The wild and unlikely history of Australia
Australia, fondly known as the Land Down Under, is a country like no other. Its history is a fascinating tapestry of ancient traditions and modern developments. From its indigenous roots to its status as a thriving modern nation, Australia’s past is full of intriguing tales. This vast land has been shaped by isolation, colonization, and innovation, making it a unique blend of cultures and landscapes. Join us as we embark on a journey through Australia’s remarkable history.
A Continent Born from Isolation: The Ancient Origins of Australia
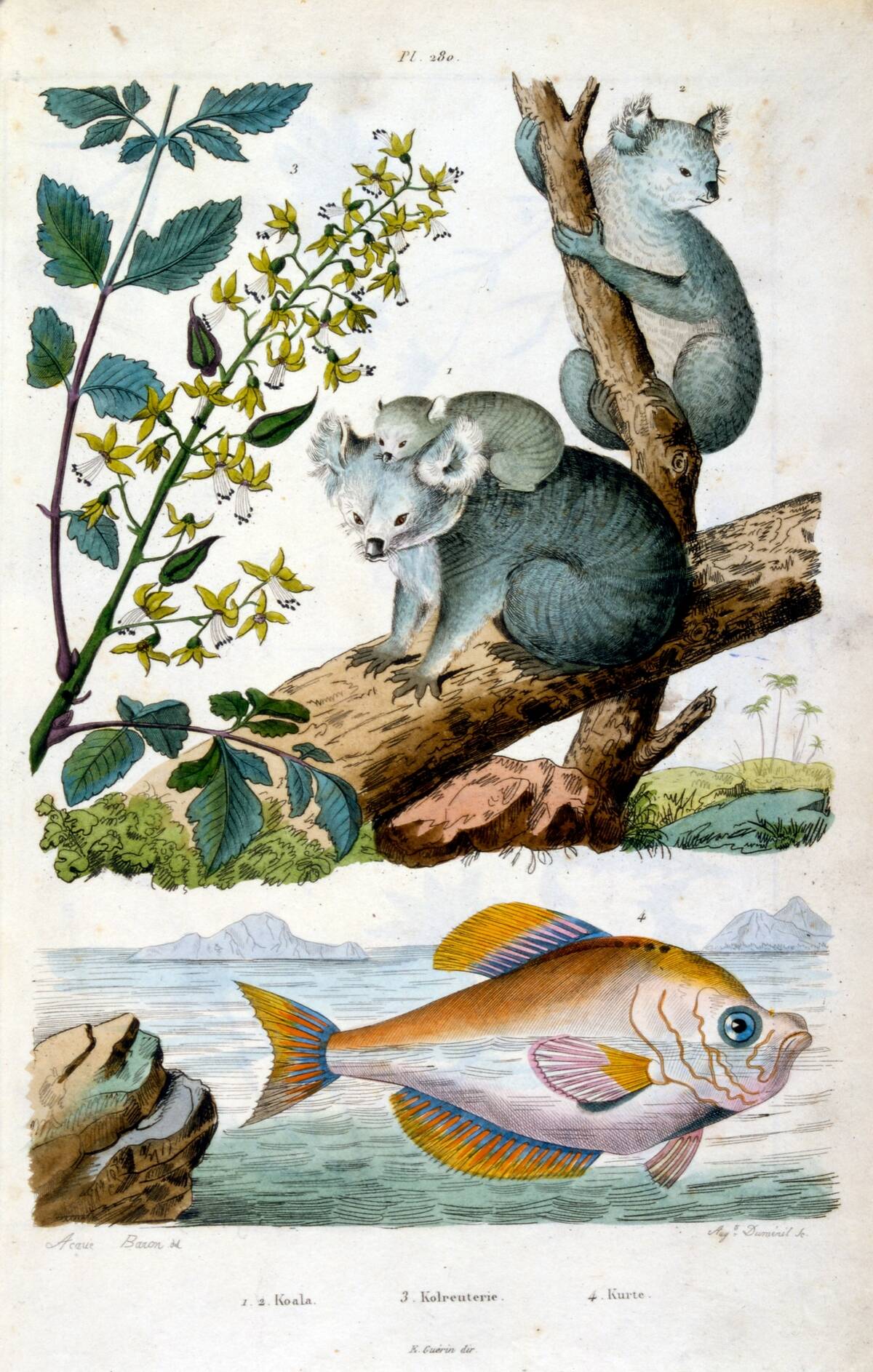

Long before modern humans arrived, Australia was a land of megafauna and unique ecosystems. Isolated from other continents for millions of years, it developed a distinct flora and fauna. The continent’s ancient origins are reflected in its incredible biodiversity, with species like the kangaroo and koala found nowhere else on Earth. This isolation has also preserved some of the oldest geological features, such as the ancient rocks of Western Australia, dating back over 2.7 billion years.
The Dreamtime: Aboriginal Culture and History
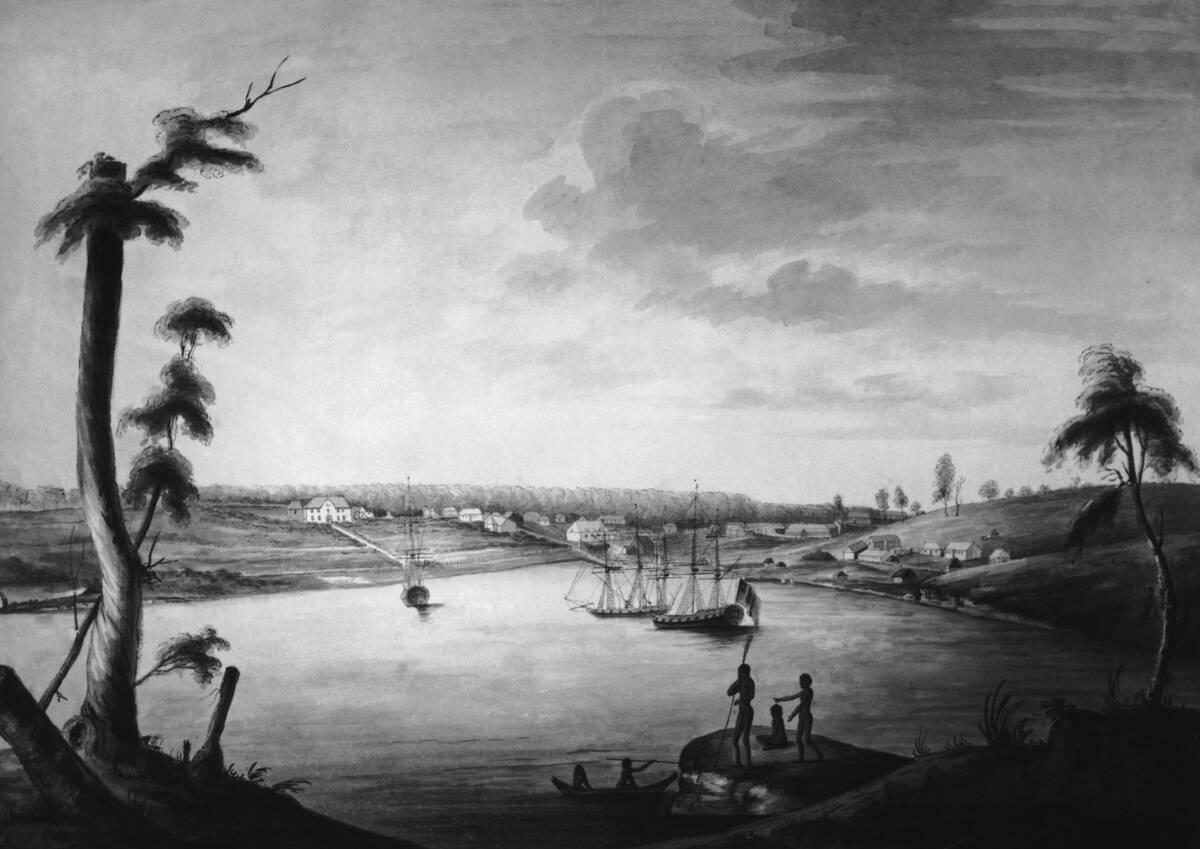
The indigenous peoples of Australia, known as Aboriginal Australians, have a rich cultural heritage. Their history stretches back over 65,000 years, making them one of the world’s oldest living cultures. Central to Aboriginal culture is the concept of the Dreamtime, which explains the origins of the land and its people. Dreamtime stories are passed down through generations, preserving the spiritual and cultural connection to the land. This deep connection is evident in their art, music, and ceremonies.
First Encounters: The Arrival of the Dutch
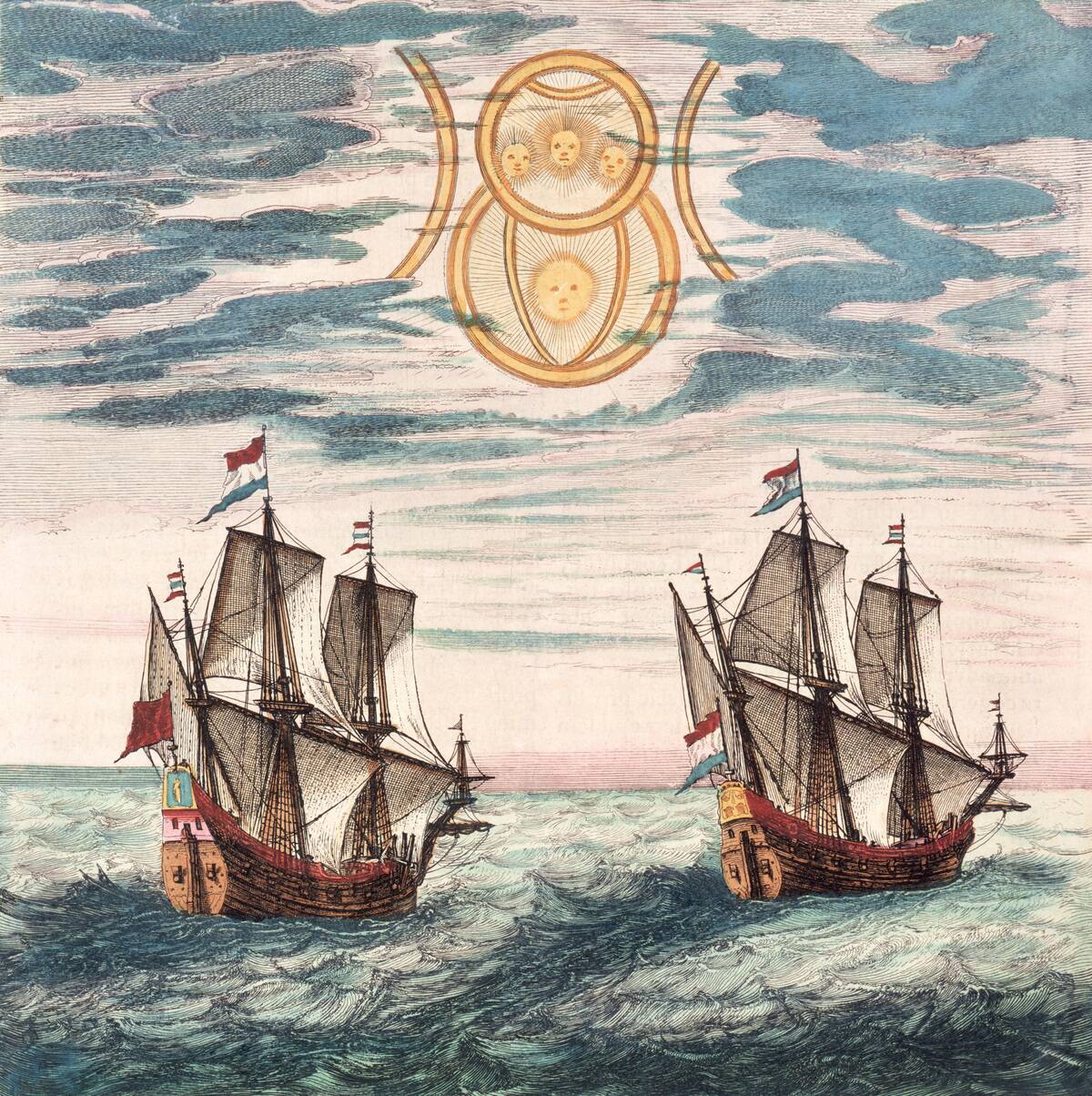

The first recorded European contact with Australia was by the Dutch in the early 17th century. In 1606, the Dutch ship Duyfken, captained by Willem Janszoon, sighted the Cape York Peninsula. Although the Dutch charted parts of the coastline, they did not settle. These early encounters marked the beginning of European interest in the continent, though it would be over a century before significant colonization efforts began. The Dutch legacy remains in place names like Arnhem Land.
Captain Cook and the British Claim
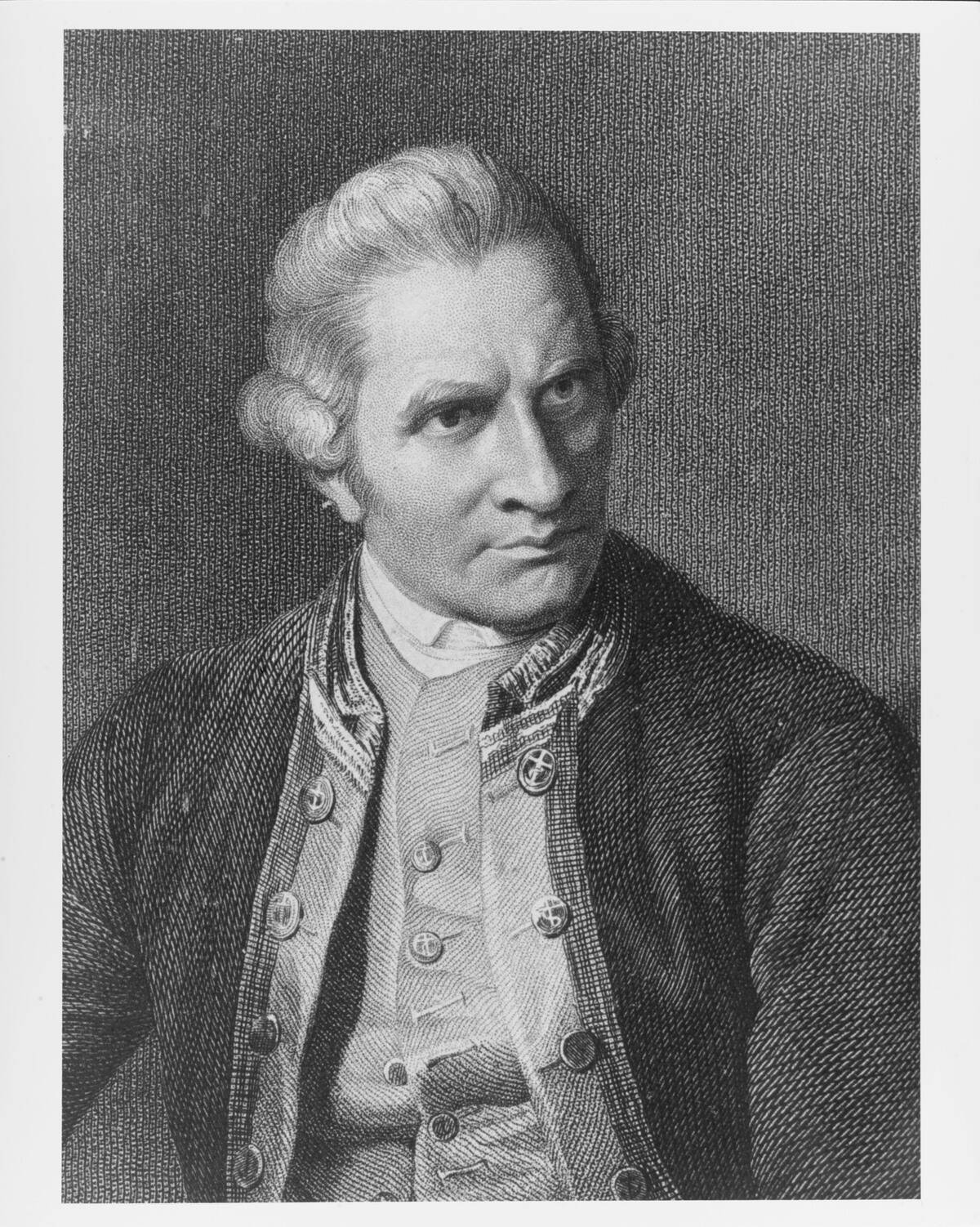

In 1770, British explorer Captain James Cook sailed the HMS Endeavour along the east coast of Australia, claiming it for Britain. Cook’s journey was pivotal, as it led to the establishment of British colonies. His detailed maps and reports opened the door for future settlers. The British claim marked the beginning of a new era for Australia, with colonization eventually leading to the displacement and disruption of indigenous communities. Cook’s voyages are a significant chapter in Australia’s colonial history.
The Penal Colony Experiment

In 1788, the First Fleet arrived in Botany Bay, establishing the first British penal colony. Australia became a destination for convicts, with over 160,000 transported over 80 years. The harsh conditions and isolation were intended as a deterrent for crime. Despite the challenges, the colonies grew, transforming into thriving settlements. This penal history is a unique aspect of Australia’s past, shaping its development and contributing to its diverse population. Sites like Port Arthur remain as reminders of this era.
Gold Rush Fever: Transforming the Economy
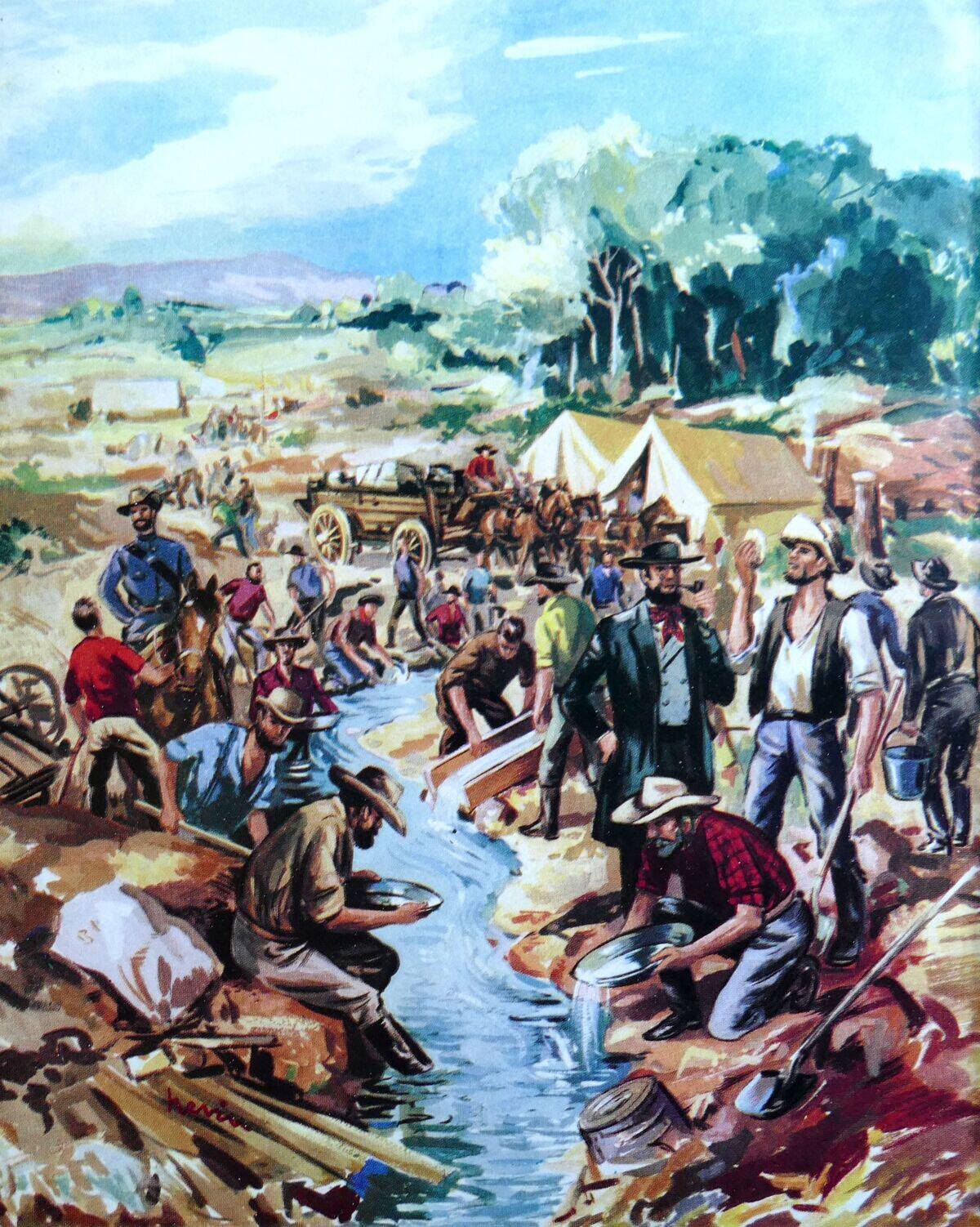

The discovery of gold in the 1850s sparked a rush that transformed Australia’s economy and society. The gold rushes attracted people from all over the world, leading to a population boom and increased wealth. Towns like Ballarat and Bendigo flourished, and infrastructure developed rapidly to support the mining activities. The influx of immigrants also contributed to the multicultural landscape of modern Australia. Gold mining was a catalyst for change, laying the foundations for Australia’s prosperity.
The Birth of a Nation: Australia’s Federation
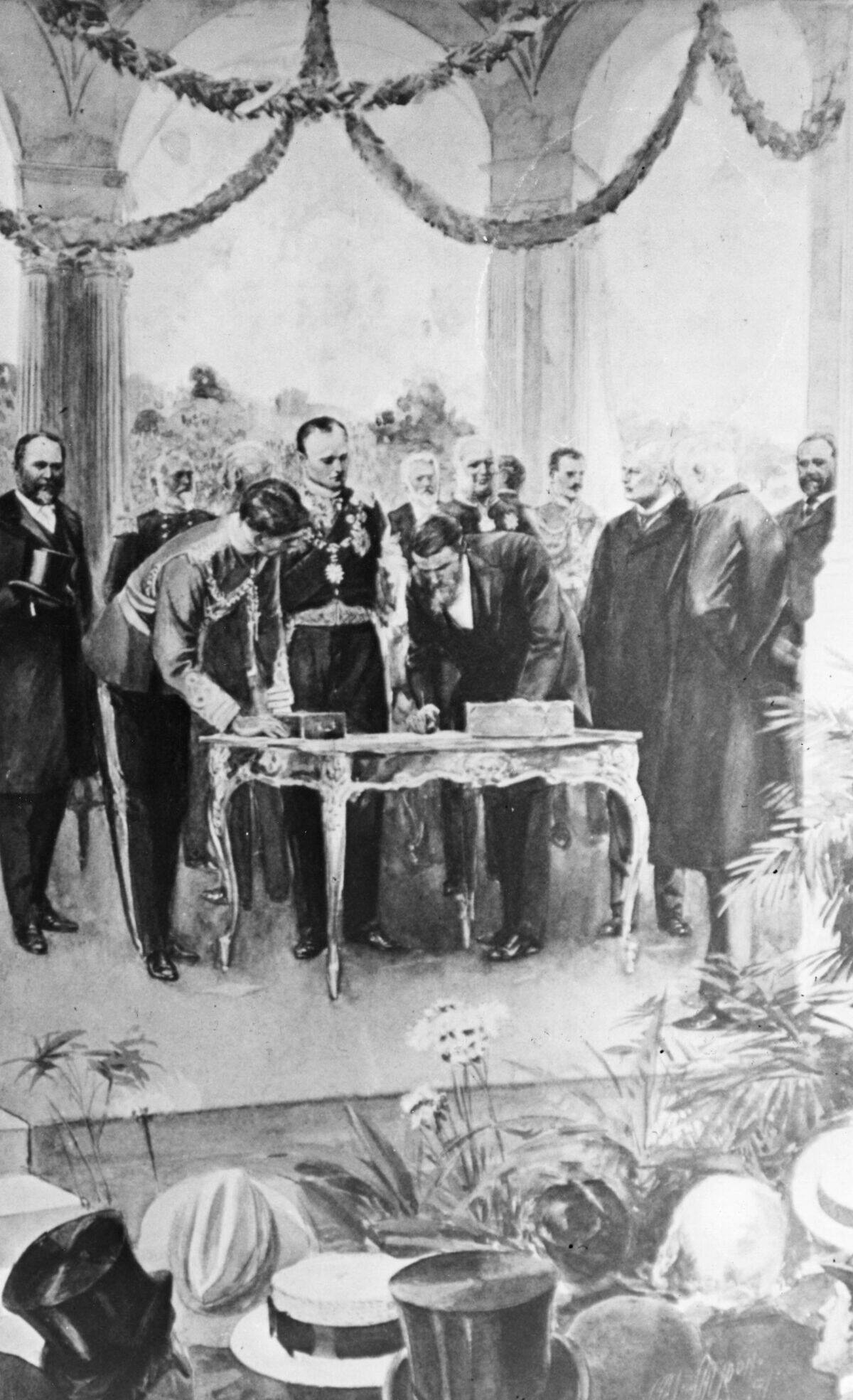

On January 1, 1901, the six separate colonies of Australia united to form the Commonwealth of Australia. This federation marked the birth of the nation as a unified entity. The move towards federation was driven by the desire for a coordinated approach to defense, trade, and immigration. The new constitution established a parliamentary democracy, and the capital was later set in Canberra. Federation was a milestone in Australia’s history, laying the groundwork for its current political and social systems.
World War Contributions: A Nation at War
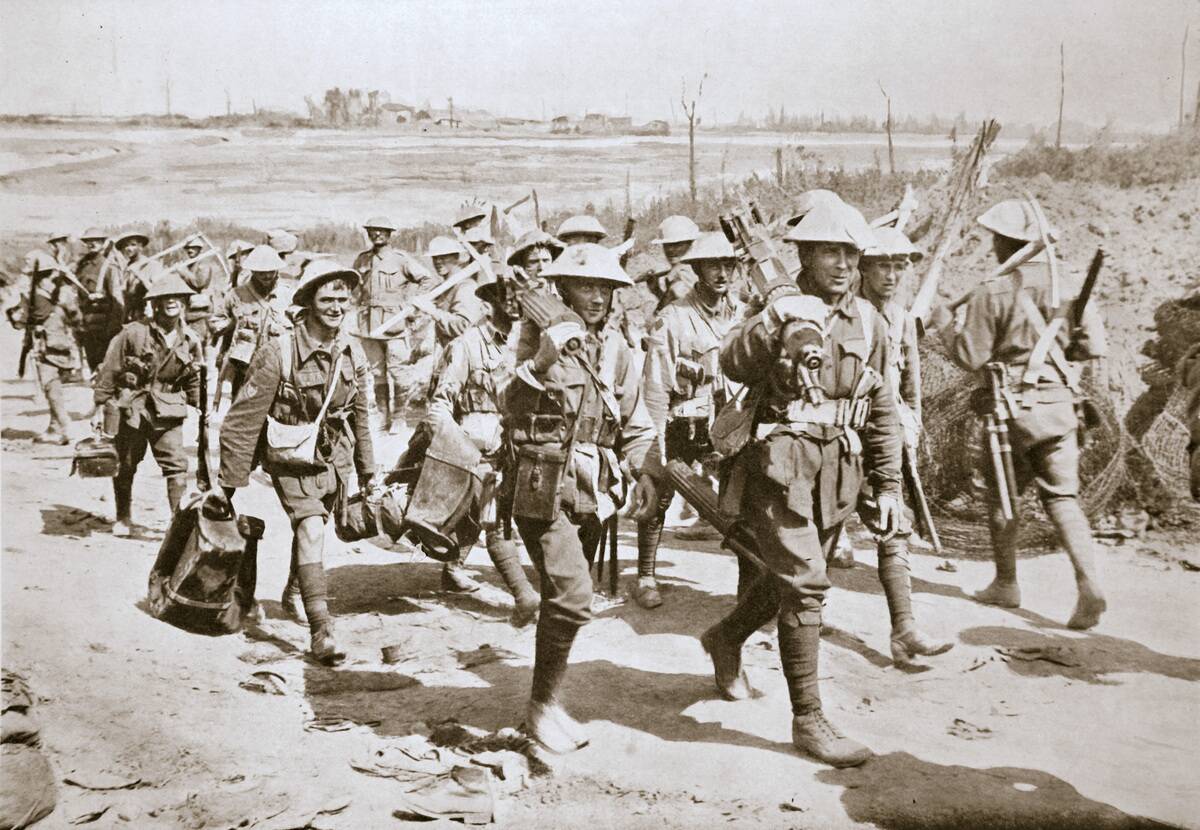

Australia’s involvement in World War I was significant, with over 400,000 Australians enlisted. The ANZAC troops gained fame for their bravery at Gallipoli in 1915, a campaign that left a lasting legacy. The war had a profound impact on the nation, with significant loss of life and economic strain. Despite these challenges, the war effort fostered a sense of national identity and international recognition. ANZAC Day is now a national day of remembrance, honoring those who served.
The Roaring Twenties and the Great Depression
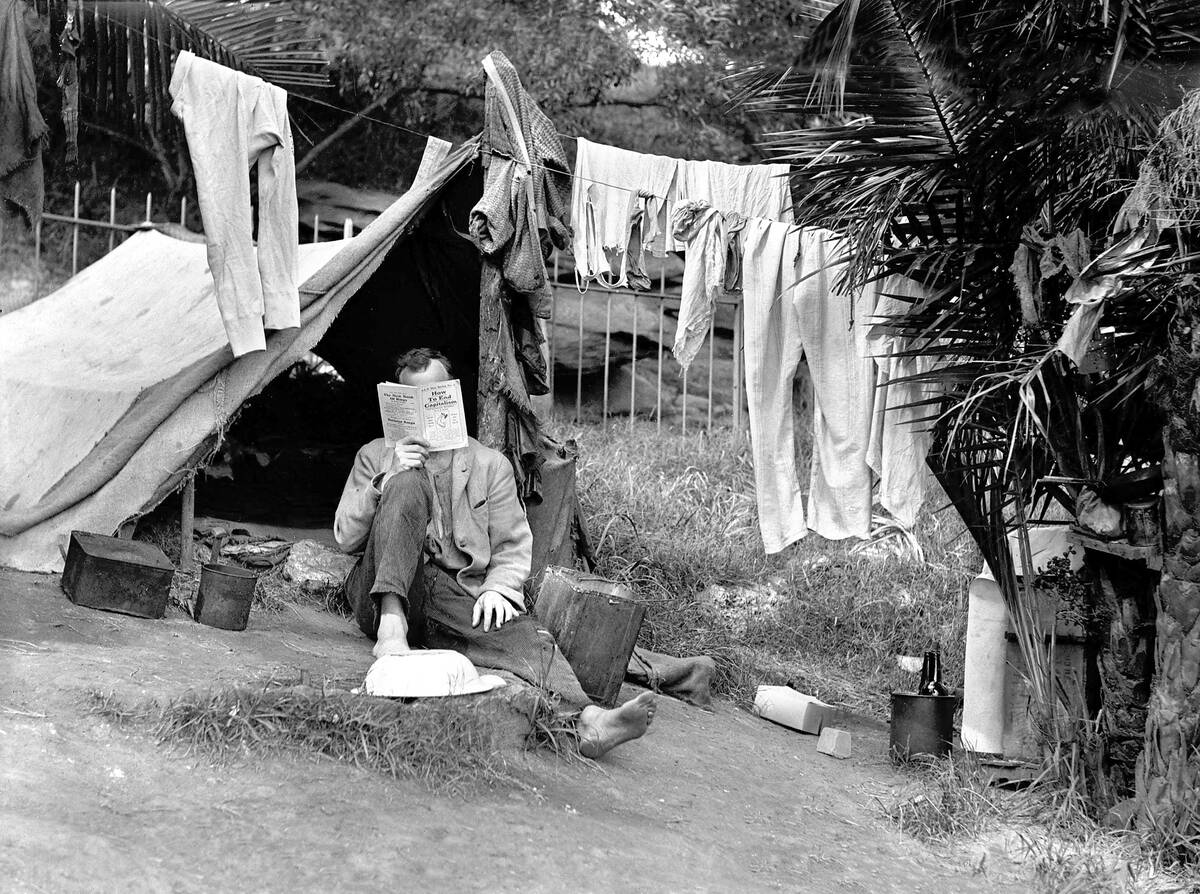

The 1920s in Australia were a time of economic growth and cultural change, often referred to as the ‘Roaring Twenties.’ However, this prosperity was short-lived, as the Great Depression hit in the 1930s. The economic downturn led to widespread unemployment and hardship. Despite these challenges, the period also saw the rise of new technologies and cultural shifts. The resilience shown during the Depression played a crucial role in shaping Australia’s future economic policies and social programs.
Australia’s Involvement in World War II
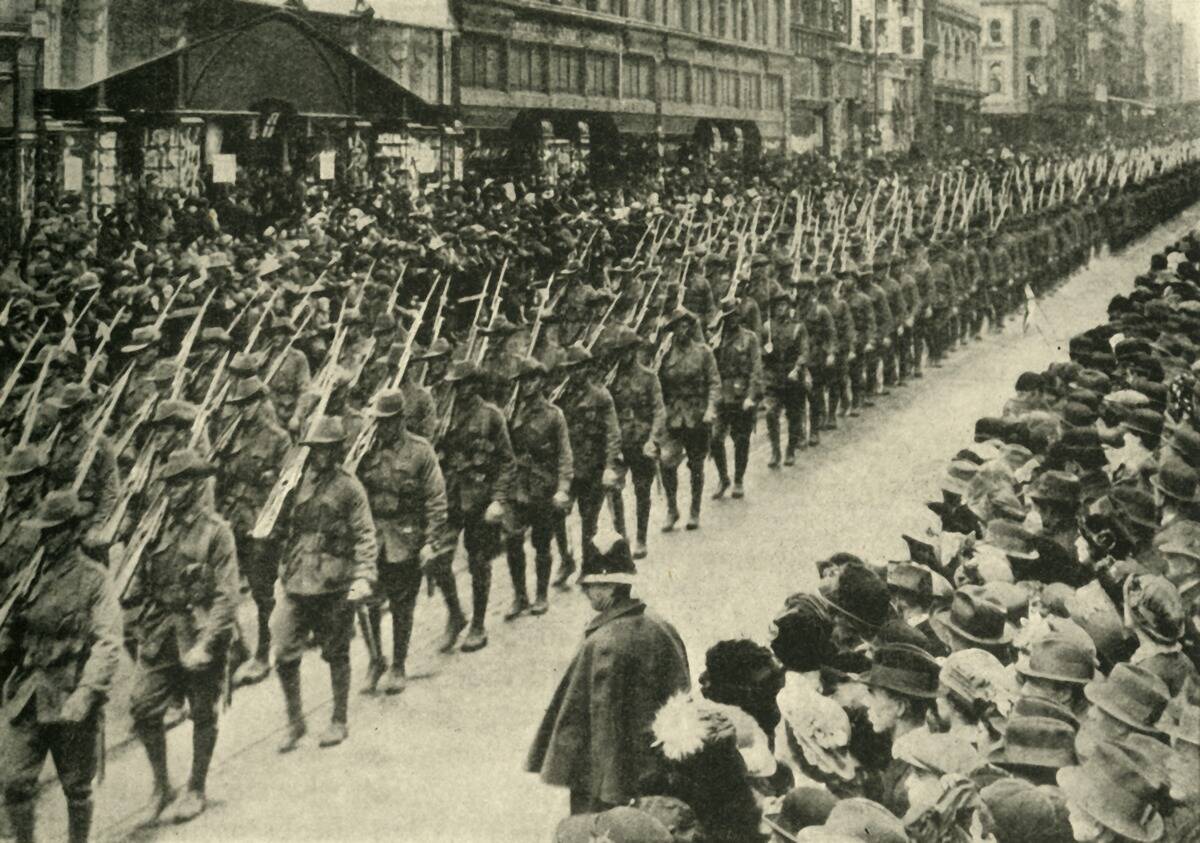

During World War II, Australia played a key role in the Pacific theater. The country faced direct threats, such as the attack on Darwin in 1942 and the Japanese submarines in Sydney Harbour. Australian forces fought alongside Allies in pivotal battles like Kokoda. The war effort boosted industrialization and led to greater international alliances, notably with the United States. Post-war, Australia emerged with a stronger national identity and a commitment to international cooperation.
Post-War Immigration Boom
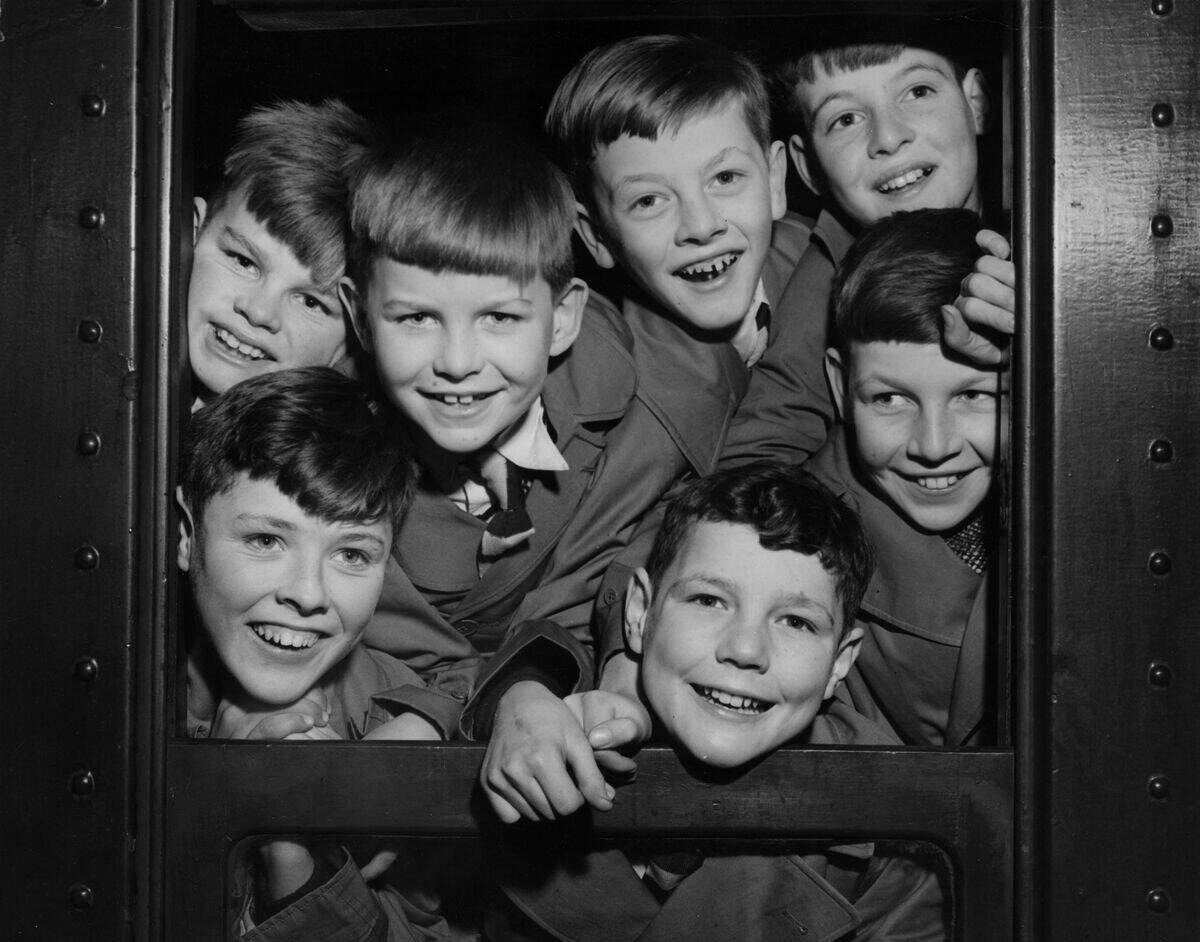

After World War II, Australia experienced a significant wave of immigration. The government launched initiatives to attract migrants, aiming to boost the workforce and populate the nation. Over two million immigrants arrived from Europe and beyond, transforming Australia’s demographic landscape. This influx brought diverse cultures and skills, enriching the nation’s social fabric. The post-war immigration boom played a critical role in shaping modern Australia, laying the foundation for its multicultural identity.
The Rise of Australian Pop Culture
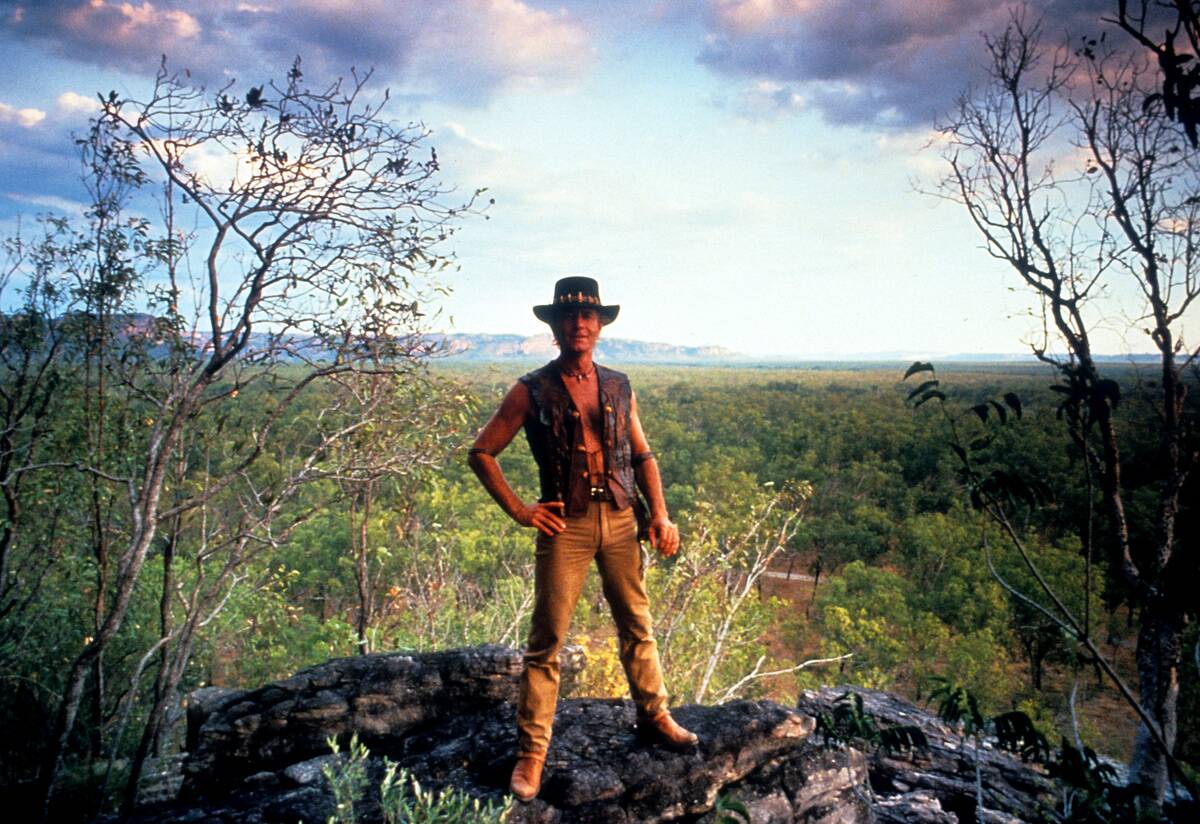

Australia’s pop culture began to gain international attention in the post-war era, with the global success of films like ‘Crocodile Dundee’ and bands like AC/DC. The unique Australian humor and lifestyle resonated worldwide, helping to shape a distinctive cultural identity. Television shows like ‘Neighbours’ and ‘Home and Away’ found audiences abroad, boosting Australia’s cultural export. This rise in pop culture has contributed significantly to Australia’s global image, showcasing its creativity and vibrant spirit.
Environmental Challenges and Conservation Efforts
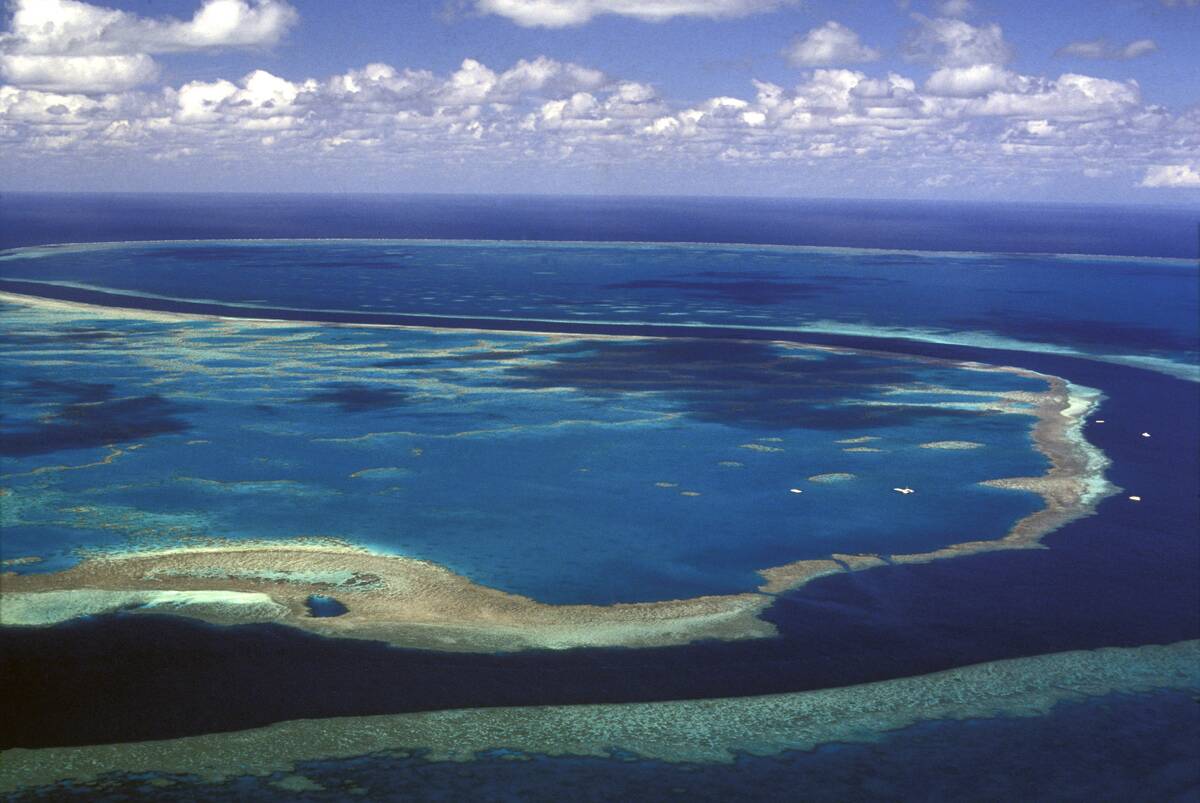

Australia faces significant environmental challenges, from bushfires to coral bleaching in the Great Barrier Reef. In response, the nation has made strides in conservation efforts. The establishment of national parks and marine reserves aims to protect its unique ecosystems. Initiatives like the Landcare movement engage communities in sustainable land management practices. Australia’s commitment to preserving its natural heritage is crucial, as it balances development with the protection of its extraordinary biodiversity.
The Indigenous Rights Movement
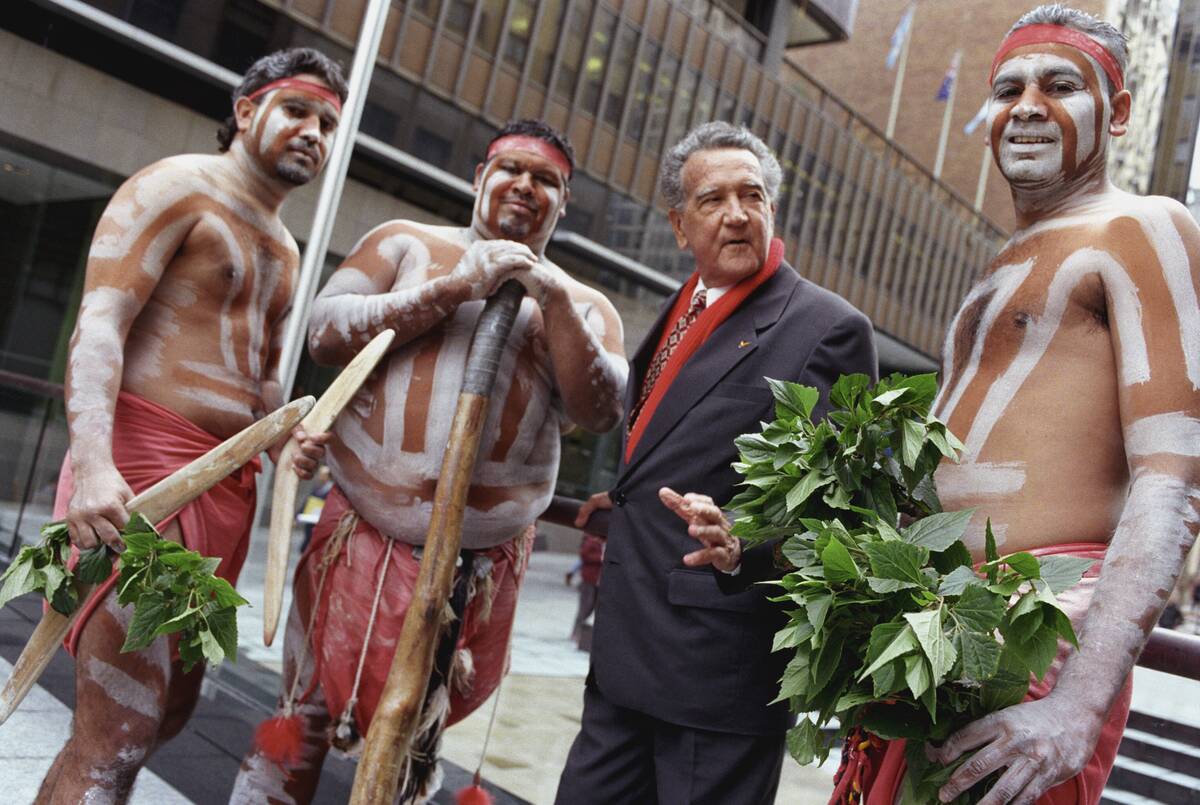

The struggle for indigenous rights in Australia has been a long and ongoing journey. The 1967 referendum was a landmark moment, allowing Aboriginal people to be counted in the census and granting the federal government power to create laws for them. The land rights movement gained momentum, leading to significant legal victories such as the Mabo decision in 1992. While progress has been made, the movement continues to address issues of inequality and seek recognition of indigenous contributions.
Australia in the Digital Age: A Global Player

In the digital age, Australia has emerged as a global player in technology and innovation. The country’s tech industry is thriving, with a focus on fintech, biotechnology, and renewable energy. Cities like Sydney and Melbourne have become hubs for startups and tech companies. Australia’s digital economy is supported by a robust infrastructure and a skilled workforce. As the nation continues to innovate, it positions itself as a leader in the global digital landscape, driving economic growth and development.
The Wonders of Australian Wildlife
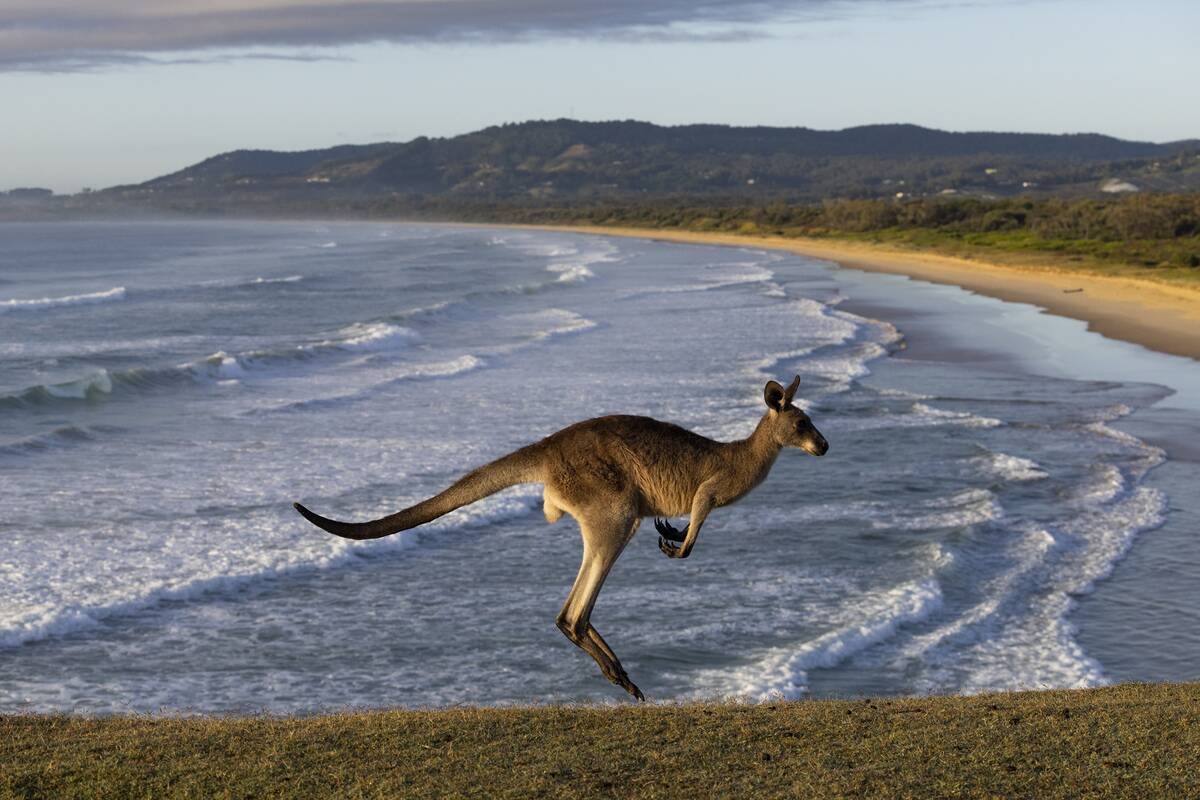

Australia is home to some of the world’s most unique and diverse wildlife. From the iconic kangaroo and koala to the elusive platypus, the country’s fauna is truly remarkable. Australia’s isolation has led to high levels of endemism, with over 80% of its mammals found nowhere else. National parks and reserves protect these species, allowing for fascinating wildlife encounters. Whether it’s the Great Barrier Reef’s marine life or the Outback’s desert creatures, Australia’s wildlife is a natural wonder.
Sporting Triumphs and National Pride
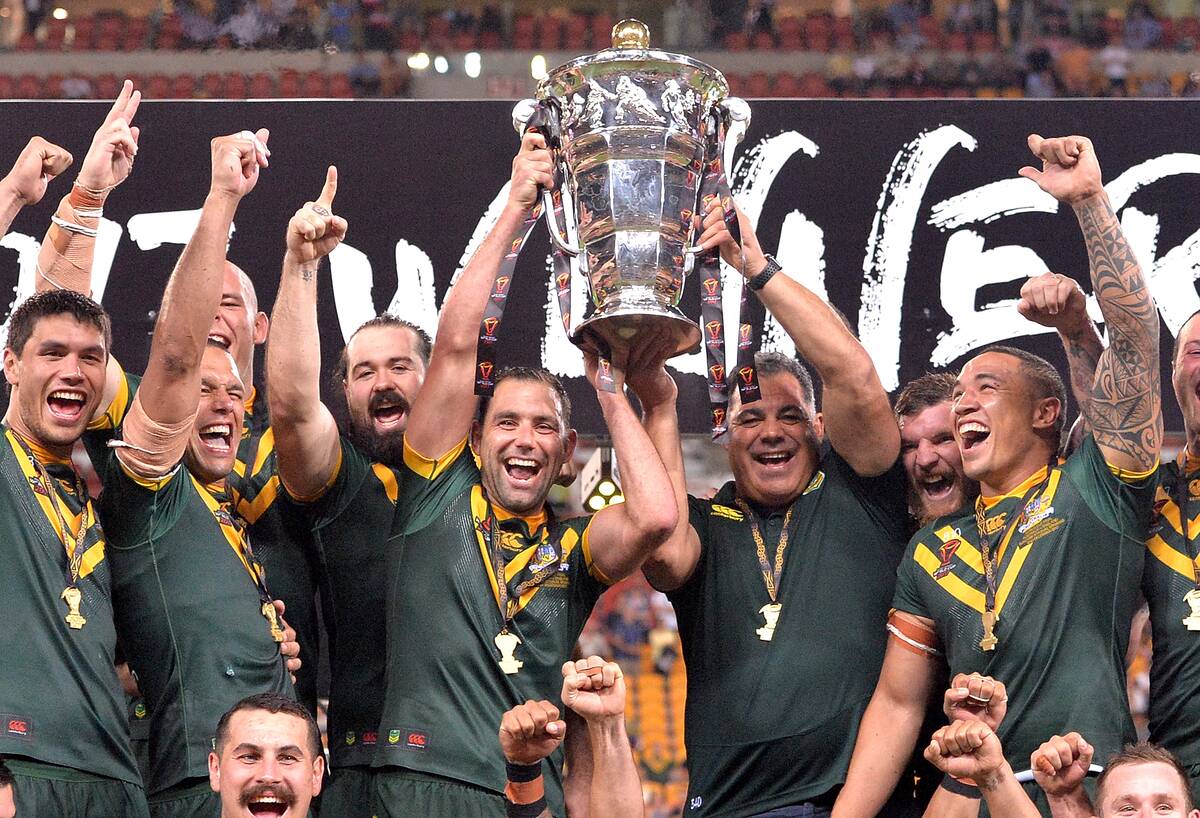

Sport is a significant part of Australian culture, fostering national pride and unity. From cricket to rugby, Australians excel in various sports on the international stage. The country has hosted major events like the Olympics and the Commonwealth Games, showcasing its sporting prowess. Achievements in sports bring the nation together, with moments like Cathy Freeman’s gold medal run at the Sydney Olympics etched in history. Sport continues to inspire Australians, reflecting the nation’s competitive spirit and love for outdoor activities.
The Modern Melting Pot: Australia’s Diverse Culture

Australia is a modern melting pot, with a rich tapestry of cultures from around the world. This diversity is reflected in its cuisine, festivals, and art. Cities like Sydney and Melbourne are vibrant cultural hubs, celebrating a multitude of traditions and communities. The embrace of multiculturalism has enriched the Australian way of life, fostering inclusivity and understanding. As a nation, Australia continues to thrive on its diversity, creating a dynamic and harmonious society for all its residents.



