How trade routes built and destroyed civilizations
Trade routes have been the lifelines of civilizations, connecting distant lands and fostering the exchange of goods, ideas, and culture. From the earliest barter systems to the global supply chains of today, these pathways have shaped economies and societies.
Imagine a world where spices, silk, and precious metals journeyed across continents, creating a web of connections long before the internet. Let’s embark on a journey through time to explore these fascinating routes.
The Dawn of Trade: Early Barter Systems

Long before currency, barter systems were the primary mode of trade. People exchanged goods directly, such as grain for livestock or tools for pottery. Imagine a world where negotiations were as simple as swapping a basket of apples for a bundle of wool.
This system thrived in local communities and laid the foundation for more complex trade networks. While challenges like finding a perfect match for trade existed, it demonstrated early human innovation in commerce.
Silk Road: The Ancient Superhighway
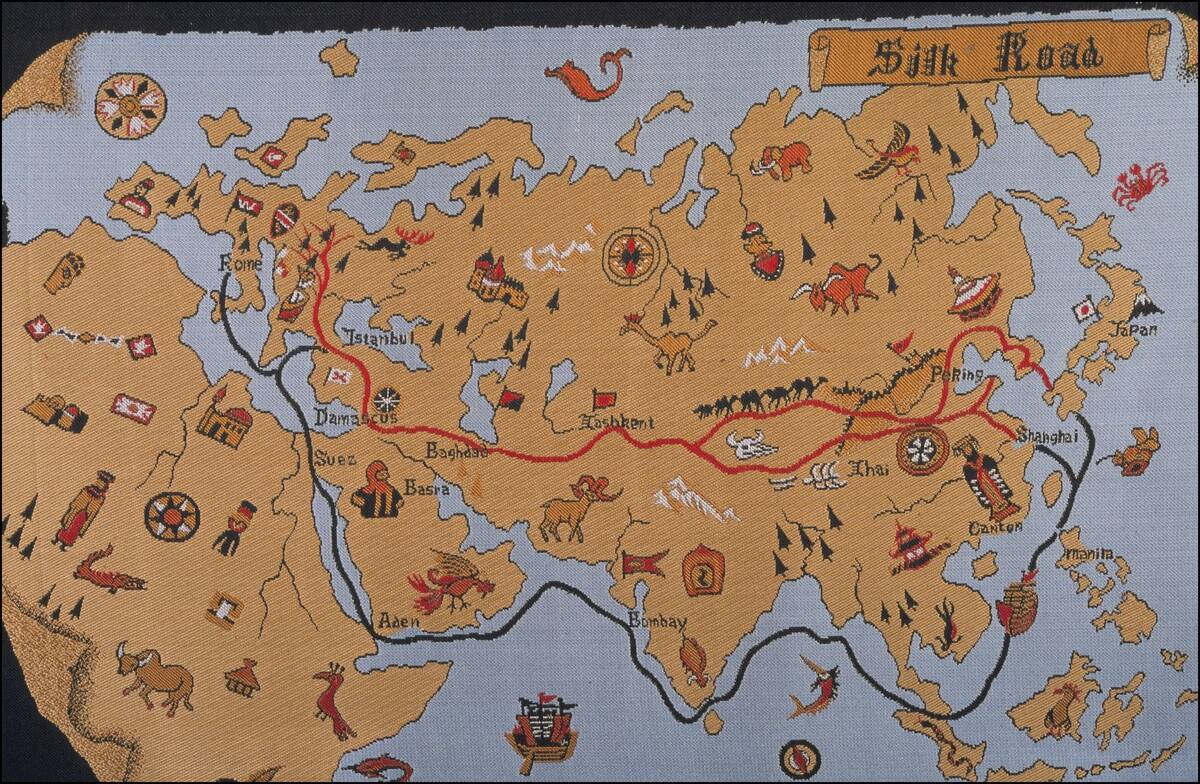
The Silk Road wasn’t just a single road but a vast network of trade routes connecting Asia with Europe. It facilitated the exchange of silk, spices, and even ideas, influencing cultures along its paths.
Traders traversed deserts and mountains, sharing not only goods but also stories and knowledge. This ancient superhighway spanned thousands of miles, making it a conduit for cultural and economic exchange between East and West. Marco Polo’s travels along this route are legendary!
Spice Routes: A Flavorful Path to Riches
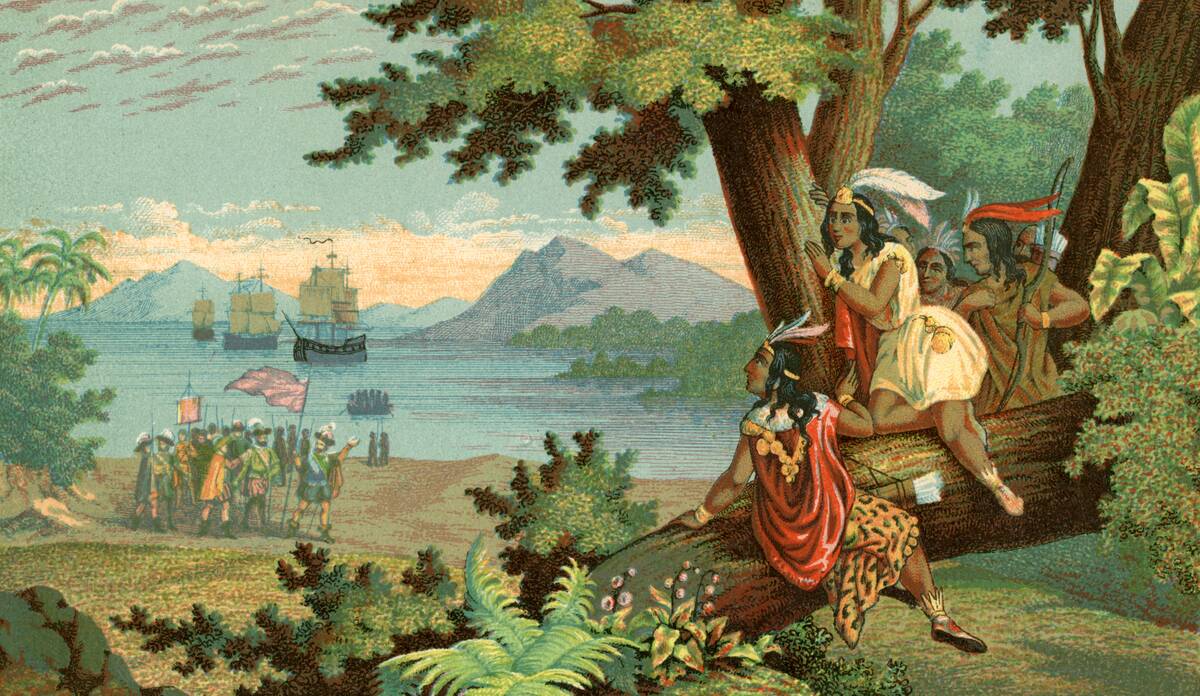

Spices, once worth their weight in gold, traveled from Asia to Europe via maritime routes. The pursuit of these exotic flavors like cinnamon and pepper led to exploration and the eventual discovery of new lands.
These routes were not just about spices; they also fostered cultural exchanges, with merchants sharing tales of distant lands. The allure of spices fueled maritime exploration, leading to the discovery of the Americas by Columbus.
The Maritime Marvel: Indian Ocean Trade Networks
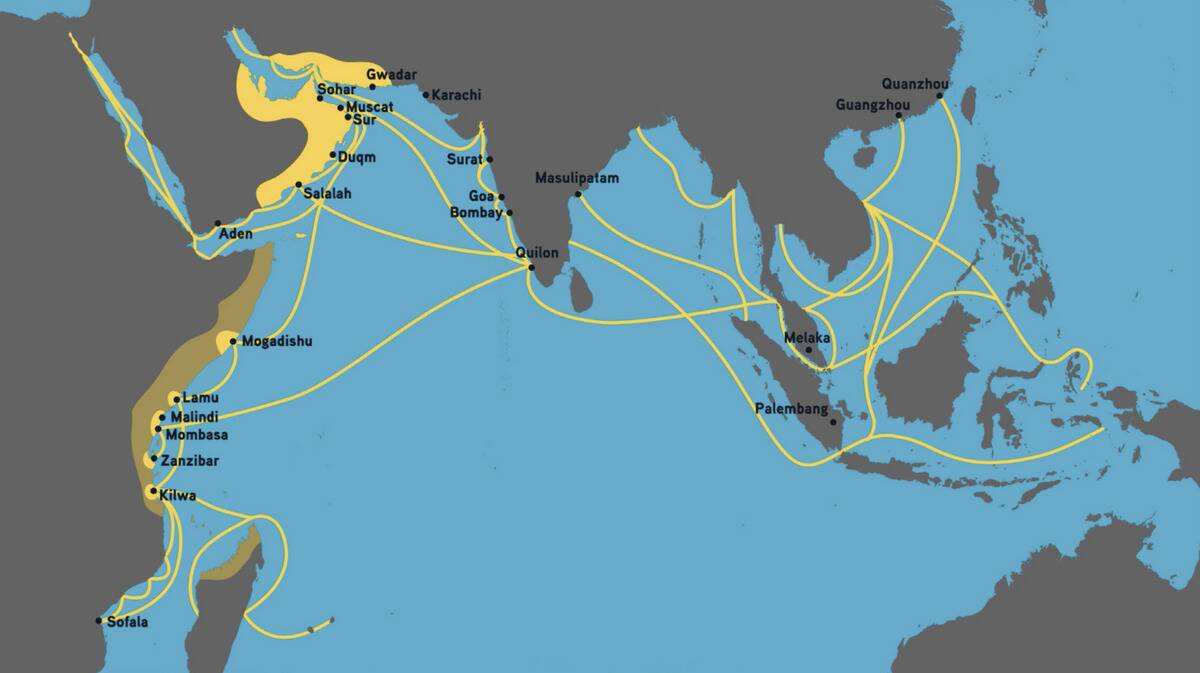
The Indian Ocean trade networks connected East Africa, the Middle East, India, and Southeast Asia, creating a bustling maritime economy. This vast network was crucial for the exchange of goods like textiles, ivory, and spices.
Monsoon winds played a pivotal role, dictating the timing of voyages. These trade routes were not only about commerce but also cultural exchanges, as evidenced by the spread of Islam and Hinduism along the coasts of the Indian Ocean.
The Rise of the Roman Empire: Trade as a Foundation
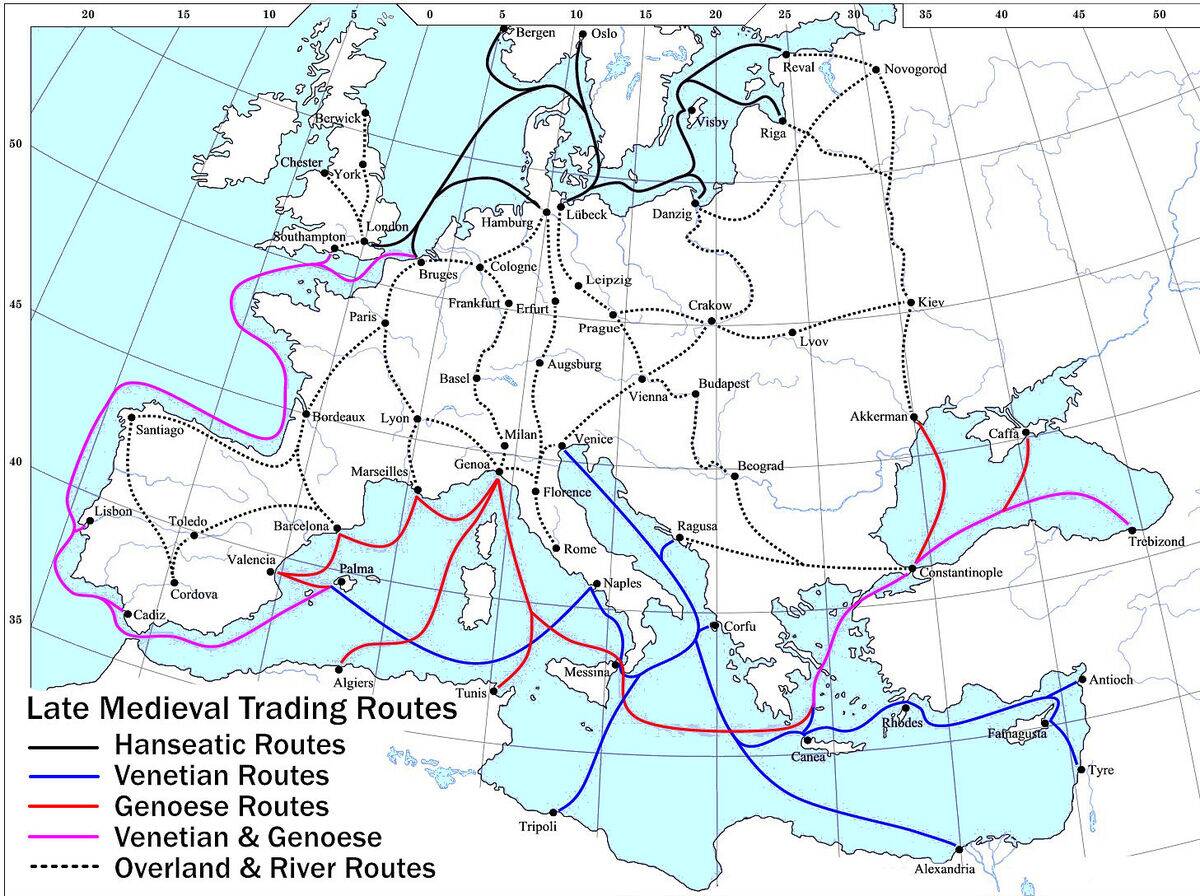
The Roman Empire thrived on a robust trade network that spanned Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. Roads, aptly termed “all roads lead to Rome,” facilitated the movement of goods and people.
The empire’s trade brought in luxury items like silk and spices, fueling its economy. Roman coins found in distant lands highlight the empire’s extensive reach. Trade wasn’t just economic for Rome; it was integral to its power and stability.
The Trans-Saharan Trade and the Wealth of African Kingdoms
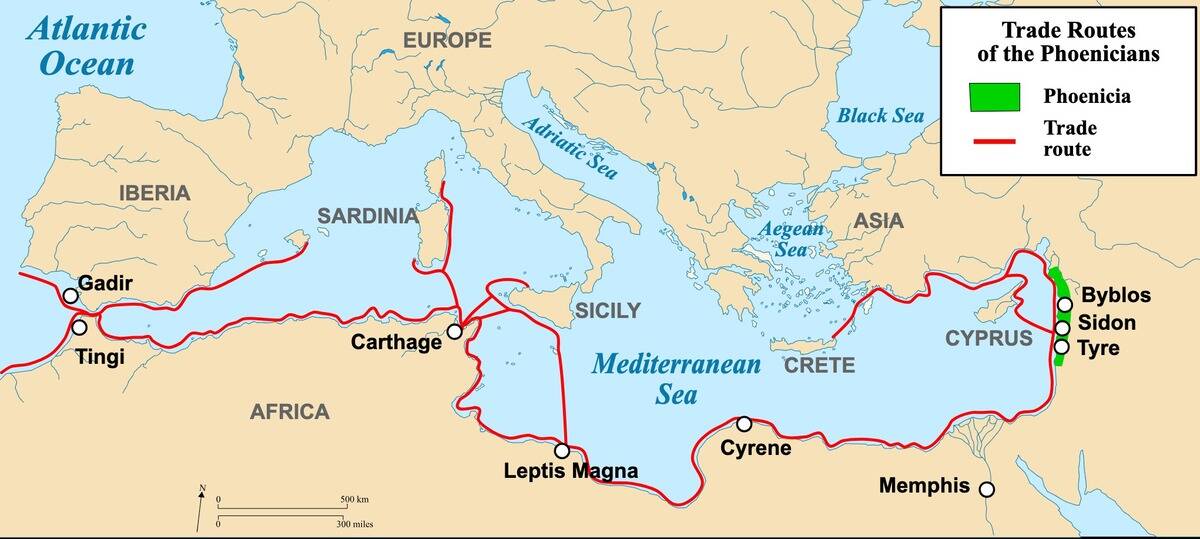
The trans-Saharan trade routes connected West Africa with the Mediterranean, trading gold, salt, and other commodities. These routes led to the rise of powerful African kingdoms like Mali and Ghana. Caravans of camels crossed the Sahara, exchanging goods and culture.
The wealth generated from this trade helped build magnificent cities like Timbuktu, a center of learning and culture. The legacy of these routes is evident in the rich history of West Africa.
The Columbian Exchange: New Worlds Collide
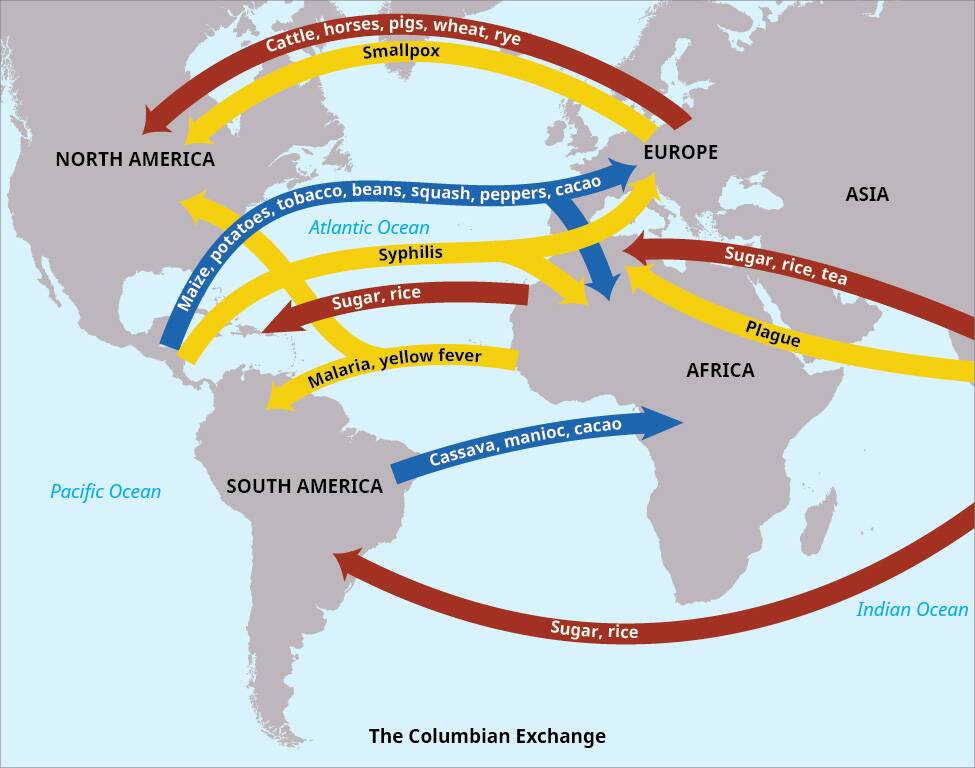
The Columbian Exchange marked a pivotal moment in trade history, as the Old and New Worlds connected. This exchange wasn’t just about goods but also plants, animals, and even diseases.
Potatoes and tomatoes from the Americas transformed European diets, while horses and wheat traveled west. The impact of this exchange was profound, reshaping economies, cultures, and populations. However, it also brought unintended consequences, such as the spread of diseases like smallpox.
The Hanseatic League: A Medieval Trade Powerhouse
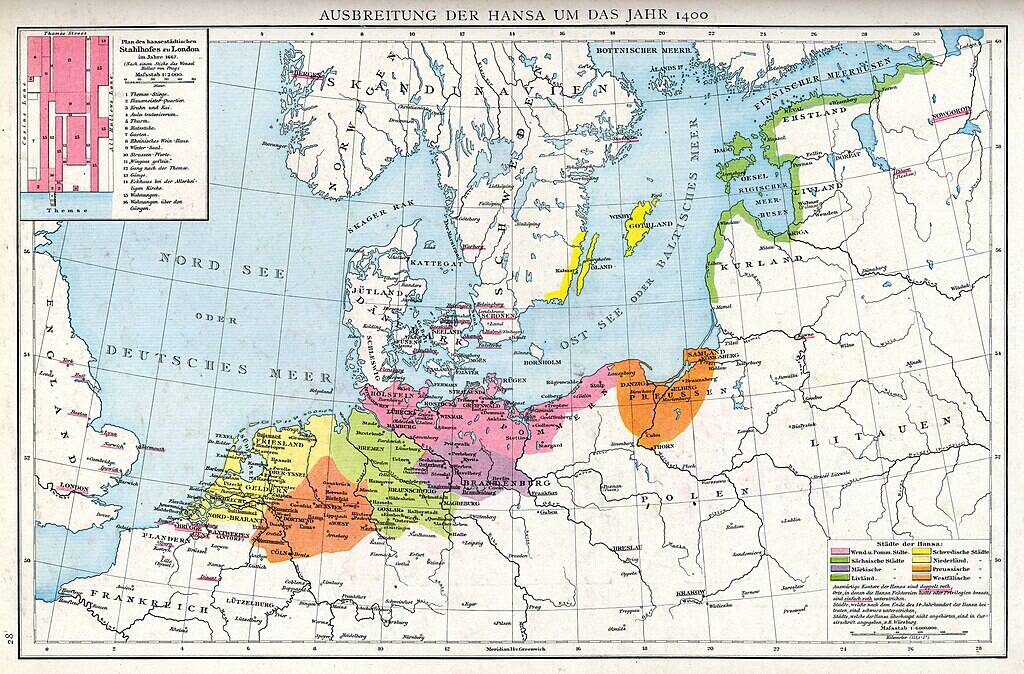
In medieval Europe, the Hanseatic League was a powerful alliance of North German towns and cities. This league dominated trade in the Baltic and North Seas, dealing in goods like timber, furs, and fish.
The league’s influence extended beyond commerce, impacting politics and culture in the region. It established a network of trade routes that facilitated economic growth, showcasing the power of cooperation. The Hanseatic League remains a testament to medieval trade ingenuity.
The Impact of the British East India Company on Global Trade
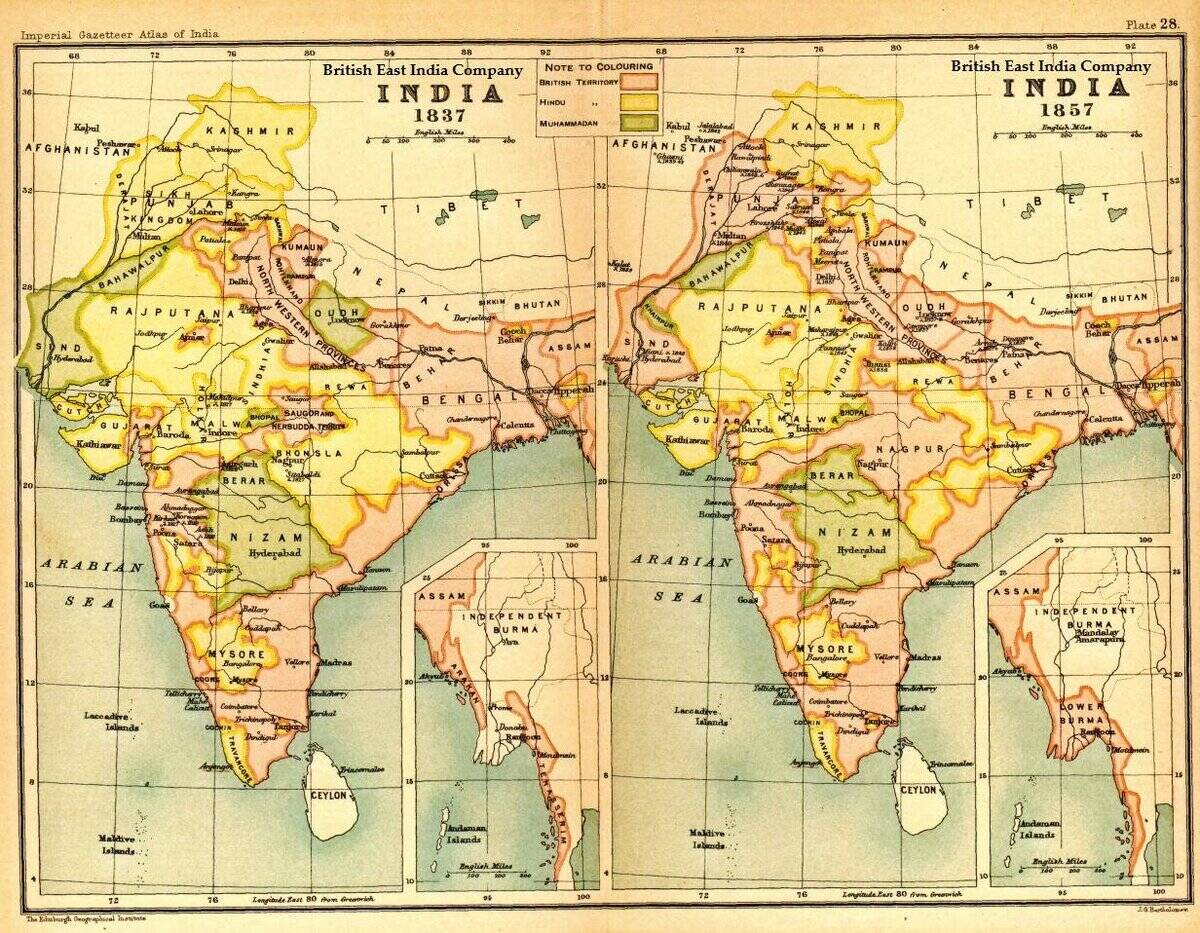
The British East India Company played a crucial role in shaping global trade during the 17th and 18th centuries. This company held a monopoly on trade between Britain and the East Indies, dealing in spices, tea, and textiles.
Its power was so vast that it even governed territories in India. The company’s impact was profound, influencing not just commerce but also politics and colonial expansion. Its legacy is both a tale of trade and imperial ambition.
How Trade Routes Fueled the Renaissance
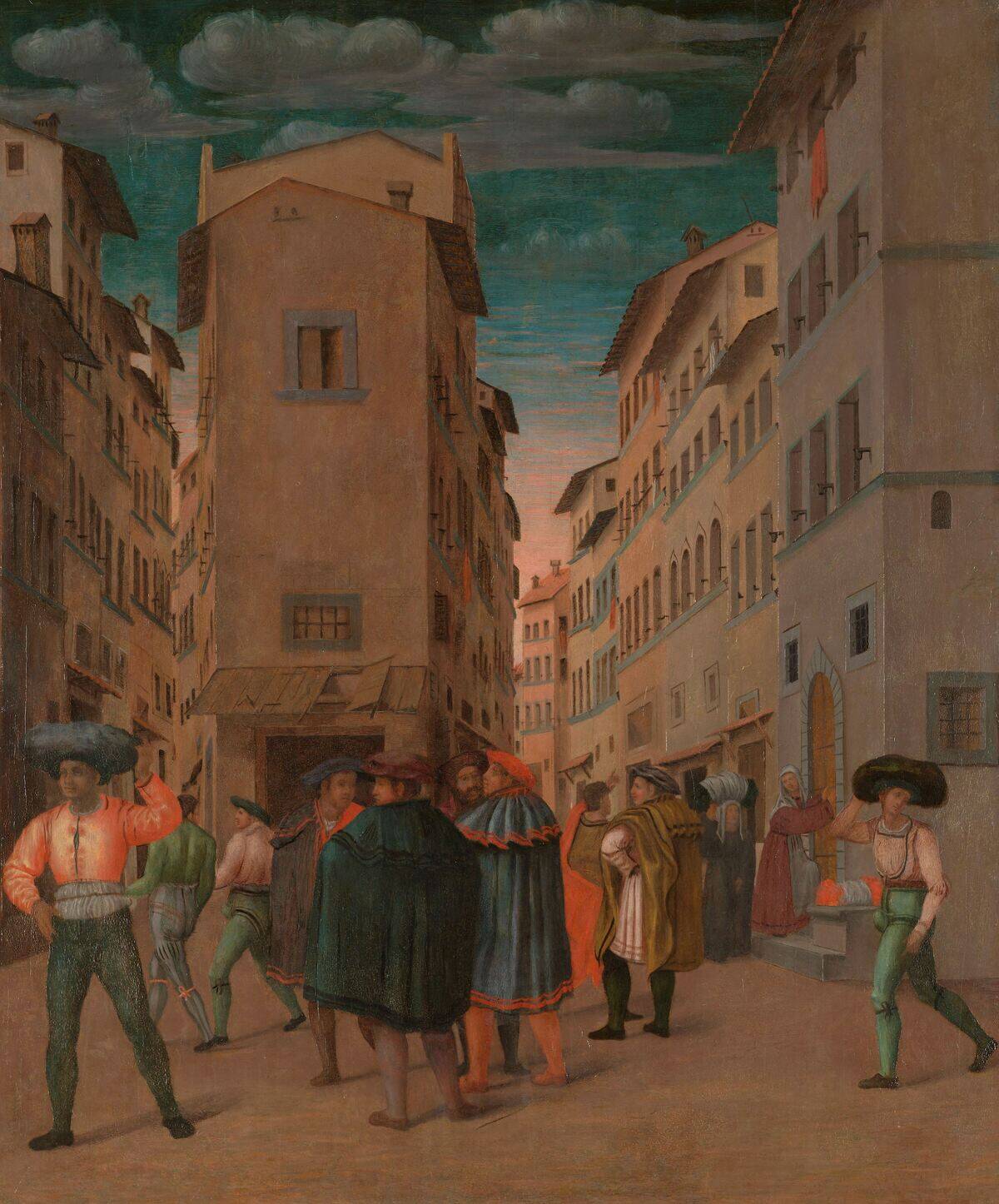

Trade routes were instrumental in fueling the Renaissance, a period of cultural and intellectual revival in Europe. The wealth generated from trade allowed patrons to support artists and scholars. Cities like Florence and Venice, rich from trade, became centers of Renaissance art and culture.
The exchange of ideas along these routes also played a role, as scholars shared knowledge and innovations. This period marked a flourishing of creativity and learning, thanks to the power of trade.
The Downfall of the Byzantine Empire: Trade Shifts and Consequences
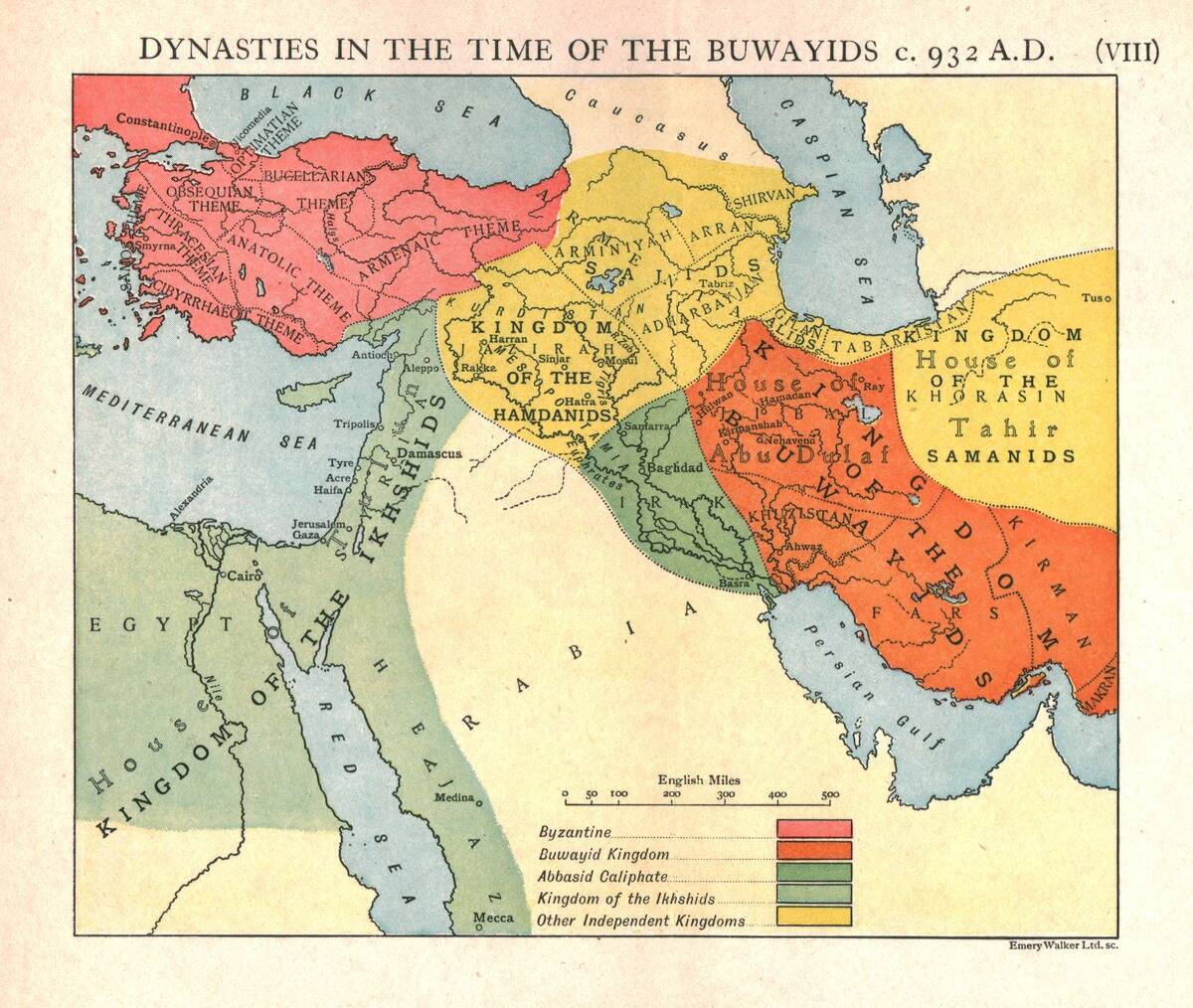
The Byzantine Empire, once a trade powerhouse, faced decline as trade routes shifted. The rise of Ottoman control over key routes disrupted Byzantine commerce. Constantinople, a critical trade hub, lost its prominence, impacting the empire’s economy.
The fall of Constantinople in 1453 marked the end of the Byzantine Empire, reshaping trade in the region. This shift in trade dynamics had lasting effects, paving the way for new powers to emerge on the global stage.
The Role of Trade in the Spread of Ideas and Culture

Trade routes have always been conduits for more than just goods; they’ve been pathways for ideas and culture. Alongside silk and spices, philosophies, religions, and technologies traversed these routes. The spread of Buddhism from India to East Asia is a testament to this cultural exchange.
Merchants, travelers, and scholars shared stories and knowledge, enriching societies. Trade routes were not just economic highways; they were arteries of cultural and intellectual growth.
Disease and Decline: The Black Death’s Journey Along Trade Routes
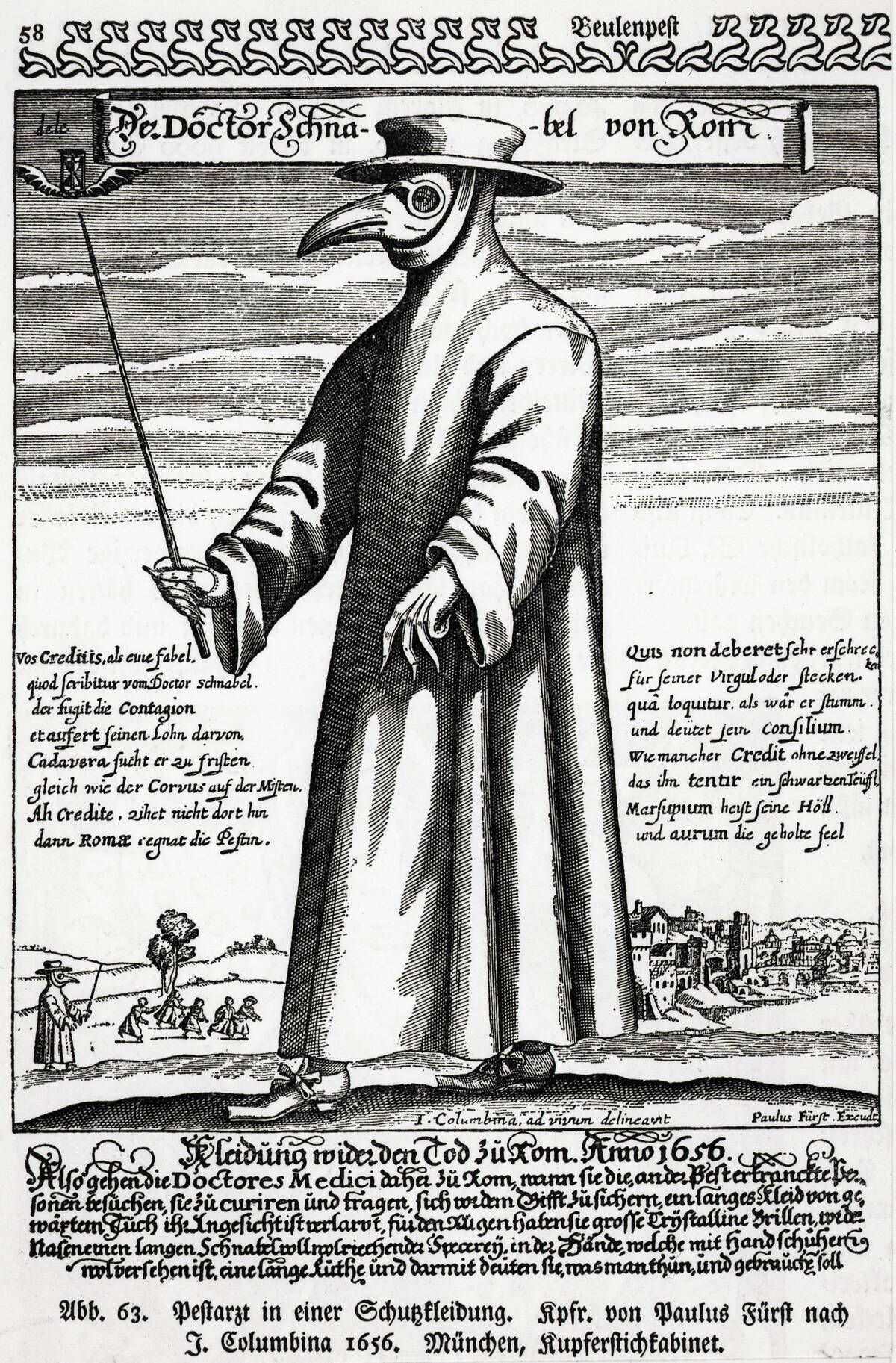

The Black Death, one of history’s deadliest pandemics, spread along trade routes in the 14th century. Originating in Asia, it traveled to Europe via the Silk Road and maritime routes. The movement of goods and people facilitated the rapid spread of the disease, leading to massive population declines.
This pandemic had profound social and economic impacts, altering the course of history. It serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of trade and the unintended consequences it can bring.
Modern Trade Routes: The Global Supply Chain Network
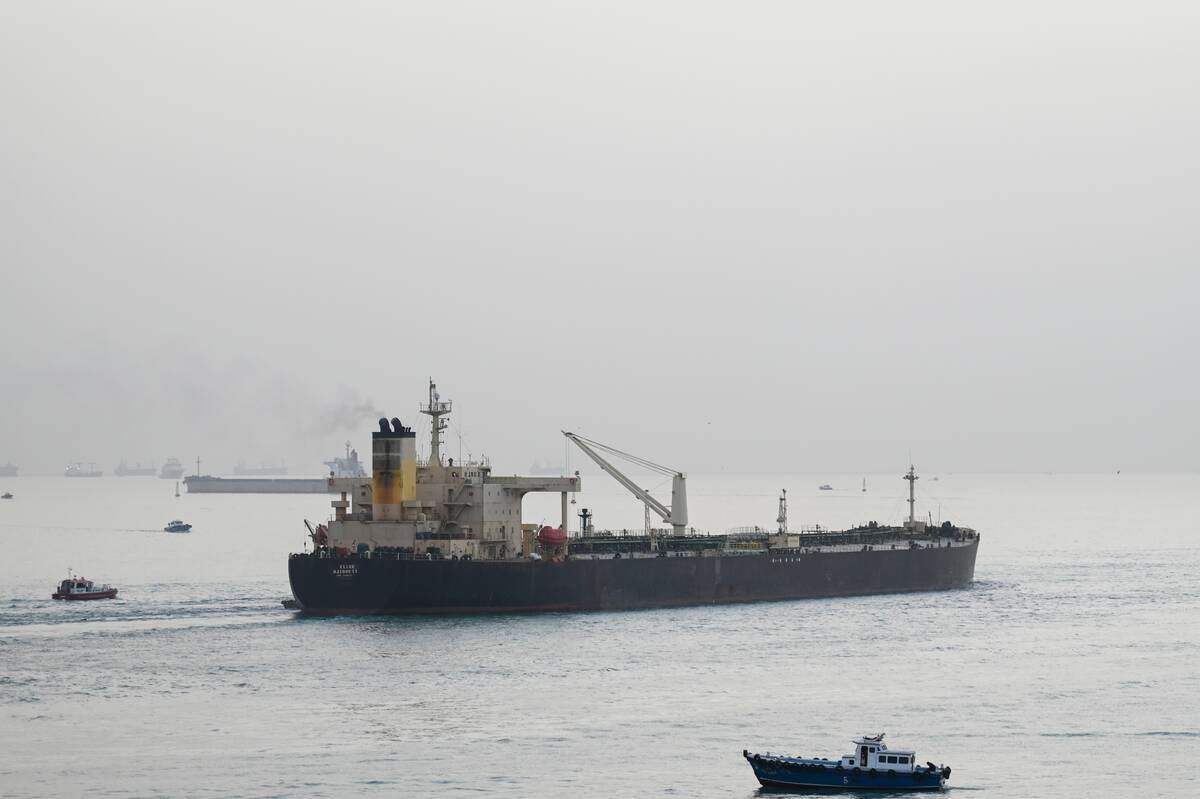

Today’s trade routes are a complex web of global supply chains, connecting manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers worldwide. From the Suez Canal to the Panama Canal, these routes are crucial for the movement of goods.
Technology and logistics innovations have transformed trade, making it faster and more efficient. However, modern trade faces challenges like geopolitical tensions and environmental concerns. As we navigate the future, the evolution of trade routes continues to shape our world.



