The creation of the Geneva Conventions and war crimes
The Geneva Conventions serve as a cornerstone in the laws of war, aiming to protect those who are not participating in hostilities. These international treaties focus on safeguarding civilians, medical personnel, and those who have laid down their arms.
War crimes, on the other hand, are violations of these laws. The conventions thus provide a framework to prosecute those who commit atrocities during conflicts, ensuring some level of humanity in the chaos of war.
The Origins of the Geneva Conventions

The Geneva Conventions originated from a need to address the brutalities observed in 19th-century warfare. With rising global conflicts, there was an urgent call for a standardized set of rules to protect the vulnerable.
The initial gathering in Geneva in 1864 marked the first steps towards codifying these humanitarian principles. This pioneering effort laid the groundwork for what would become a comprehensive set of international laws governing armed conflict.
Historical Context: Warfare Before the Conventions

Before the Geneva Conventions, warfare was largely unregulated, often resulting in horrific suffering for soldiers and civilians alike. There were few, if any, protections for those captured or wounded, leaving them at the mercy of their captors.
This lack of regulation highlighted the dire need for international consensus on the humane treatment of non-combatants and prisoners, ultimately leading to the establishment of the conventions.
The Role of Henry Dunant and the Battle of Solferino
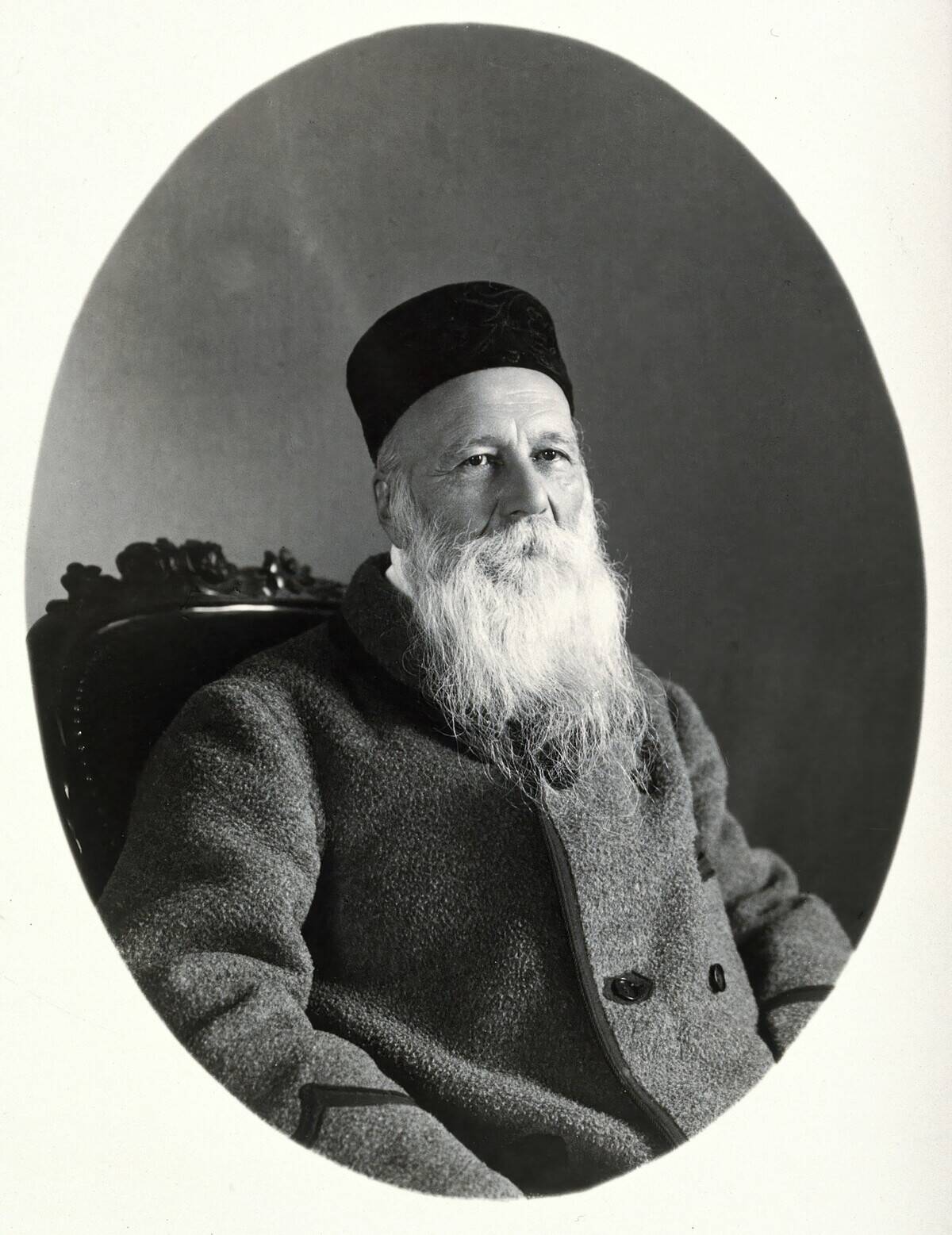

Henry Dunant, a Swiss businessman, was deeply moved by the aftermath of the Battle of Solferino in 1859. Witnessing the suffering of thousands of wounded soldiers, he was inspired to advocate for an international agreement to aid war casualties.
In 1862, he published his book, A Memory of Solferino. Dunant’s efforts were instrumental in the creation of the first Geneva Convention, earning him recognition as a key figure in international humanitarian law.
The Establishment of the International Committee of the Red Cross
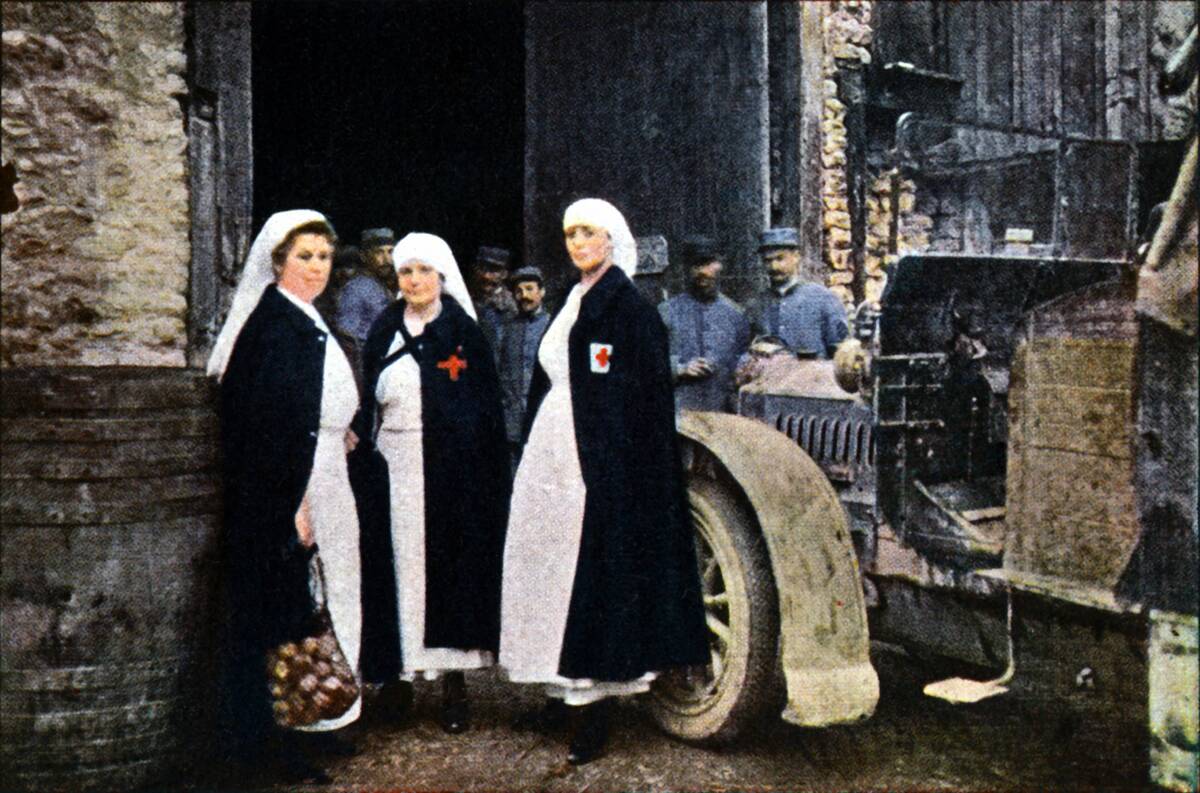

The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) was founded in 1863, largely due to the advocacy of Henry Dunant and a group of like-minded individuals. The ICRC aimed to provide neutral and impartial aid to those affected by conflict.
It quickly became a vital organization, playing a crucial role in the development and implementation of the Geneva Conventions, and continues to be a leading force in humanitarian efforts worldwide.
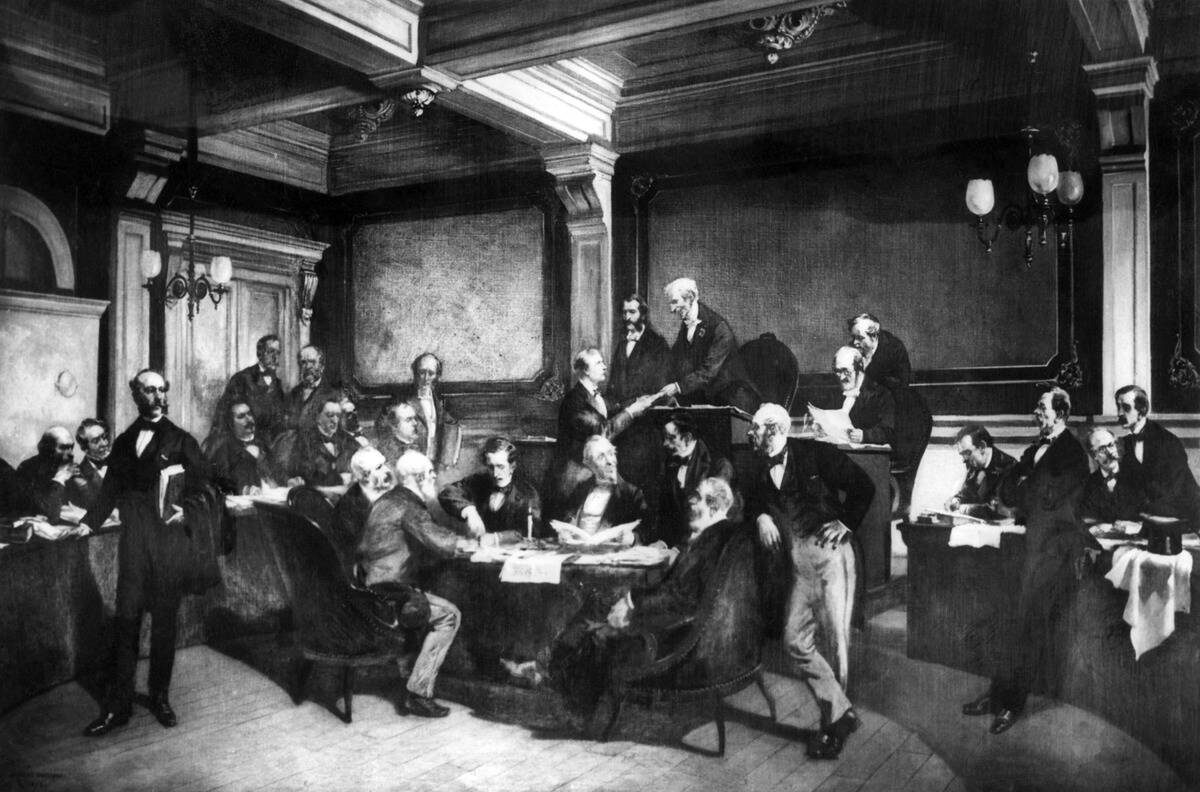
The First Geneva Convention of 1864

The inaugural Geneva Convention, signed in 1864, focused on the treatment of wounded soldiers on the battlefield. This landmark treaty established the principle of neutrality for medical staff and facilities, ensuring they could operate without fear of attack.
It also introduced the Red Cross emblem as a symbol of protection, a sign that remains internationally recognized and respected today.
Expanding the Protections: Subsequent Conventions

Following the success of the 1864 Convention, additional treaties were established to broaden the scope of protections. These subsequent conventions extended safeguards to include naval warfare, prisoners of war, and civilian populations.
Each new treaty built upon the foundation of the original, reflecting the evolving nature of warfare and the continuous need for updated humanitarian standards.
The Hague Conventions and Their Influence
The Hague Conventions, held in 1899 and 1907, complemented the Geneva Conventions by addressing the conduct of warfare itself. These treaties introduced regulations on the use of weapons and military tactics, aiming to limit unnecessary suffering.
While distinct from the Geneva Conventions, the Hague Conventions played a significant role in shaping modern international humanitarian law, reinforcing the principles of humanity and justice in conflict.
The Horrors of World War I and the Need for Stronger Laws

World War I exposed the inadequacies of existing international laws in addressing the horrors of modern warfare. The unprecedented scale of destruction and the use of chemical weapons highlighted the urgent need for stronger legal frameworks.
This global conflict served as a harsh reminder of the importance of robust international agreements to protect human rights in times of war, setting the stage for future revisions of the Geneva Conventions.
The 1929 Conventions: Adding New Protections

In response to the lessons learned from World War I, the 1929 Geneva Conventions introduced significant new protections for prisoners of war. These included requirements for humane treatment and adequate living conditions.
This revision was a crucial step in strengthening international humanitarian law, ensuring that those captured during conflict would be treated with dignity and respect, regardless of the circumstances of their capture.
World War II: A Catalyst for Change

The atrocities committed during World War II underscored the critical need for comprehensive international agreements on the conduct of war. The widespread violations of human rights during this period acted as a powerful catalyst for change.
In the war’s aftermath, the global community was galvanized into action, leading to a comprehensive overhaul of the Geneva Conventions to prevent future atrocities and protect human dignity.
The 1949 Conventions: A Comprehensive Overhaul

The Geneva Conventions of 1949 represented a significant expansion and revision of earlier treaties. These new conventions addressed a wide range of issues, including the protection of civilians during conflict and the treatment of prisoners of war.
The 1949 agreements laid a robust foundation for modern international humanitarian law, setting a new standard for the conduct of armed conflicts and the protection of victims.
Key Provisions of the Geneva Conventions

The Geneva Conventions encompass a range of key provisions designed to protect individuals in war. These include the humane treatment of prisoners of war, the protection of civilians, and the prohibition of torture and inhumane treatment.
These provisions serve as the backbone of international humanitarian law, providing a framework to ensure that even in the chaos of conflict, human rights are respected and upheld.
The Additional Protocols: Enhancing the Conventions

In 1977, two Additional Protocols were adopted to enhance the Geneva Conventions, reflecting the changing nature of warfare. These protocols expanded protections for victims of international and non-international conflicts, including civilians and combatants.
By addressing issues such as the conduct of hostilities and the protection of cultural property, the Additional Protocols strengthened the legal framework established by the original conventions.
Defining War Crimes: A Legal Perspective

War crimes are serious violations of the laws and customs applicable in armed conflict, as defined by the Geneva Conventions and other international treaties. These include acts such as willful killing, torture, and taking hostages.
Legal frameworks provide mechanisms to prosecute individuals responsible for such crimes, underscoring the international community’s commitment to holding perpetrators accountable and ensuring justice for victims.
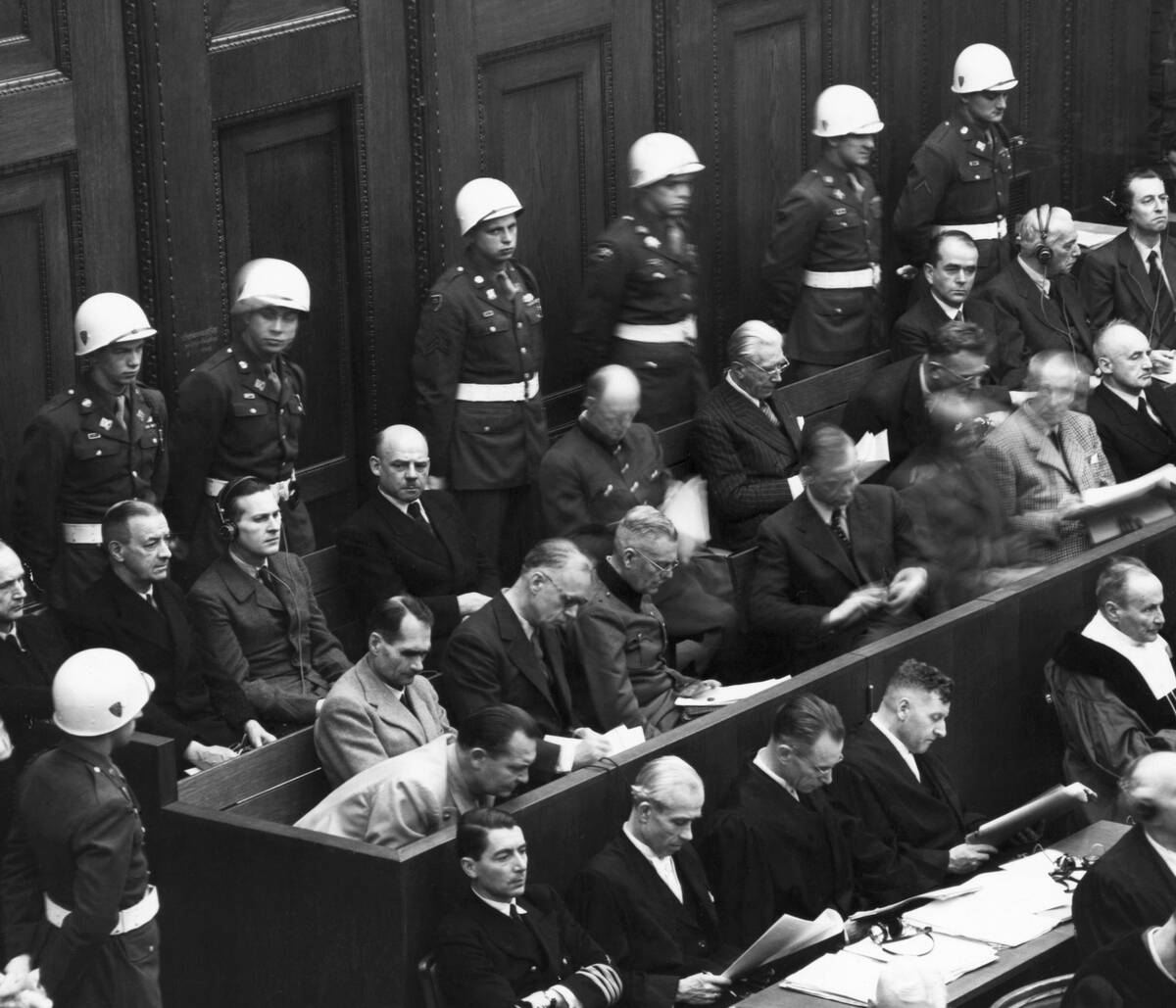
Famous War Crime Trials and Their Impact

The Nuremberg Trials, held after World War II, are among the most famous war crime trials in history. These proceedings set a precedent for the prosecution of war crimes and crimes against humanity.
The trials demonstrated that individuals, including state leaders, could be held accountable for their actions, reinforcing the principles of justice and deterrence in the international arena. This legacy continues to influence the prosecution of war crimes today.
The Role of the United Nations in Upholding the Conventions

The United Nations plays a crucial role in upholding the Geneva Conventions by promoting international peace and security. Through various agencies, the UN monitors compliance with international humanitarian law and facilitates dialogue among member states.
The organization’s efforts aim to prevent conflicts, protect human rights, and ensure accountability for violations, reinforcing the principles enshrined in the Geneva Conventions.
Contemporary Challenges: Modern Warfare and New Technologies

Modern warfare presents new challenges for the application of the Geneva Conventions. The rise of cyber warfare, drones, and autonomous weapons systems complicates the enforcement of existing laws.
These technologies blur the lines of accountability and raise ethical questions. As warfare evolves, the international community must adapt the legal framework to address these emerging issues, ensuring that humanitarian principles remain relevant in the digital age.
The Importance of the Geneva Conventions Today

The Geneva Conventions remain as vital today as they were when first enacted. They provide a universal standard for the humane treatment of individuals during armed conflict, serving as a beacon of hope in times of war.
Despite the challenges posed by modern conflicts, the conventions continue to guide the actions of nations and organizations, underscoring the enduring importance of international humanitarian law.
How Individuals Can Contribute to Upholding International Law

Individuals can play a role in upholding international law by staying informed about the Geneva Conventions and advocating for compliance. Supporting humanitarian organizations, such as the Red Cross, and participating in awareness campaigns can make a difference.
By promoting the principles of humanity and justice, individuals contribute to a global culture that values and respects the rules of war, fostering a more just and peaceful world.




