Agreements that quietly shaped the modern world
Throughout history, agreements, treaties, and conventions have quietly steered the course of nations. These deals, often struck behind closed doors, have crafted the world we know today.
From ancient accords to modern pacts, these unseen handshakes have dictated everything from borders to trade, and even how we interact in the digital age. Let’s explore some of the most pivotal agreements that have left an indelible mark on human history.
The Magna Carta: The Birth of Modern Law
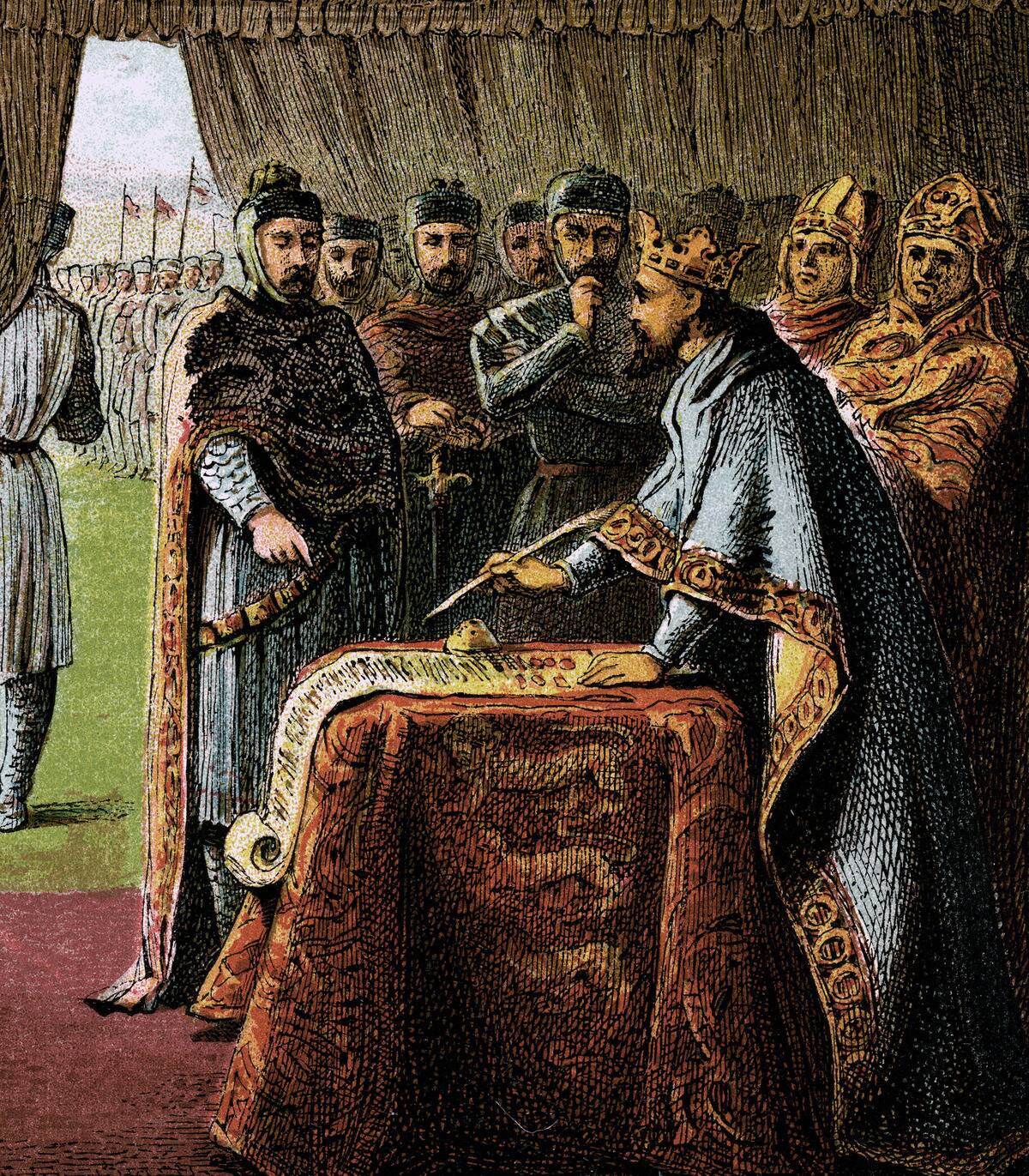

The Magna Carta, signed in 1215, is often hailed as the cornerstone of modern democracy and legal systems. King John of England was coerced into sealing this ‘Great Charter’ by his rebellious barons, setting a precedent for the principle that everyone, including the king, was subject to the law.
This document laid the foundation for constitutional law, influencing later documents like the U.S. Constitution and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
The Treaty of Westphalia: Laying Down the Law of Nations
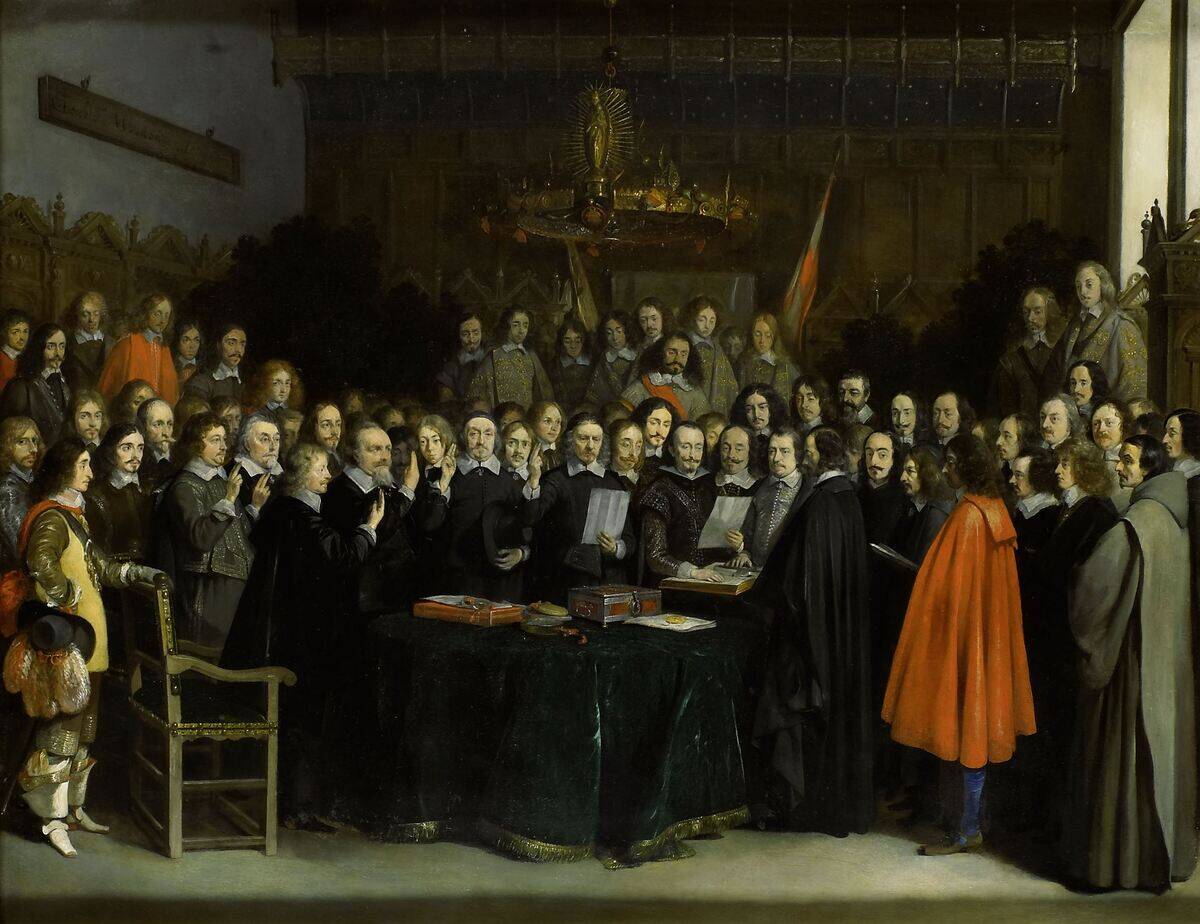

In 1648, the Treaty of Westphalia ended the Thirty Years’ War in Europe, marking a turning point in international relations. It introduced the concept of state sovereignty, which became a defining element of the modern state system.
By recognizing the independence of various territories, it paved the way for the rise of nation-states and established a new order where diplomacy and negotiation took precedence over military might.
The Bretton Woods Agreement: Crafting the Economic Order

The Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944 was instrumental in shaping the post-World War II economic landscape. Delegates from 44 Allied nations gathered in New Hampshire to establish a system of monetary management that led to the creation of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank.
This agreement aimed to foster economic stability and prevent the financial chaos that followed the First World War, setting the stage for decades of global economic growth.
The Geneva Conventions: Setting the Rules for War

The Geneva Conventions, first adopted in 1864 and expanded in subsequent years, are a series of treaties that set the standards for international law for humanitarian treatment in war. They protect those not participating in hostilities, such as civilians, and those who are no longer participating, like the wounded and prisoners of war.
These conventions underscore the importance of humane treatment and have been ratified by nearly every nation, underscoring their universal acceptance.
The United Nations Charter: An Anthem of Peace
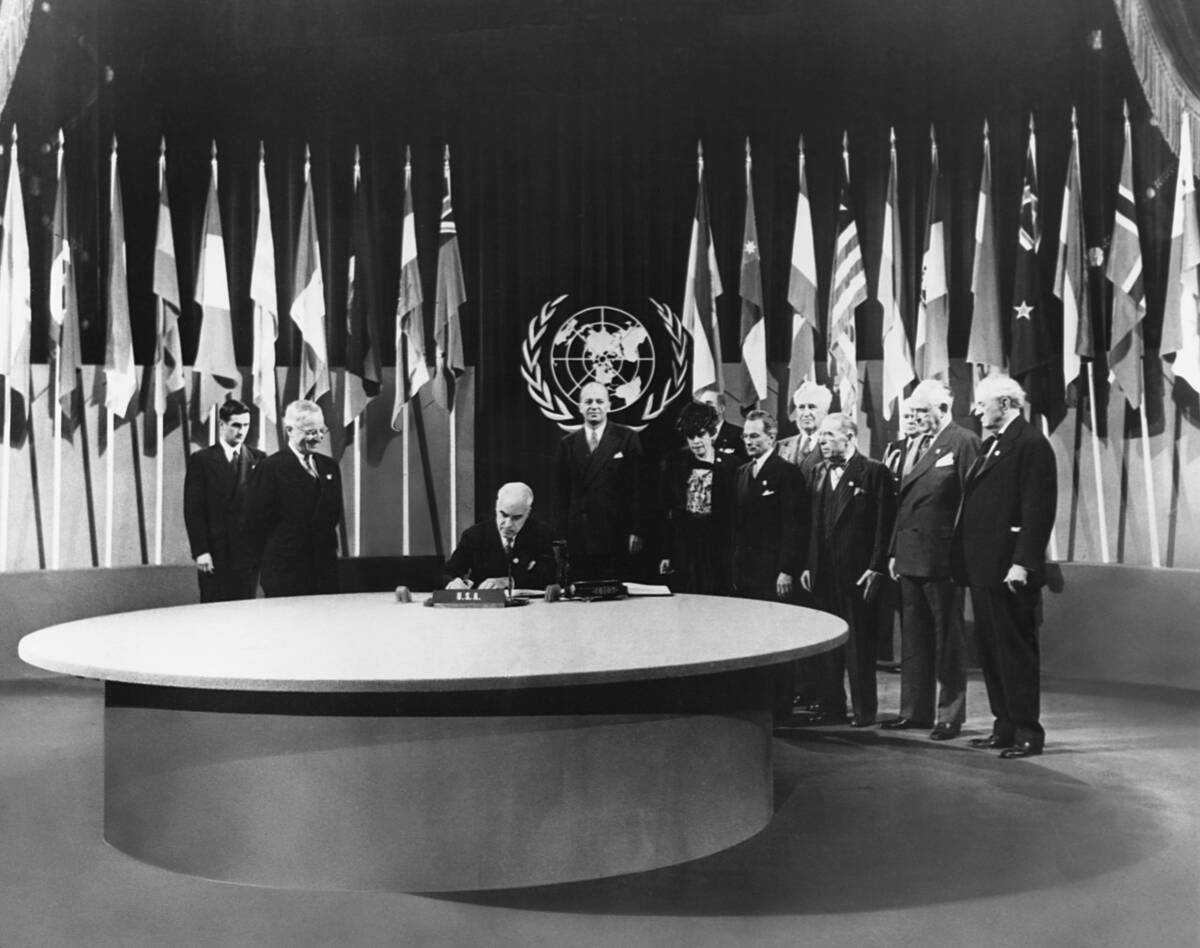

Signed in 1945, the United Nations Charter established the UN with the primary aim of preventing future conflicts and fostering peace. This international treaty laid down principles for international cooperation and conflict resolution, emphasizing human rights, social progress, and justice.
Its creation marked a pivotal shift towards multilateralism and has been a cornerstone in promoting global peace and security ever since.
The North Atlantic Treaty: A Commitment to Collective Security

The North Atlantic Treaty, signed in 1949, is the founding document of NATO, a military alliance formed in the aftermath of World War II. It was designed to counter the Soviet threat and ensure collective defense, stating that an attack on one member is an attack on all.
This treaty not only solidified transatlantic ties but also played a crucial role in maintaining peace and security during the Cold War era.
The Kyoto Protocol: Pioneering Environmental Responsibility

The Kyoto Protocol, adopted in 1997, marked a significant step in international efforts to combat climate change. It was the first treaty to commit countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the premise that global warming is a result of human activities.
Although it faced challenges and criticism, the protocol laid the groundwork for future environmental agreements, including the Paris Climate Agreement.
The Schengen Agreement: The Rise of Borderless Travel

Signed in 1985, the Schengen Agreement revolutionized travel within Europe by abolishing internal border checks among participating countries. This agreement not only facilitated the free movement of people and goods but also symbolized a step towards European integration.
Today, it encompasses 26 countries, making travel within Europe seamless and fostering cultural and economic exchange across the continent.
The World Trade Organization Agreements: Promoting Global Commerce

Formed in 1995, the World Trade Organization (WTO) is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations. Its agreements are negotiated and signed by a large majority of the world’s trading nations and ratified in their parliaments.
These agreements aim to ensure that trade flows as smoothly, predictably, and freely as possible, lifting millions out of poverty by fostering economic growth and development.
The Paris Climate Agreement: A Global Pact for the Planet

Adopted in 2015, the Paris Climate Agreement represents a historic commitment by 196 countries to combat climate change and limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius.
It emphasizes the role of each nation in reducing emissions and adapting to climate impacts. This landmark accord is pivotal in uniting countries under a common cause to safeguard the planet for future generations.
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT): Opening Up World Markets

Established in 1947, the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) aimed to promote international trade by reducing or eliminating trade barriers such as tariffs and quotas.
It provided a framework for negotiating trade agreements and a process for resolving disputes, eventually leading to the creation of the World Trade Organization. GATT played a crucial role in the expansion of global trade post-World War II.
The Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty: Containing the Atomic Age

The Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), effective since 1970, is a landmark international treaty aimed at preventing the spread of nuclear weapons and technology. It promotes the peaceful use of nuclear energy and aims for nuclear disarmament.
With 191 states parties, it is one of the most widely adhered to arms control agreements, playing a crucial role in maintaining global security and preventing nuclear proliferation.
The European Union Treaties: Forging a Unified Continent

The European Union (EU) is built on a series of treaties, beginning with the Treaty of Rome in 1957, which established the European Economic Community. These treaties have progressively integrated member states, creating a single market and fostering political and economic cooperation.
The Lisbon Treaty, which took effect in 2009, further strengthened the EU’s powers and streamlined its operations, solidifying its role as a unified political entity.
The International Space Treaty: Peaceful Cooperation Beyond Earth

The Outer Space Treaty, signed in 1967, is the cornerstone of international space law. It prohibits the placement of nuclear weapons in space and limits the use of celestial bodies to peaceful purposes.
By emphasizing cooperation and the peaceful exploration of space, it has enabled numerous international collaborations in space exploration, symbolizing humanity’s shared interest in the cosmos and the peaceful use of the final frontier.
The Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women: Advancing Gender Equality

Adopted in 1979 by the United Nations General Assembly, this convention aims to eliminate discrimination against women and promote gender equality.
Often described as an international bill of rights for women, it covers various aspects of women’s lives, including political rights, health, and education. It has been ratified by 189 countries, highlighting its global impact in advancing women’s rights and gender equality worldwide.
The Digital Millennium Copyright Act: Navigating the Internet Age
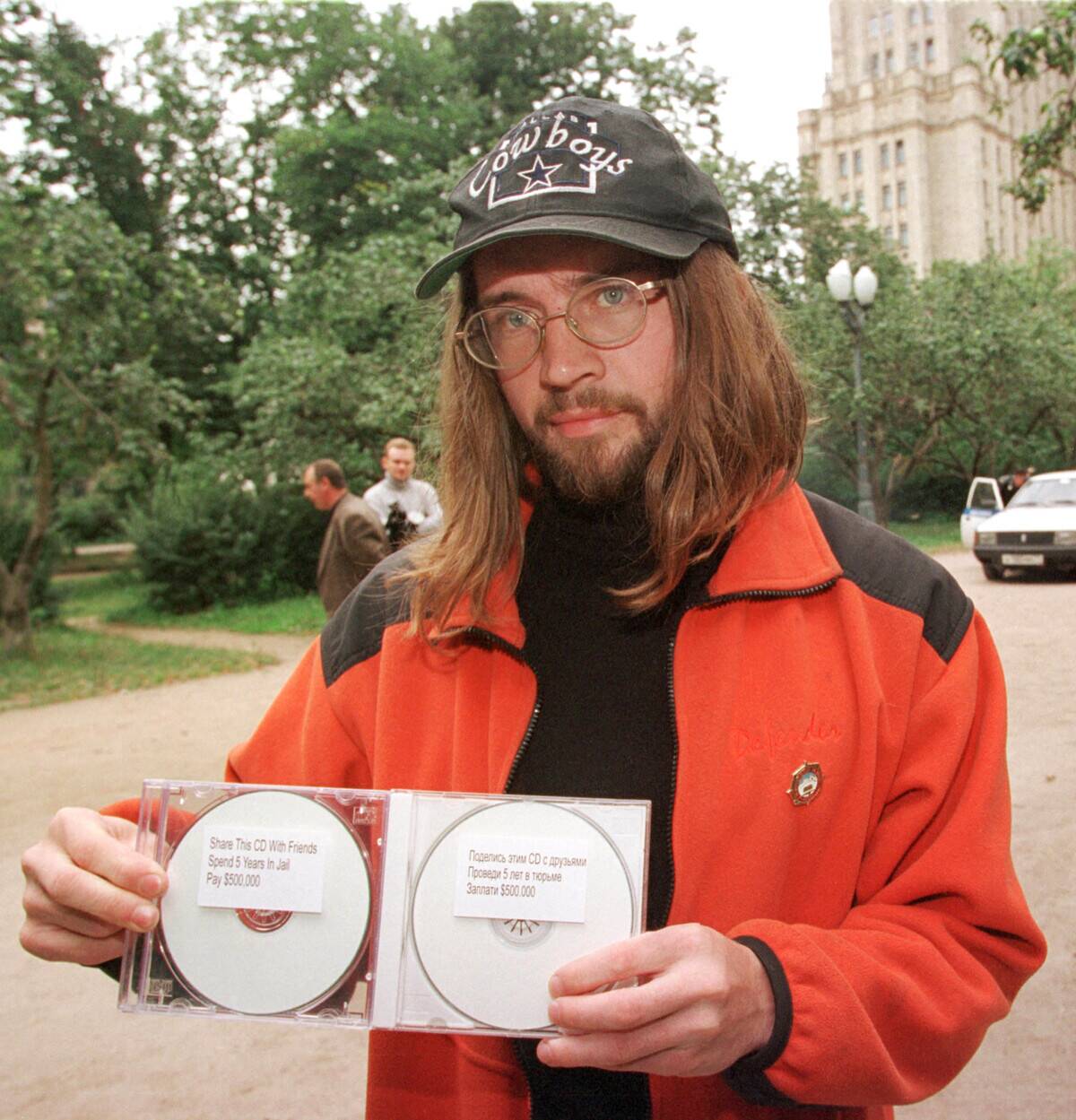

Enacted in 1998, the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) addresses the challenges of copyright enforcement in the digital age. It criminalizes the production and dissemination of technology intended to circumvent digital rights management measures.
The DMCA has shaped the legal landscape of the internet, balancing the interests of copyright holders with the need for technological innovation and free expression.
The South China Sea Code of Conduct: Navigating Tensions in Troubled Waters

The South China Sea Code of Conduct is an ongoing diplomatic effort aimed at managing tensions in the South China Sea, a region fraught with territorial disputes. While not yet finalized, it represents a significant step towards peaceful resolution and cooperation among claimant nations.
The code seeks to prevent conflicts and promote stability in this strategically important and resource-rich region, underscoring the importance of diplomacy in resolving complex maritime issues.