How steam engines changed the world
Steam engines, with their rhythmic chugging and billowing plumes of steam, captivate the imagination like few other machines. These mighty engines once symbolized progress and innovation, capturing the hearts of both engineers and laypeople alike.
There’s something undeniably charming about their intricate parts working in harmony, a testament to human ingenuity. From powering railways to transforming industries, steam engines have left an indelible mark on history.
The Birth of Steam: From a Simple Idea to a Revolutionary Force
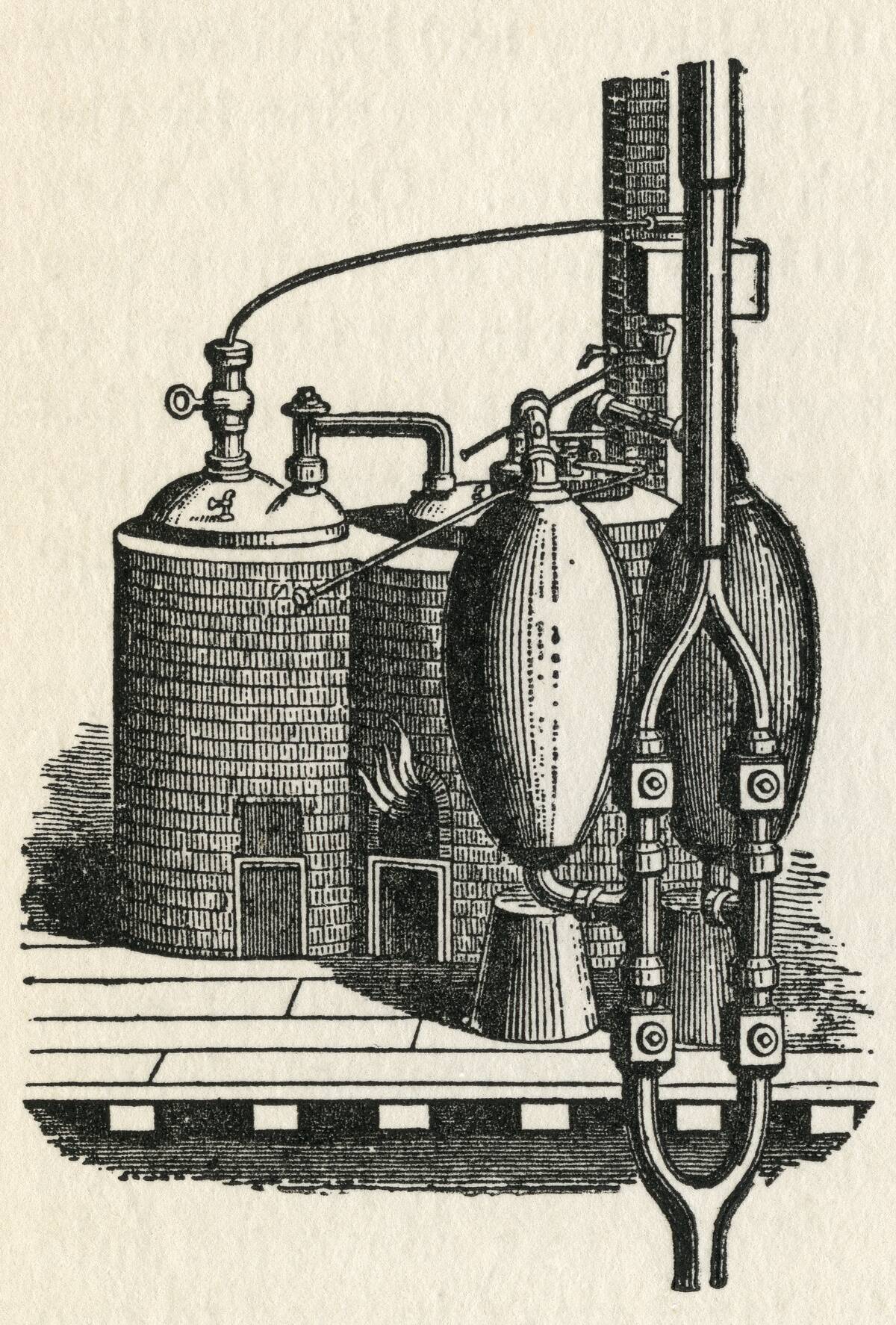
The journey of steam power began in the late 17th century with the invention of the steam pump by Thomas Savery. This initial step was crucial, paving the way for further innovations. By the 18th century, James Watt’s improvements to the steam engine made it more efficient, sparking the Industrial Revolution.
Watt’s separate condenser was a game-changer, reducing waste and increasing power, revolutionizing industries and forever altering the technological landscape.
All Aboard! The Advent of Steam-Powered Railways
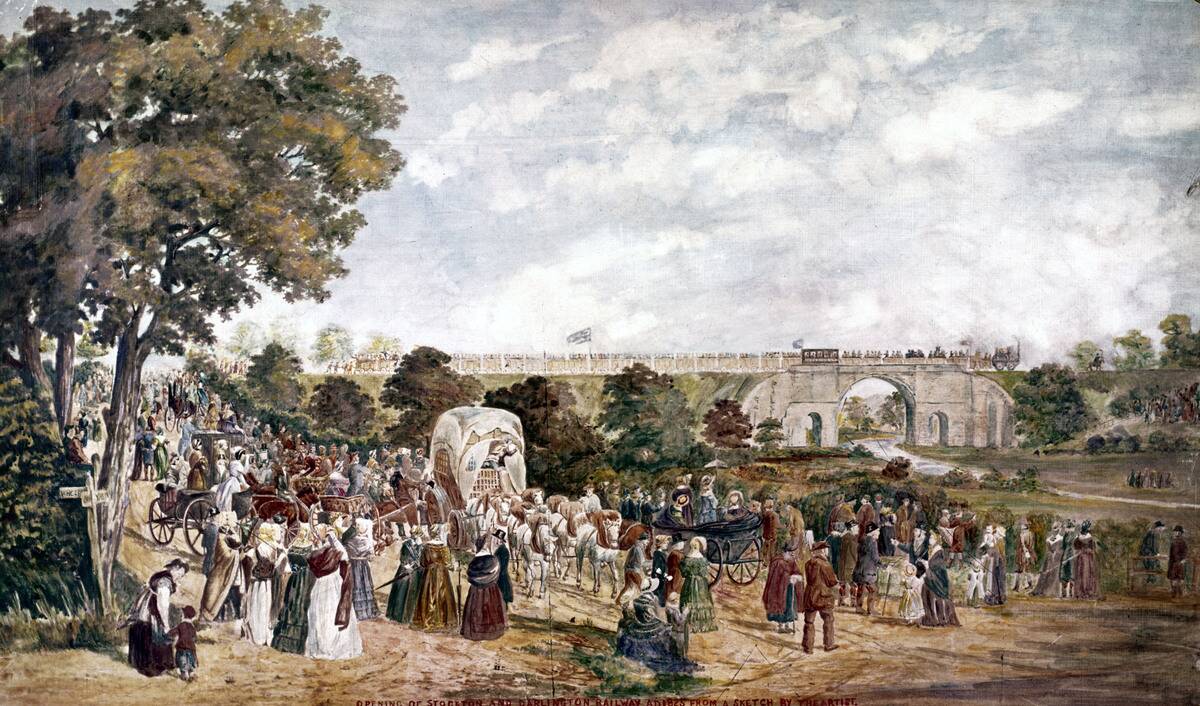

Steam-powered railways changed the way people traveled and traded goods. The Stockton and Darlington Railway, opened in 1825, was the first public railway to use steam locomotives.
These early trains could reach speeds of up to 15 miles per hour, which was revolutionary at the time. George Stephenson’s Rocket further solidified the steam engine’s role in transportation, achieving speeds of 30 miles per hour during the Rainhill Trials in 1829.
Full Steam Ahead: Transforming Transportation Forever
The impact of steam engines on transportation was monumental. By the mid-19th century, railways had expanded across Europe and North America, drastically reducing travel times. The ability to move large quantities of goods quickly and efficiently helped spur economic growth.
The Transcontinental Railroad, completed in 1869, connected the U.S. coast to coast, demonstrating steam power’s ability to overcome natural barriers and connect distant communities.
Steam on the High Seas: Changing Maritime Travel
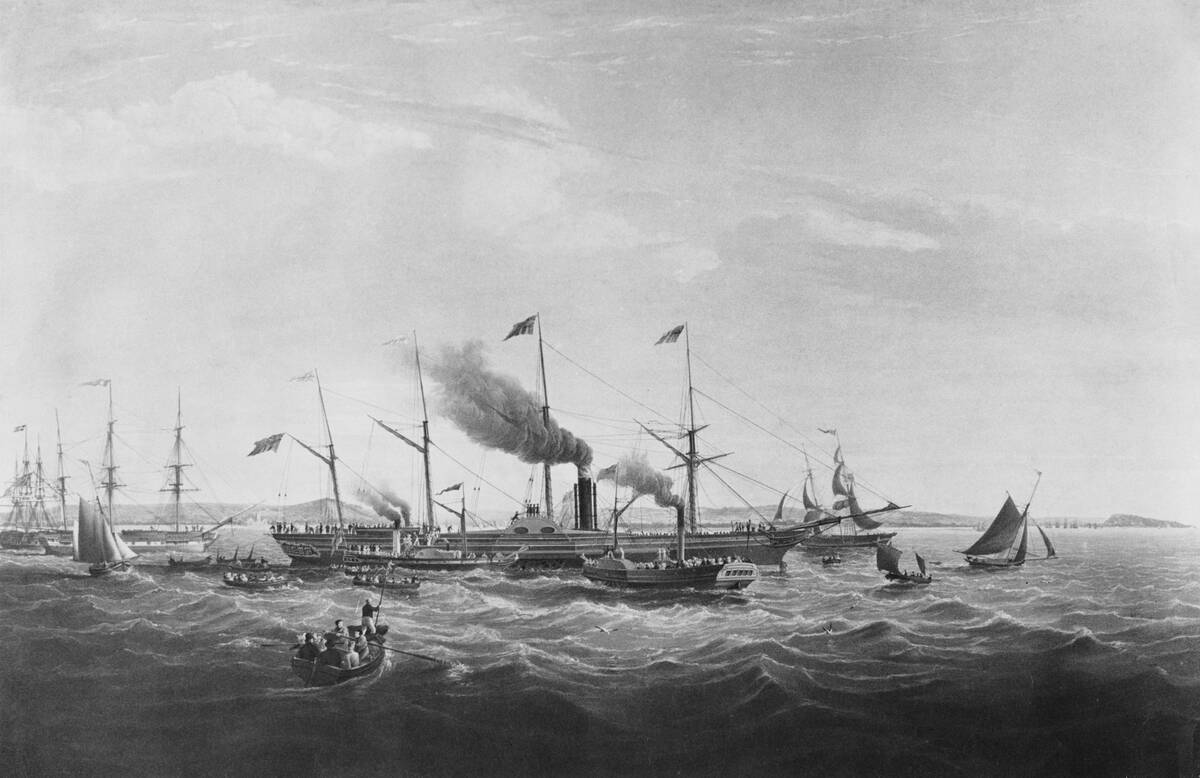

Steam technology didn’t just revolutionize rail; it also made waves in maritime travel. The SS Great Western, launched in 1838, was one of the first steam-powered ships to cross the Atlantic.
This marked a significant shift from sail to steam, reducing travel time from months to weeks. The introduction of steamships enabled more reliable and faster maritime travel, thus opening up new possibilities for international trade and immigration.
The Industrial Revolution: Fueled by Steam

The steam engine was the driving force behind the Industrial Revolution, powering factories and machinery that increased production capabilities. Textile mills, in particular, benefited greatly from steam power, as it allowed for mass production of goods.
Steam engines also enabled the development of new industries, such as coal mining, by providing the necessary power to pump water out of mines. It was a period of unprecedented economic growth and technological advancement.
Steam Engines in Agriculture: Plowing New Ground
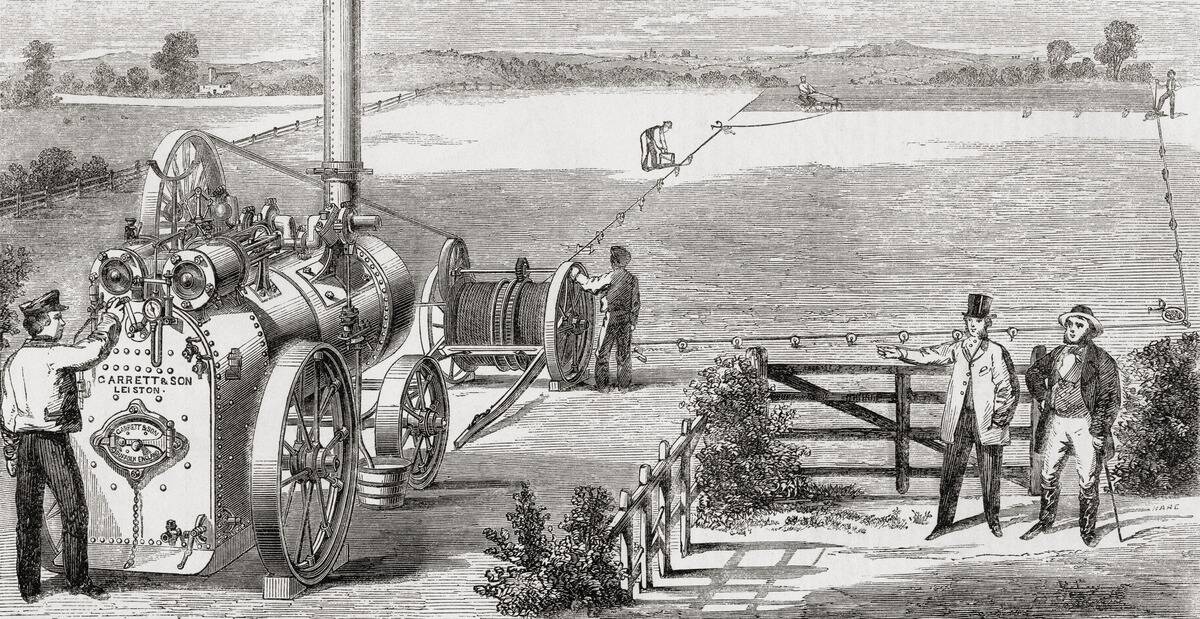
In agriculture, steam engines were a game-changer, providing the power needed for large-scale farming. Steam-powered tractors and plows could cultivate more land in less time than traditional methods.
Introduced in the 19th century, these machines allowed farmers to increase productivity and meet the demands of growing populations. The steam threshing machine also revolutionized grain processing, reducing the labor-intensive work required to separate grain from chaff.
Puffing Billy and Friends: Iconic Steam Locomotives
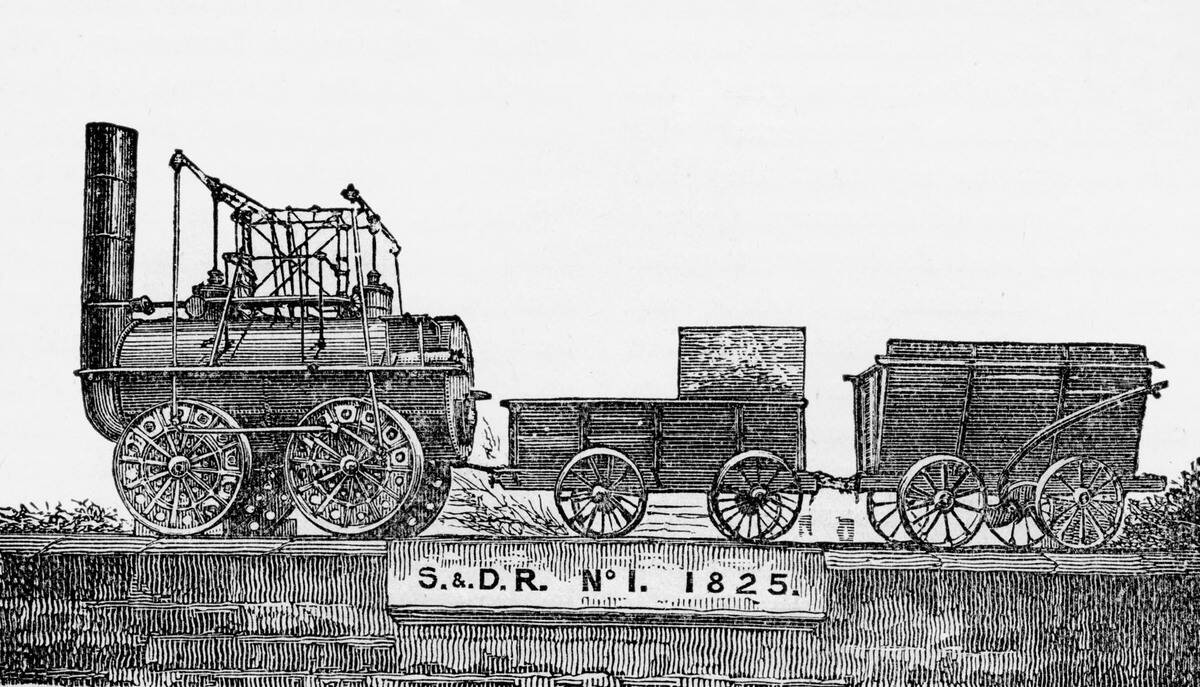
Iconic steam locomotives like Puffing Billy hold a special place in history. Built in 1813, Puffing Billy is one of the oldest surviving steam locomotives, a testament to early engineering prowess.
The Flying Scotsman, another legendary locomotive, became the first train to officially reach 100 miles per hour in 1934. These locomotives not only helped shape transportation but also became cultural icons, representing the spirit of innovation and adventure.
Engineering Marvels: How Steam Engines Work

Steam engines operate on a simple yet effective principle: converting heat into mechanical work. Water is heated in a boiler until it becomes steam, which then expands and pushes a piston or turbine.
This mechanical motion can drive wheels or machinery, depending on the engine’s design. The genius of engineers like James Watt lies in refining these processes to maximize efficiency, turning steam engines into reliable workhorses of the industrial age.
The Global Spread: Steam Engines Around the World
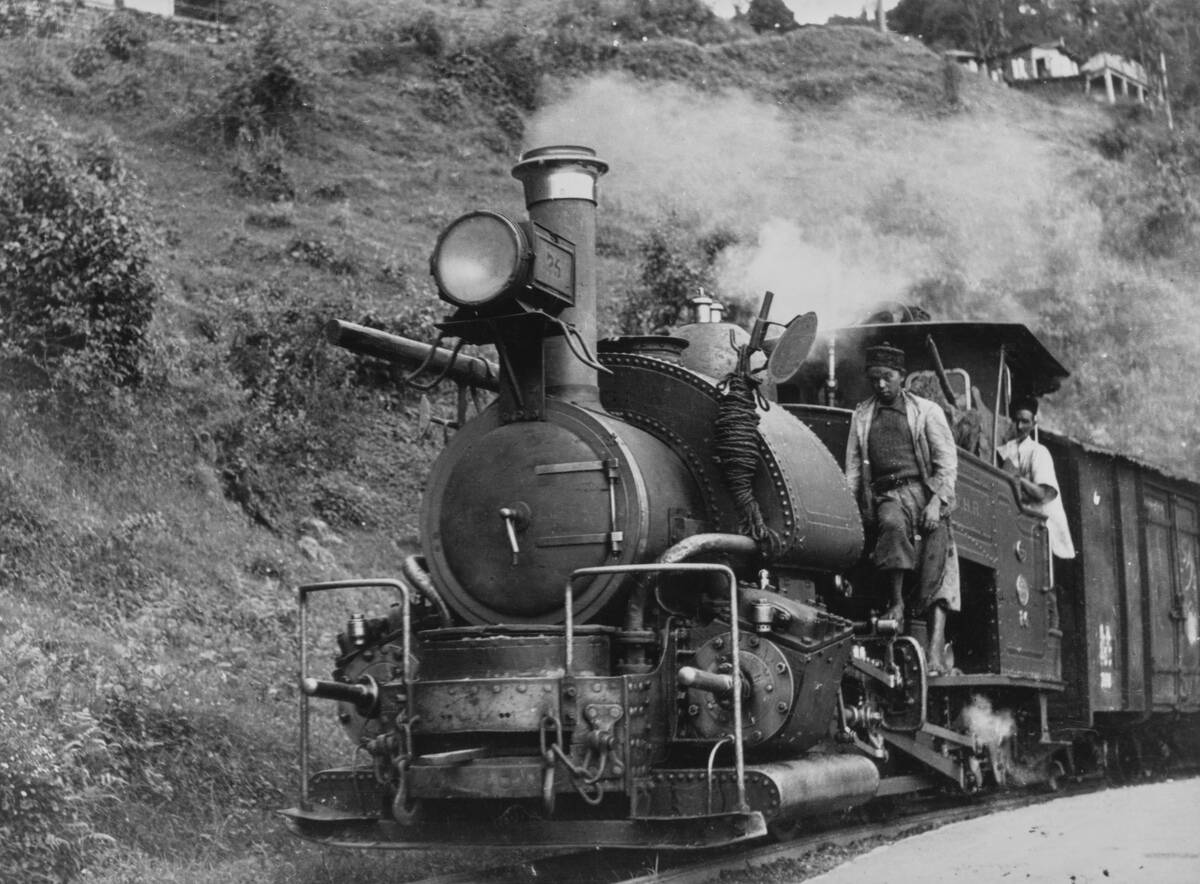

The influence of steam engines quickly spread beyond Europe and North America. In India, steam locomotives played a crucial role in developing the railway network, facilitating trade and movement.
Japan, too, embraced steam technology during the Meiji Restoration, modernizing its industries and infrastructure. Across the globe, steam engines transformed societies by connecting remote regions and fostering economic growth, highlighting their universal impact on global development.
The Social Impact: Connecting Communities and People
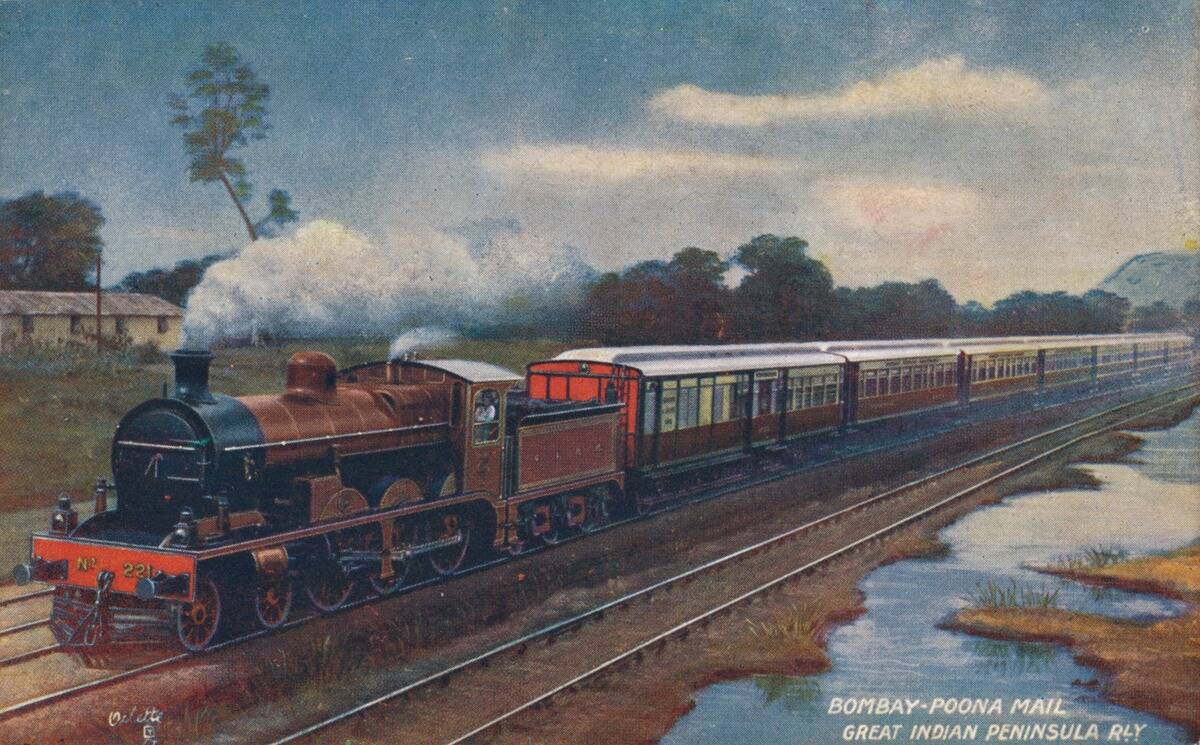

Steam engines did more than transport goods; they connected people and communities. Railways allowed for easier travel, enabling cultural exchange and communication across regions.
Families could visit relatives more frequently, and workers commuted to cities, contributing to urbanization. The newfound connectivity brought by steam power helped break down social barriers and fostered a sense of unity and progress in an increasingly interconnected world.
The Economic Boost: Steam Engines and Trade Expansion
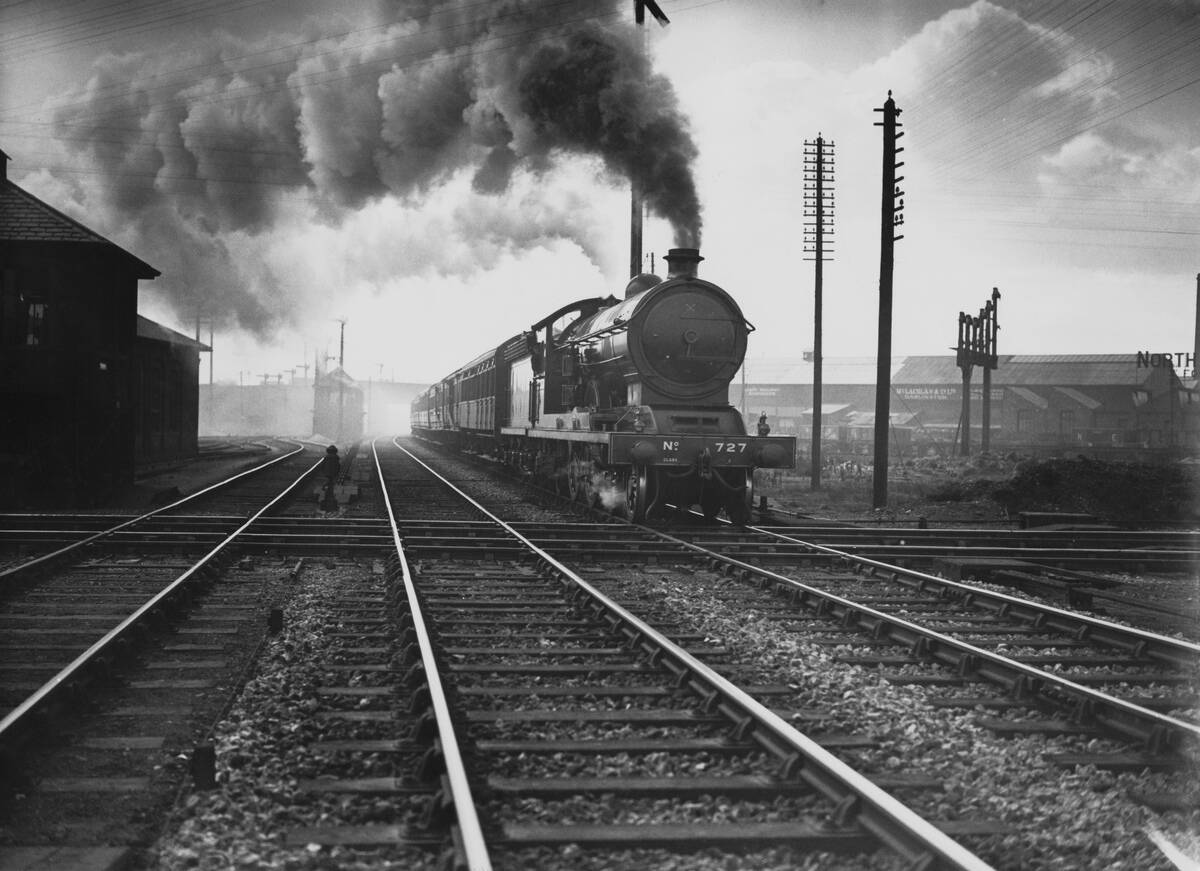

The economic impact of steam engines was profound, driving industrial growth and expanding trade. Factories powered by steam engines increased production rates, leading to a surplus of goods and the need for new markets.
Steam-powered ships and trains made transporting goods faster and cheaper, opening up international trade routes. This economic expansion facilitated wealth creation and laid the foundation for the modern global economy.
The Decline of Steam: The Rise of Diesel and Electric Power
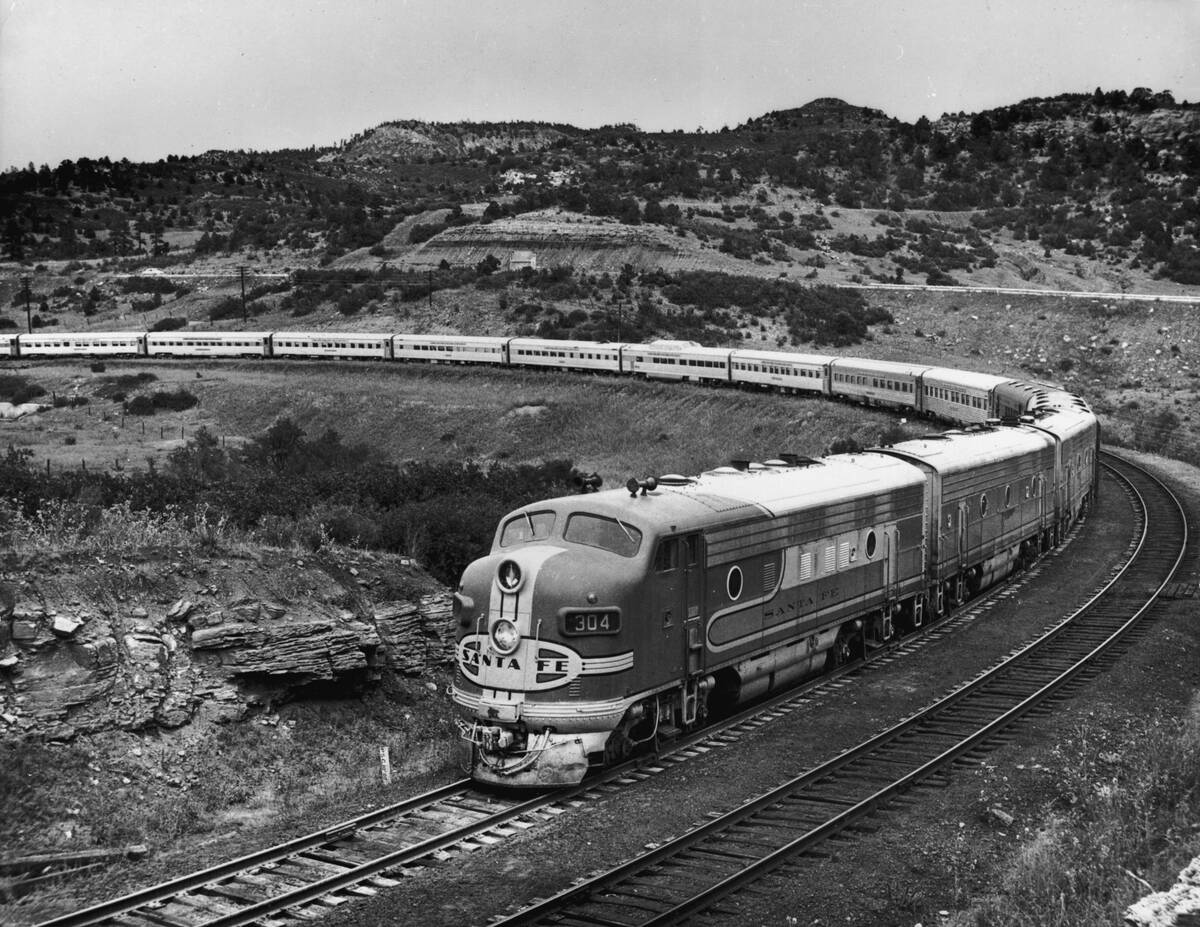

Despite their historical significance, steam engines eventually gave way to more efficient technologies. By the mid-20th century, diesel and electric engines surpassed steam in terms of efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Diesel locomotives required less maintenance and could run longer distances without refueling. Meanwhile, electric trains offered faster speeds with less environmental impact. These advancements marked the end of the steam era, but their legacy endures in history.
Preservation and Nostalgia: Steam Engines in the Modern Day
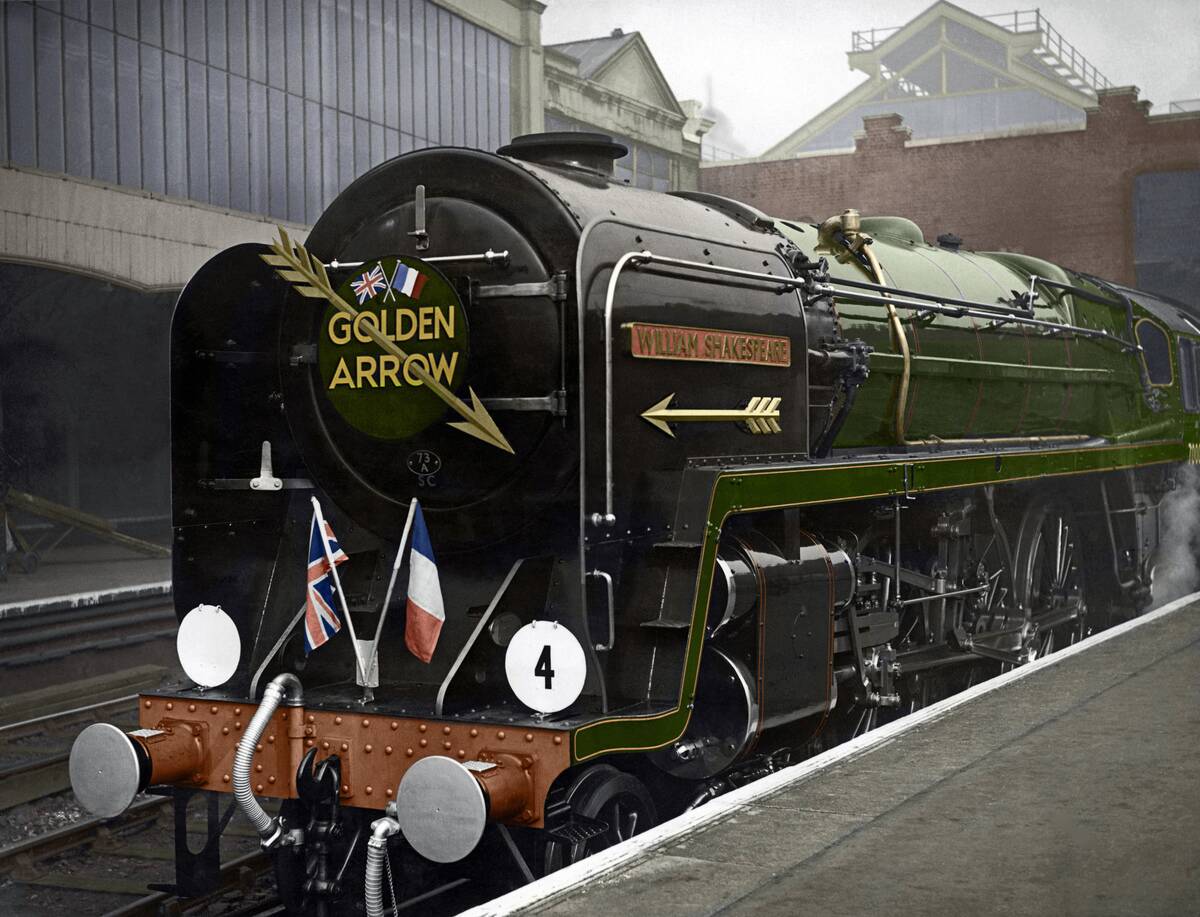

Today, steam engines are preserved as a nostalgic reminder of a bygone era. Enthusiasts and museums around the world keep these machines running, offering rides on heritage railways and maintaining them as historical artifacts.
Events like steam festivals celebrate the technology and its cultural impact, drawing crowds eager to experience the magic of steam. These preserved engines serve as a tangible link to the past, celebrating the ingenuity and spirit of the steam age.



