek pottery fragments in Egypt offers a glimpse into the ancient Mediterranean trade networks. These ceramics, often decorated with intricate designs, tell stories of Greek influence in Egyptian lands.
The presence of these fragments suggests active trade and cultural exchange between these ancient civilizations, with Greek artisanship admired far beyond its homeland. These pottery pieces are not merely artistic remnants but serve as historical evidence of the vibrant interactions across the Mediterranean.
The Enigma of the Phoenician Shipwrecks

Phoenician shipwrecks found off various coastlines tell tales of a seafaring people who were masters of ancient maritime trade. The Phoenicians, known for their robust ships and navigation skills, spread goods across the Mediterranean, including precious purple dye and glass.
These shipwrecks, sometimes laden with amphorae and other cargo, provide insights into the commercial routes and the scope of trade. Each wreck is a snapshot of a thriving civilization whose influence touched many ancient cultures.
Chinese Porcelain in the Heart of Persia
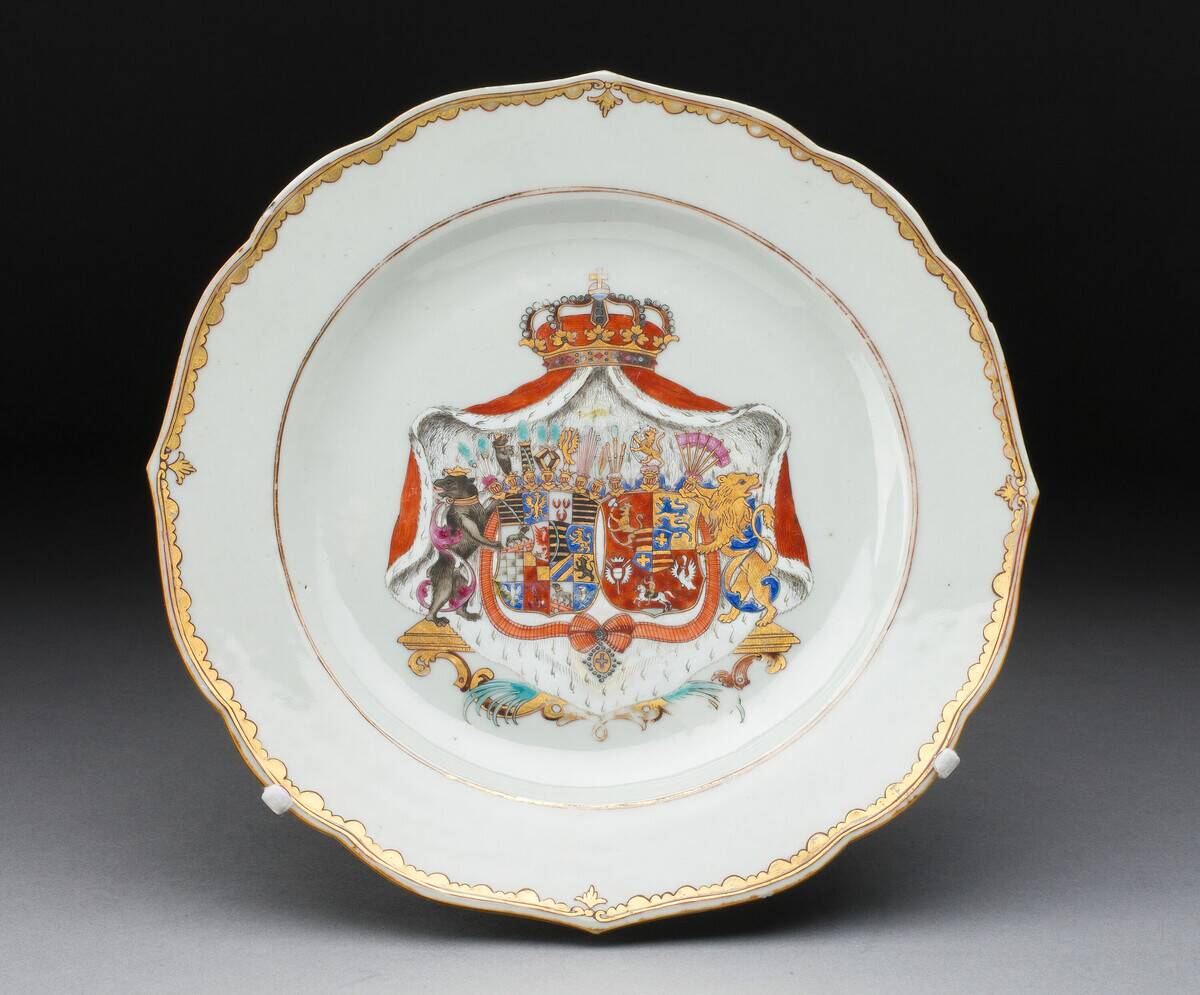

The presence of Chinese porcelain in Persia is a testament to the long-standing trade between the Far East and the Middle East. These beautifully crafted ceramics, prized for their quality and artistry, were highly sought after by Persian elites.
The porcelain pieces discovered in Persia reflect a taste for exotic luxury and an appreciation for Chinese craftsmanship. This exchange of goods highlights how trade routes like the Silk Road facilitated not only economic but also cultural exchanges.
Viking Sagas and the Silk from the East
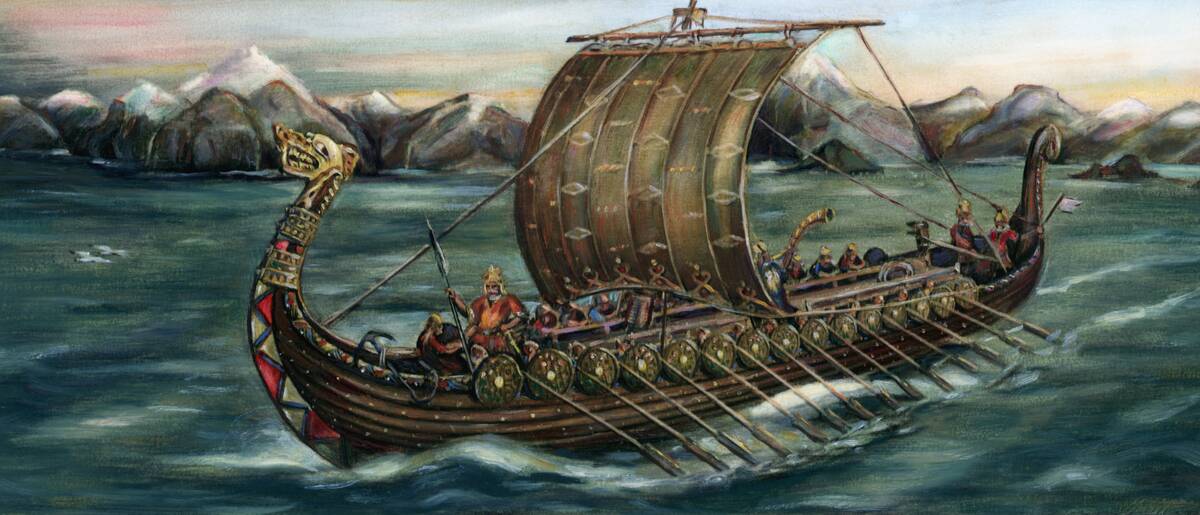

Viking sagas, with their tales of adventure and exploration, also hint at trade connections with the East. Silk, a luxurious fabric originating from China, has been found in Viking burial sites, suggesting that these Norse seafarers traded far beyond their familiar shores.
The presence of silk in Scandinavia reveals a sophisticated trading network that extended to the east, perhaps through intermediaries like the Rus or Byzantine merchants. This intercontinental trade brought a touch of Eastern opulence to the rugged North.
The Intricate Network of the Trans-Saharan Trade Routes
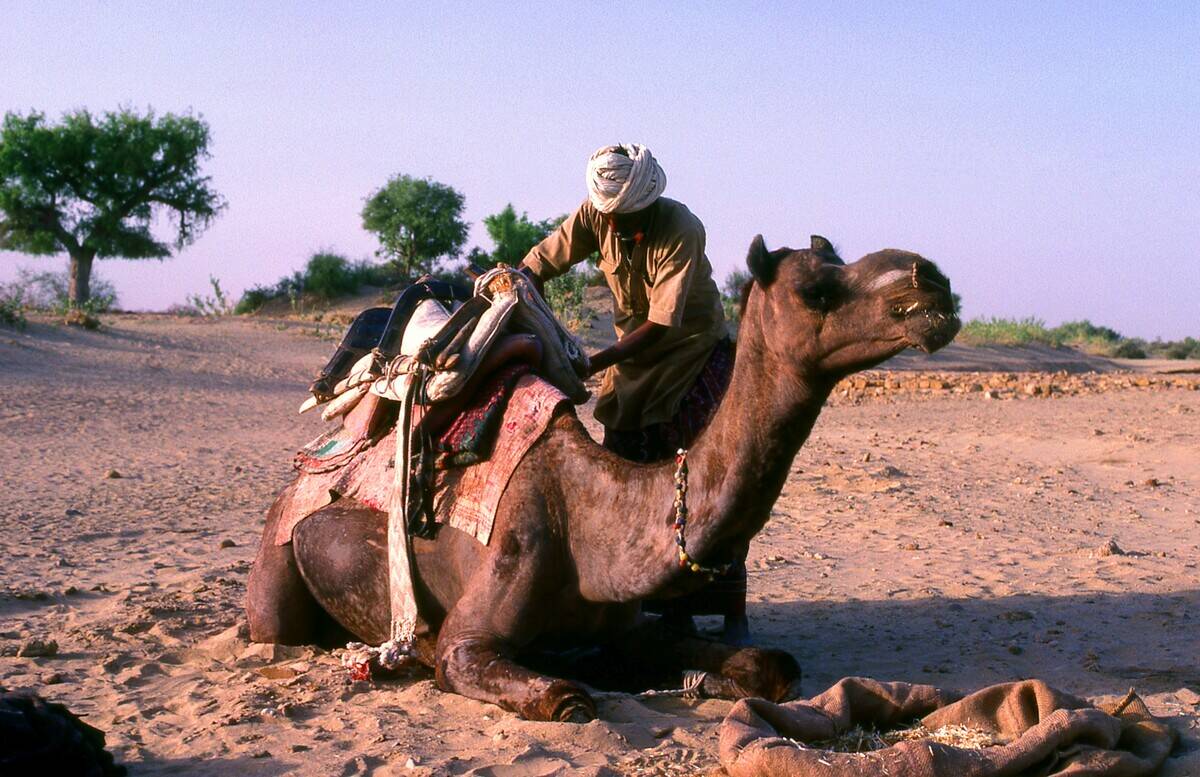

The Trans-Saharan trade routes were a complex network that connected sub-Saharan Africa with North Africa and beyond. These routes facilitated the exchange of gold, salt, and other goods, fostering economic and cultural interactions across the region.
Camel caravans traversed the harsh desert landscapes, carrying not only merchandise but also ideas and religious beliefs. The trade routes helped to spread Islam and linked distant communities, transforming the Sahara from a formidable barrier into a bridge between worlds.
The Surprising Journey of the Bronze Age Axes

Bronze Age axes discovered in distant lands have puzzled archaeologists, hinting at extensive trade networks. These metal tools, essential for ancient societies, have been found far from their production sites, indicating long-distance exchange.
The distribution of these axes suggests that trade routes spanned across Europe, facilitating the movement of ideas and technologies. These artifacts are more than mere tools; they are clues to understanding the dynamics of trade and interactions in the ancient world.
Amber Road: From the Baltic Sea to Ancient Rome

The Amber Road was a trade route that connected the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean, with amber being the prized commodity. This fossilized tree resin was highly valued in ancient Rome for its beauty and supposed magical properties.
The journey of amber from the northern forests to the heart of the Roman Empire highlights the demand for exotic goods and the lengths to which traders would go to acquire them. The route itself facilitated cultural exchanges and the spread of technologies between northern and southern Europe.
Beads and Baubles: Micro-Artifacts with Macro-Stories
![Ancient [redacted] collar, 1st century BC.](https://media.tellmebest.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/ancient-egyptian-collar-1st-century-bc-68854.jpeg)
Beads and other small artifacts often hold vast stories of trade and cultural exchange. These tiny items, made from materials like glass, shell, and stone, traveled great distances, carried by traders and exchanged in bustling markets. Each bead encapsulates a journey, revealing connections between distant communities.
Their widespread distribution points to vibrant trade networks and the human desire to adorn and express oneself, linking people across continents through fashion and personal expression.
The Curious Case of the Lapis Lazuli
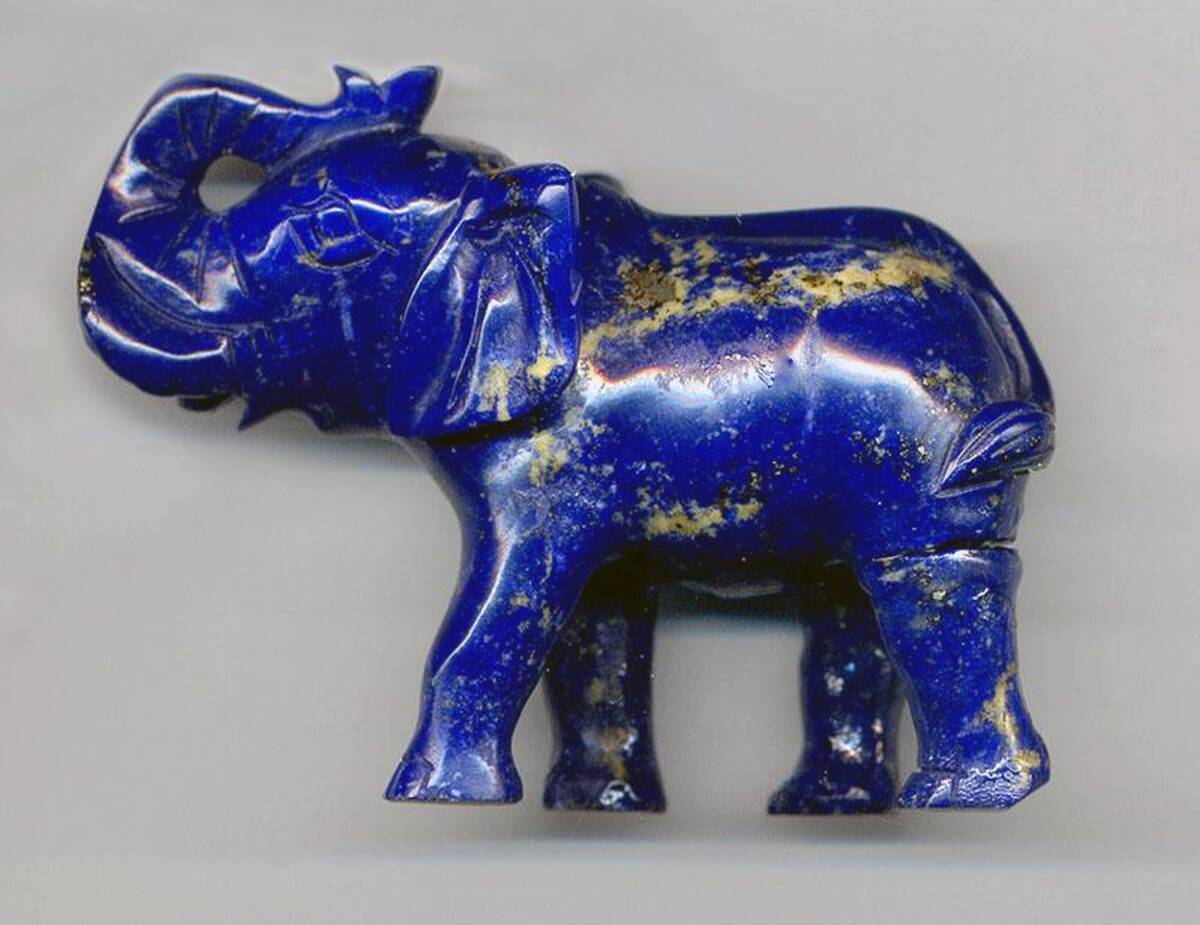

Lapis Lazuli, a vibrant blue stone, has been treasured for millennia, with its origins tracing back to mines in Afghanistan. Its journey across the ancient world, reaching as far as Egypt and Mesopotamia, highlights the extensive trade routes of the time.
The stone was used in jewelry and as a pigment, prized for its intense color. The demand for Lapis Lazuli not only drove trade but also influenced art and craftsmanship, showcasing the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations through shared appreciation for beauty.
Ancient Textiles: Weaving Stories of Cross-Continental Trade
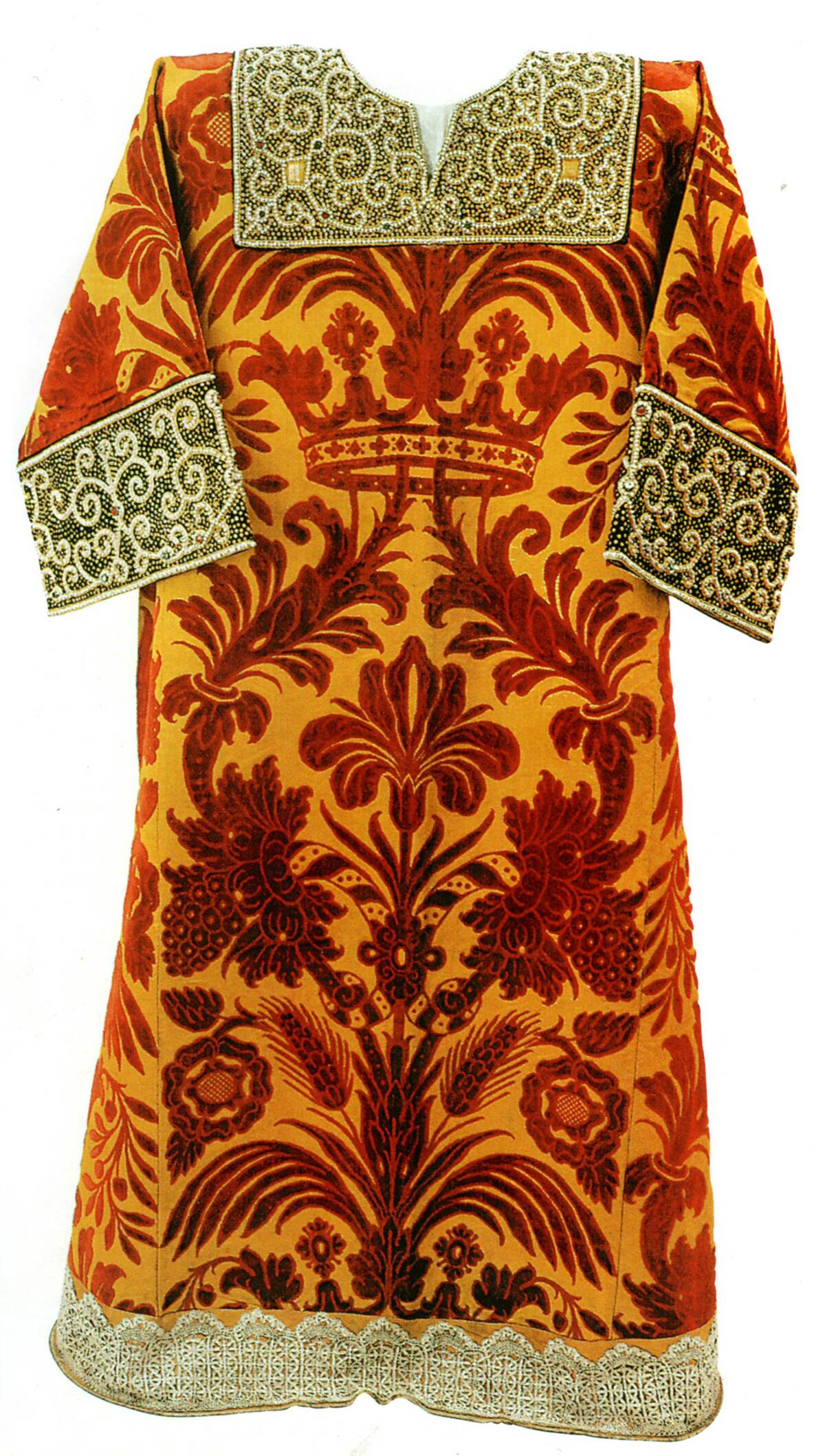

Textiles were among the most traded goods in ancient times, with their production and exchange weaving stories of cultural interaction. Fragments of ancient textiles found in various archaeological sites reveal the complex trade networks that spanned continents.
These fabrics, made from materials like wool, linen, and silk, reflect the artistry and technological advancements of their makers. The movement of textiles facilitated not just economic exchange but also the spread of styles, techniques, and cultural practices across regions.
The Role of Spices in Connecting Civilizations

Spices played a pivotal role in ancient trade, acting as both commodities and cultural bridges. From the fragrant cinnamon of Sri Lanka to the pungent black pepper of India, these aromatic treasures were highly sought after.
Spices traveled vast distances, influencing cuisines and medicinal practices across the world. The spice trade not only brought economic prosperity but also facilitated cultural exchange, with recipes and culinary techniques adapting to incorporate new flavors, fostering a global palate.
The Spread of Metallurgy: A Cross-Continental Exchange Story

Metallurgy, the art of working with metals, spread across continents, transforming societies. Techniques for smelting and forging metals like bronze and iron traveled along trade routes, facilitating technological advancements.
Artifacts reveal how knowledge of metallurgy was shared between cultures, leading to innovations in tools, weapons, and art. This exchange of metallurgical techniques underscores the interconnectedness of ancient civilizations, as they learned from each other and adapted new technologies to suit their needs.



