Elements mined in ancient times that still power modern life
Throughout history, minerals have played a crucial role in shaping civilizations. These natural treasures, from opulent gold to vibrant lapis lazuli, not only fueled economies but also inspired culture and innovation.
Today, while the world of technology and industry has evolved dramatically, the legacy of ancient minerals continues to impact our daily lives. Their stories highlight the ingenious ways our ancestors utilized these resources, often in ways we still find valuable.
Gold: From Ancient Treasures to Modern Electronics
Gold has been coveted since ancient times for its beauty and rarity. The Egyptians crafted elaborate jewelry and burial masks from gold, symbolizing wealth and divine connection.
Fast forward to today, and gold’s excellent conductivity makes it indispensable in electronics, from smartphones to satellites. Despite its modern applications, the allure of gold remains unchanged, embodying both opulence and innovation as it bridges the past with the present.
Silver: The Shimmering Element That Keeps on Giving
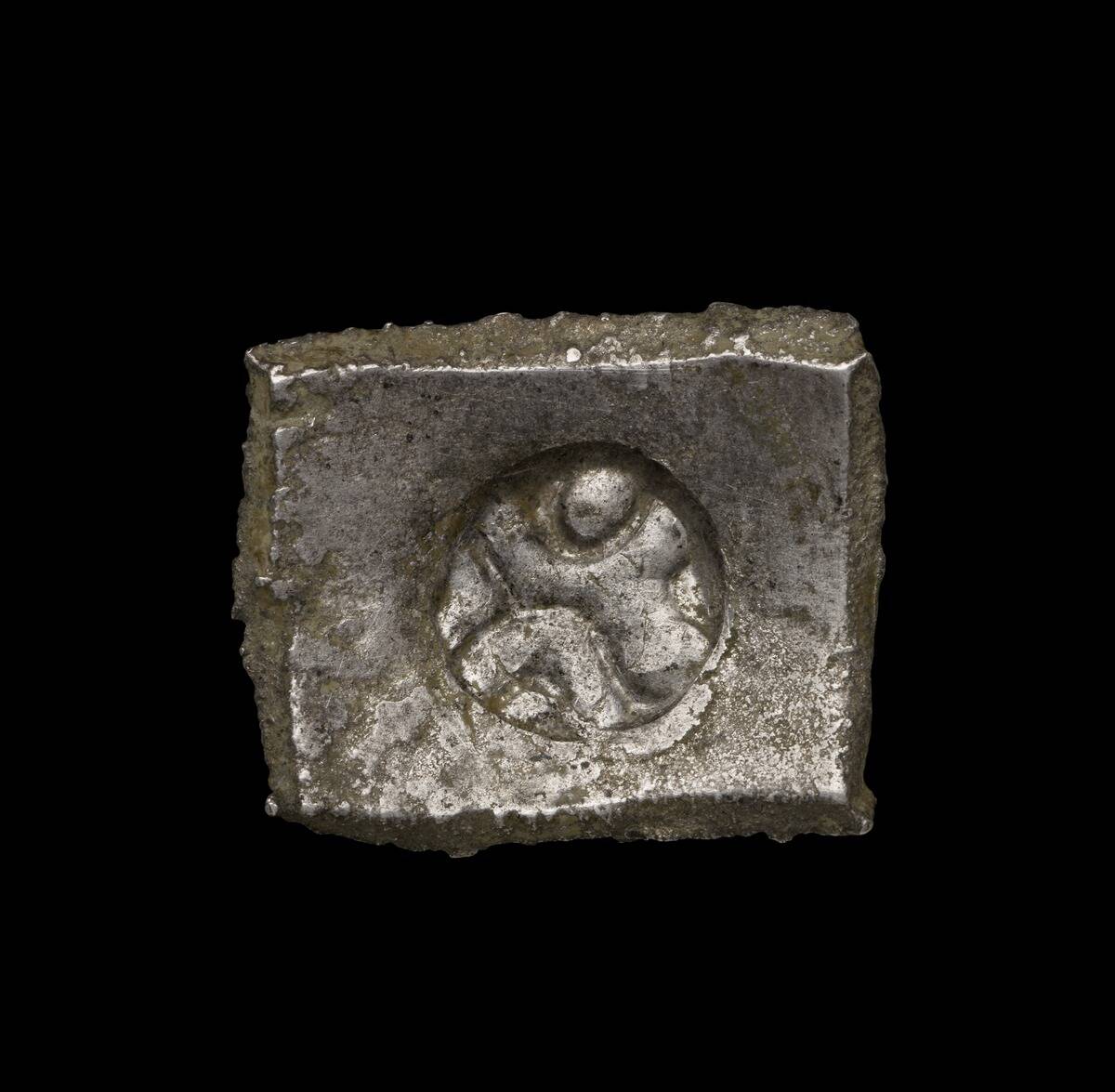

Silver’s lustrous appeal captivated ancient civilizations, who used it for coins, jewelry, and ornate tableware. Beyond its shimmer, silver boasts impressive antibacterial properties, a fact not lost on ancient healers.
Today, it’s still employed in medical devices and water purification systems. As technology advances, silver’s conductive properties also make it a staple in renewable energy industries, proving its timeless versatility.
Copper: Bridging Ancient Craftsmanship and Today’s Technology
The ancient world harnessed copper for tools, weapons, and art, with its malleability and durability making it a craftsman’s favorite. In modern times, copper remains a key player in electrical wiring due to its excellent conductivity.
This reddish-brown metal is also essential in renewable energy technologies, such as solar panels and wind turbines, highlighting its continued significance from ancient innovations to today’s technological advancements.
Lead: From Ancient Pipes to Contemporary Batteries
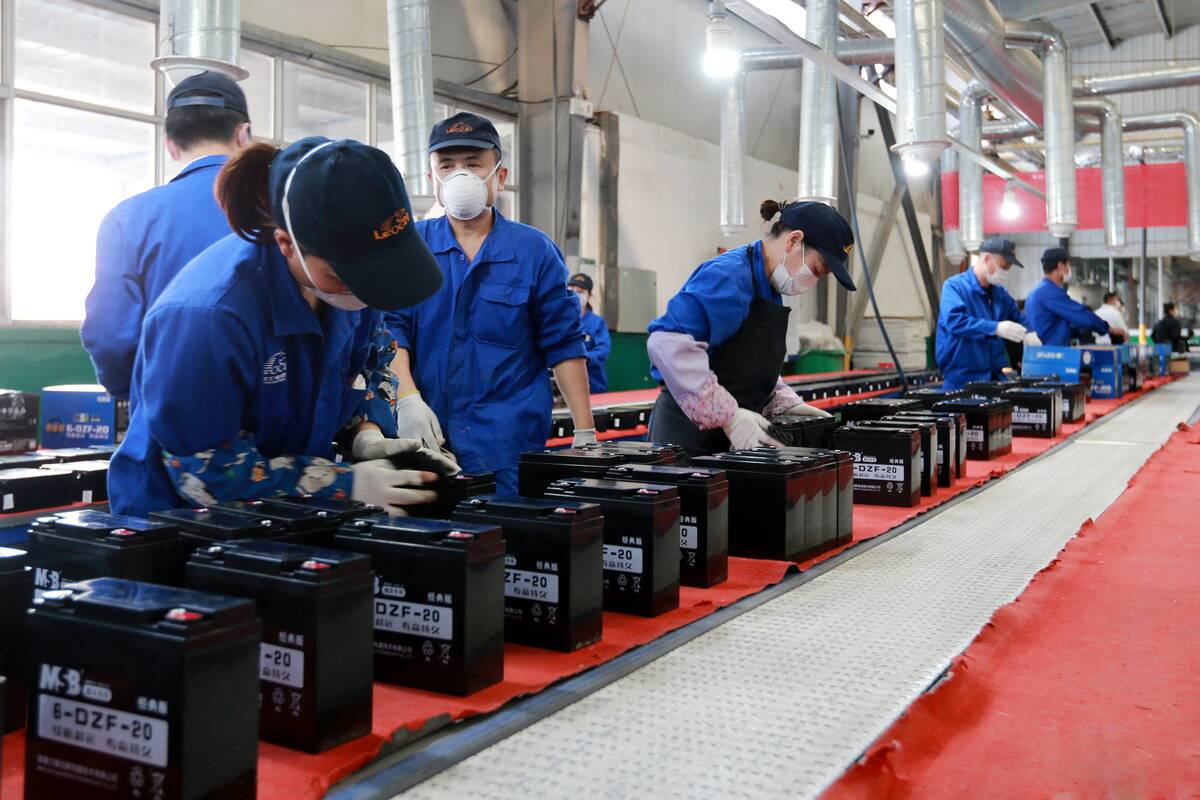

Lead has a storied past, with the Romans using it for pipes and aqueducts due to its malleability and resistance to corrosion. While lead’s use in plumbing has ceased due to health concerns, lead-acid batteries are crucial for starting cars and providing backup power.
Despite its checkered history, lead remains an integral part of modern infrastructure and technology, reflecting its complex legacy.
Iron: The Backbone of Civilization From Then Until Now

Iron’s strength and abundance made it a cornerstone of ancient civilization, from the construction of tools and weapons to the iconic Iron Age. Its significance endures today, forming the backbone of modern infrastructure, including skyscrapers and bridges.
Steel, an iron alloy, continues to dominate industries due to its versatility and strength, showcasing iron’s lasting impact on human progress and innovation.
Tin: An Ancient Alloy Ingredient With Modern Applications

Tin, often combined with copper to create bronze, played a pivotal role in ancient toolmaking. Its ability to prevent corrosion made it valuable in producing durable items.
Today, tin is a key component in soldering for electronics, ensuring strong connections in circuit boards. From ancient bronze tools to modern gadgets, tin’s utility has been a constant through the ages, illustrating its lasting relevance.
Mercury: An Element of Mystery in Ancient and Modern Times

Mercury, with its liquid form at room temperature, fascinated ancient civilizations, who believed it held mystical properties. It was used in rituals and medicine, despite its toxicity.
In modern times, mercury finds its place in scientific instruments like thermometers and barometers. Its enigmatic nature and unique properties continue to intrigue scientists and historians alike, highlighting its dual legacy of wonder and caution.
Zinc: From Ancient Healing to Modern Galvanization

Zinc’s benefits were recognized by ancient healers who used it in ointments and medicinal compounds. Today, it plays a crucial role in galvanization, a process that protects steel from corrosion.
Zinc’s role in human health is also well-established, being vital for immune function and wound healing. This versatile mineral bridges ancient practices with modern industry, underscoring its enduring importance.
Platinum: The Rare Element With Lasting Impact

Platinum’s rarity and resistance to tarnish made it a symbol of prestige in ancient civilizations, though its uses were limited. Today, platinum is a key player in automotive catalytic converters, reducing harmful emissions.
Its application in jewelry remains, but its industrial use has expanded, reflecting its transition from a rare luxury to a vital component in modern technology and environmental protection.
Sulfur: From Ancient Remedies to Modern Industry
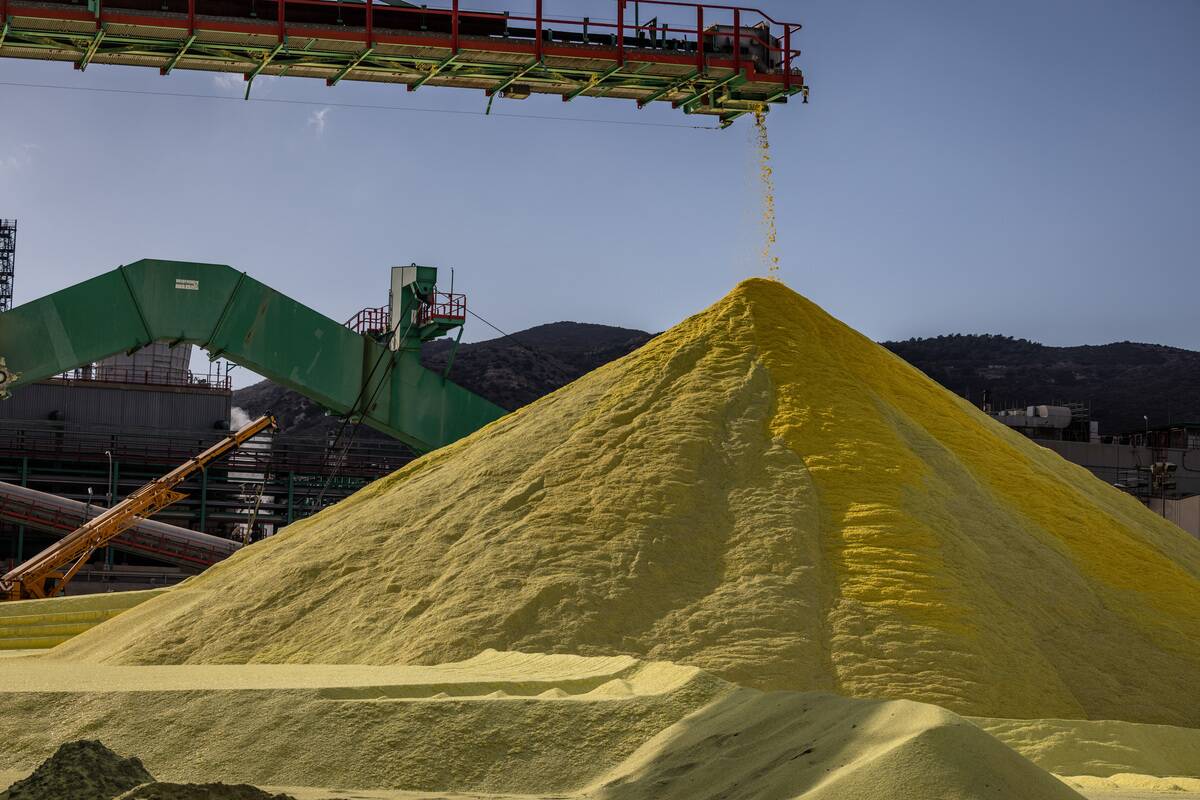

Sulfur has been known since antiquity, with ancient texts describing its use in medicine and religious rituals. Its distinct yellow color and pungent smell made it easy to recognize.
In the modern era, sulfur is indispensable in the production of fertilizers and chemicals. From ancient remedies to industrial applications, sulfur’s significance has evolved, yet its utility remains as crucial as ever.
Aluminum: The Lightweight Marvel of Then and Now
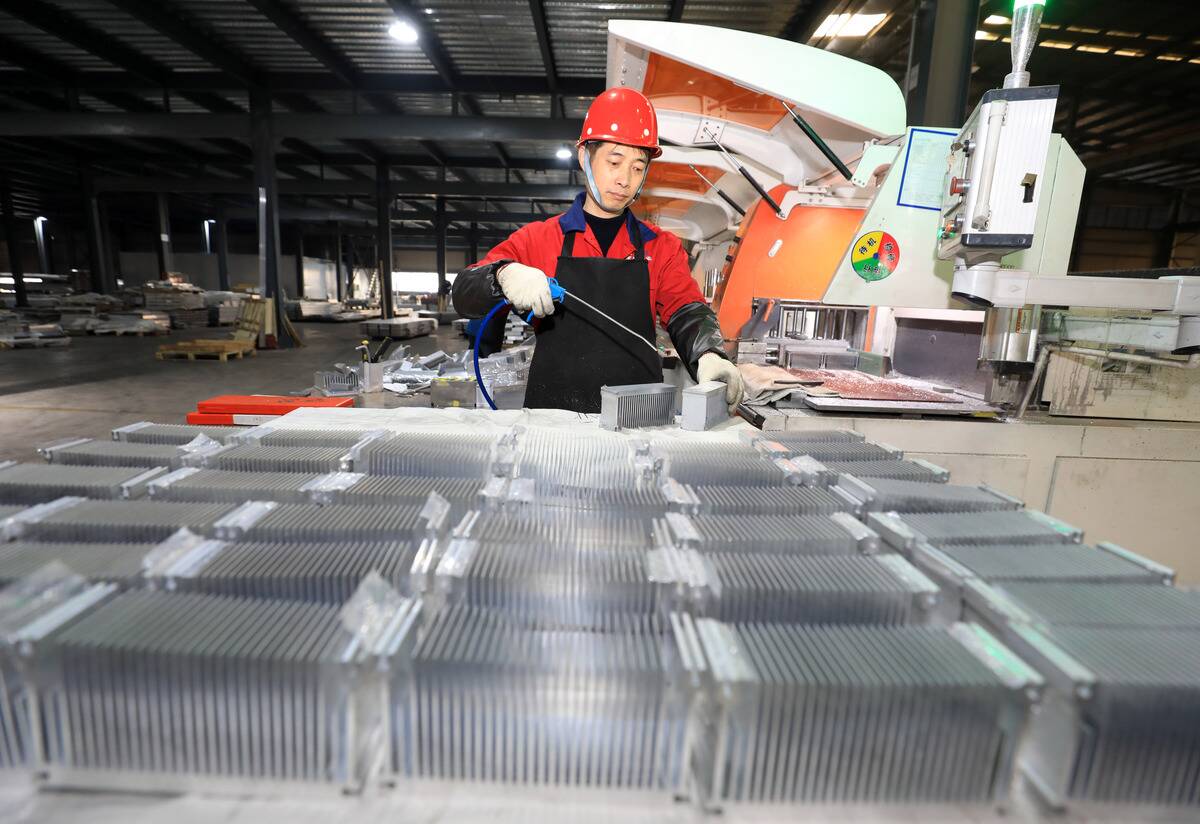

Though aluminum is abundant, it wasn’t until the 19th century that it was isolated, making it a precious material at the time. Now, aluminum’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties make it indispensable in the aerospace and transportation industries.
Its journey from a rare curiosity to a ubiquitous material reflects the advancements in extraction and processing techniques, highlighting its transformation from rarity to everyday utility.
Antimony: A Curious Element With a Storied Past and Present

Antimony’s use dates back to ancient Egypt, where it was used in cosmetics, particularly the black eyeliner known as kohl. Its utility extends to modern times, where it is used in flame retardants and lead-acid batteries.
Despite its historical and contemporary applications, antimony remains a lesser-known element, intriguing scientists and historians with its diverse uses and storied history.
Arsenic: From Ancient Pigments to Modern Uses

Arsenic was historically used in pigments and as a poison, with a reputation both feared and revered. In modern times, its role has shifted to include uses in electronics and wood preservation.
Advances in understanding arsenic’s properties have led to safer applications, transforming its narrative from a symbol of danger to a controlled component in various industries, showcasing its complex legacy.
Lapis Lazuli: Ancient Beauty, Modern Inspiration

Lapis lazuli, with its deep blue color and golden flecks, was a prized gemstone in ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, often used in jewelry and religious artifacts. Its allure continues today in art and decorative items, symbolizing luxury and creativity.
This vibrant stone’s enduring beauty serves as a source of inspiration for artists and designers, bridging ancient aesthetics with contemporary design.




