How music evolved over time from Gregorian chant to modern pop
Music has been a cornerstone of human culture for centuries, evolving through time to become the rich tapestry it is today. From the solemn chants of ancient monks to the vibrant beats of modern pop, each era has brought its own unique sound.
The journey of music is a fascinating one, showcasing not only the creativity of composers and musicians but also the technological and cultural shifts of society. Let’s dive into this melodious journey and explore the milestones that have defined the soundscape of our world.
The Origins: Understanding Gregorian Chant
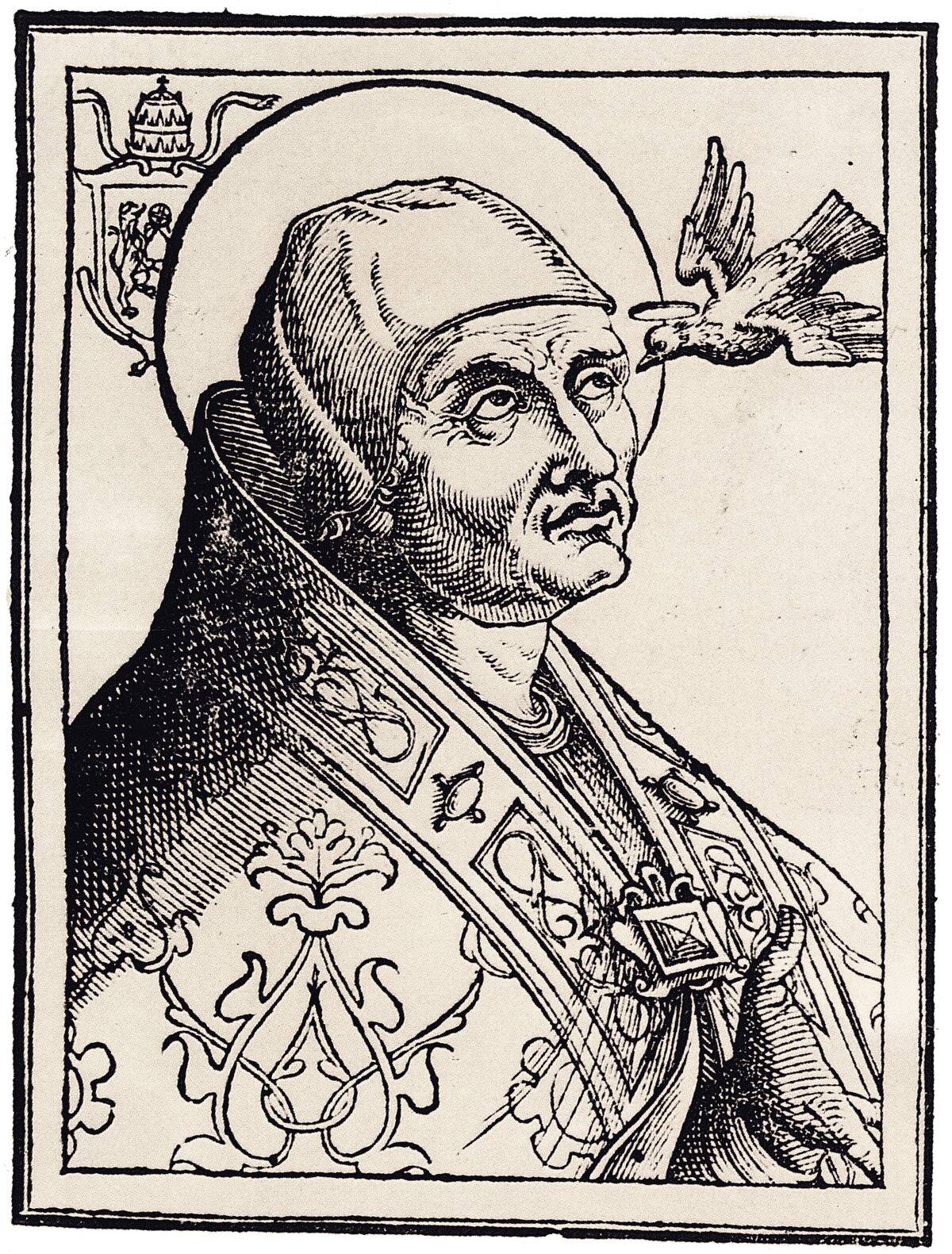

Gregorian chant is one of the earliest forms of music in the Western world, characterized by its monophonic, unaccompanied vocal music. Named after Pope Gregory I, it was developed during the 9th and 10th centuries.
These chants were primarily liturgical, used in church services to enhance the spiritual experience. Their serene and meditative quality provided a backdrop for religious contemplation, setting the stage for the future of Western music.
The Role of Monasteries and Monks in Musical Beginnings
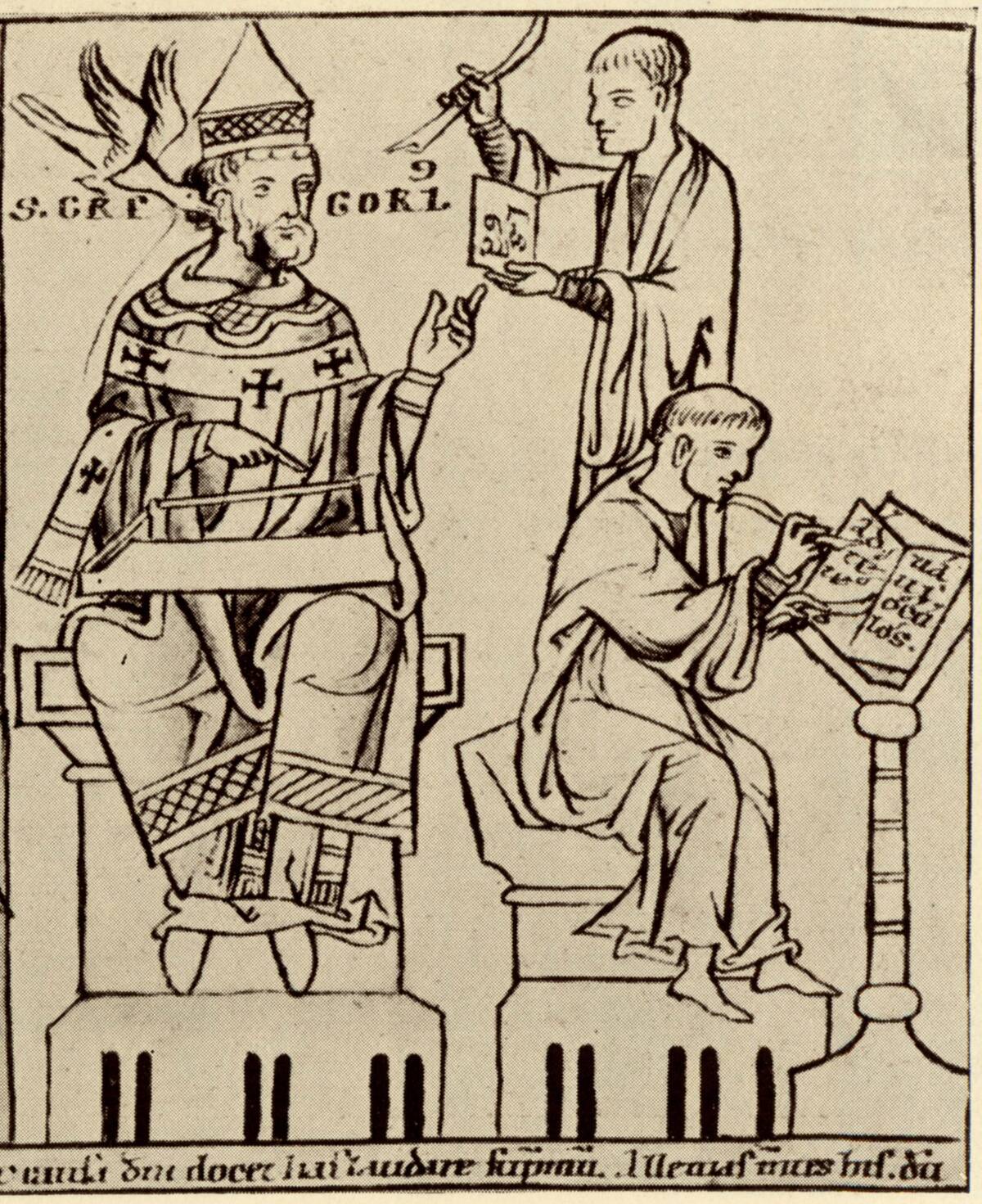

Monasteries played a crucial role in the development of early music, serving as centers of learning and culture. Monks meticulously transcribed music onto parchment, ensuring the preservation and dissemination of Gregorian chants.
These religious communities were responsible not only for composing new works but also for teaching music theory, laying the groundwork for future musical innovation. The disciplined life of a monk was intertwined with music, as it was an integral part of their daily worship and community life.
The Transition from Monophony to Polyphony

The shift from monophony to polyphony marked a significant evolution in music, introducing multiple, independent melodies played simultaneously. This transition began in the Middle Ages, with notable developments occurring in the Notre Dame School of polyphony in Paris.
Composers like Léonin and Pérotin pioneered this style, creating more complex and textured musical compositions. Polyphony added depth and richness to music, paving the way for the intricate harmonies of the Renaissance.
The Rise of the Renaissance and Secular Music
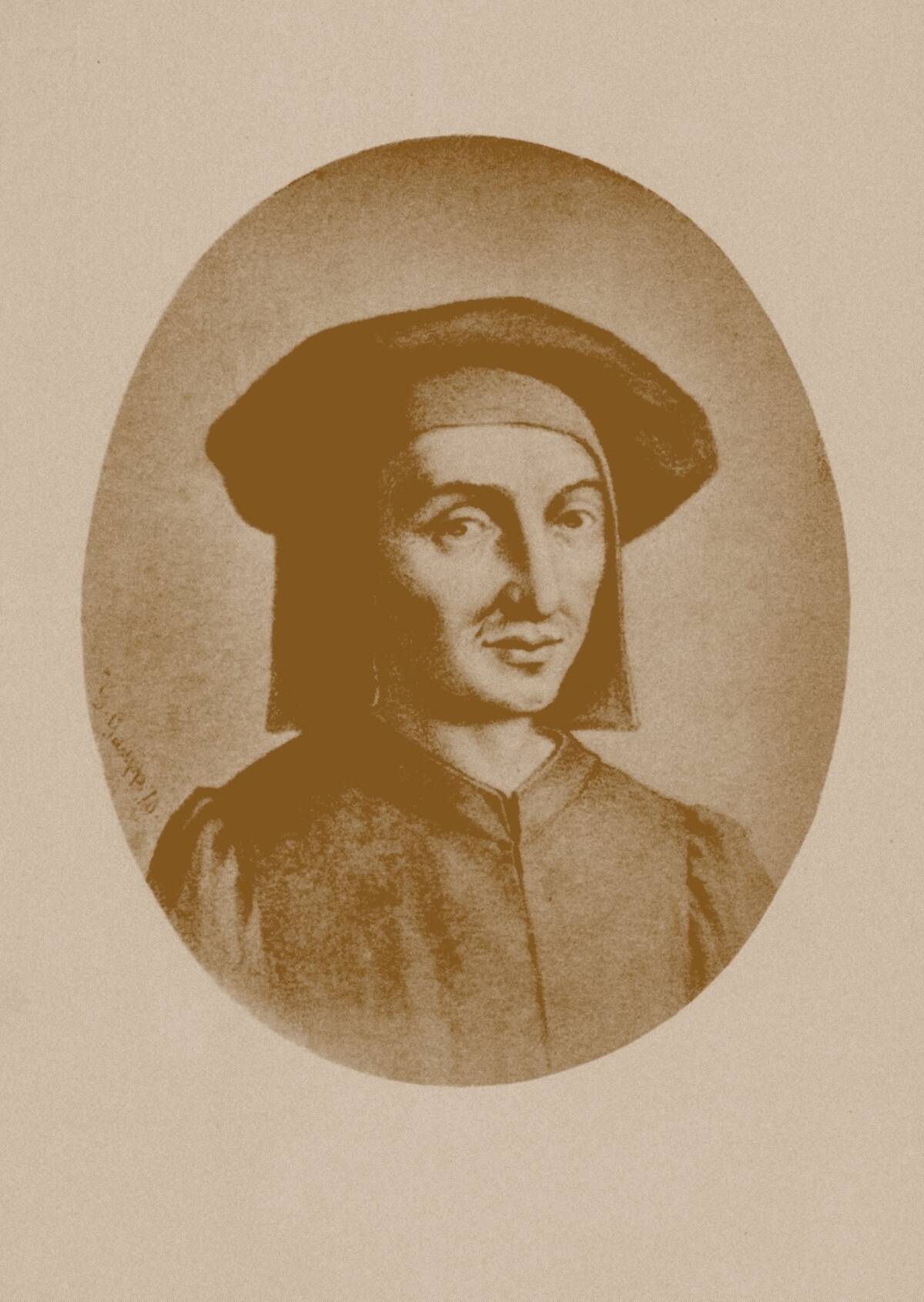

During the Renaissance, music began to flourish beyond the walls of the church as secular themes gained popularity. Composers like Josquin des Prez (pictured) and Palestrina explored new forms, including madrigals and chansons.
The invention of the printing press by Johannes Gutenberg also played a pivotal role, making sheet music more accessible. This era saw a blossoming of creativity, as musicians sought to express human emotions and experiences through their art, reflecting the broader cultural Renaissance.
Baroque Brilliance: The Birth of Opera

The Baroque period, spanning from approximately 1600 to 1750, witnessed the birth of opera, a dramatic art form combining music, acting, and scenery. Claudio Monteverdi’s “L’Orfeo” is often credited as the first great opera (though not the first in existence), debuting in 1607.
This era also saw the rise of instrumental music, with composers like Johann Sebastian Bach and Antonio Vivaldi pushing musical boundaries. The ornate and expressive style of Baroque music set the stage for the symphonic grandeur of the Classical era.
Classical Era: The Age of Symphonies and Sonatas
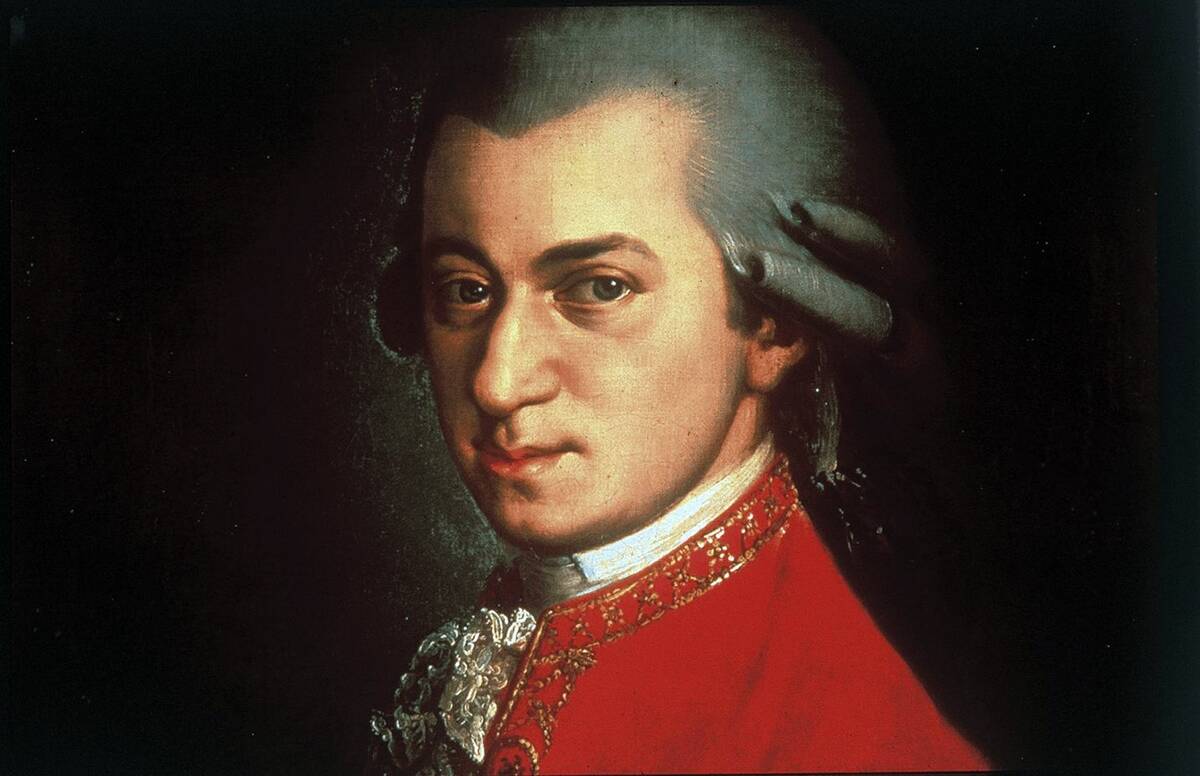

The Classical era, which spanned the late 18th to early 19th centuries, is often associated with the elegance and clarity of composers like Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and Ludwig van Beethoven. This period saw the development of the symphony and sonata, with a focus on balanced structures and expressive melodies.
The music reflected the ideals of the Enlightenment, emphasizing order and reason while still allowing for emotional depth. The Classical era laid the groundwork for the intense expressiveness of the Romantic period.
The Romantic Period: Emotion and Expression in Music
The Romantic period, spanning the 19th century, brought an emphasis on emotion and individual expression in music. Composers like Franz Schubert, Johannes Brahms, and Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky sought to convey deep feelings and narratives through their works.
This era saw the rise of the virtuoso performer, with figures like Franz Liszt and Niccolò Paganini (pictured) captivating audiences with their technical prowess. Romantic music explored themes of nature, love, and the supernatural, often pushing the boundaries of traditional forms.
The Advent of Jazz: A New American Sound
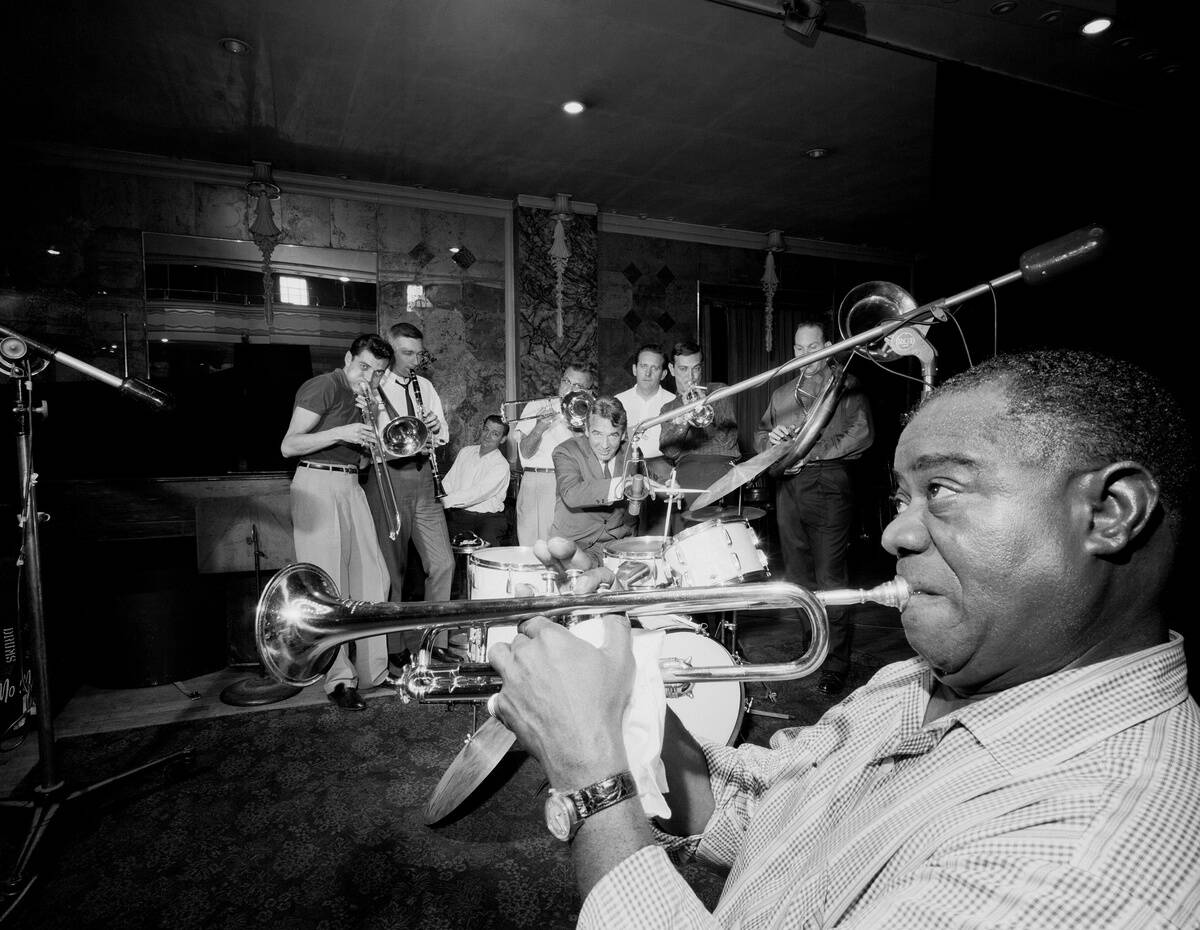

Jazz emerged in the early 20th century, originating in the African American communities of New Orleans. It is characterized by its syncopated rhythms, improvisation, and blues influences. Legends like Louis Armstrong (pictured in the foreground) and Duke Ellington helped popularize jazz, bringing it to a wider audience.
The genre’s flexibility and innovation made it a significant cultural force, influencing many other styles of music. Jazz’s impact can still be felt today, as it continues to evolve and inspire musicians worldwide.
Blues and Its Influence on Modern Genres
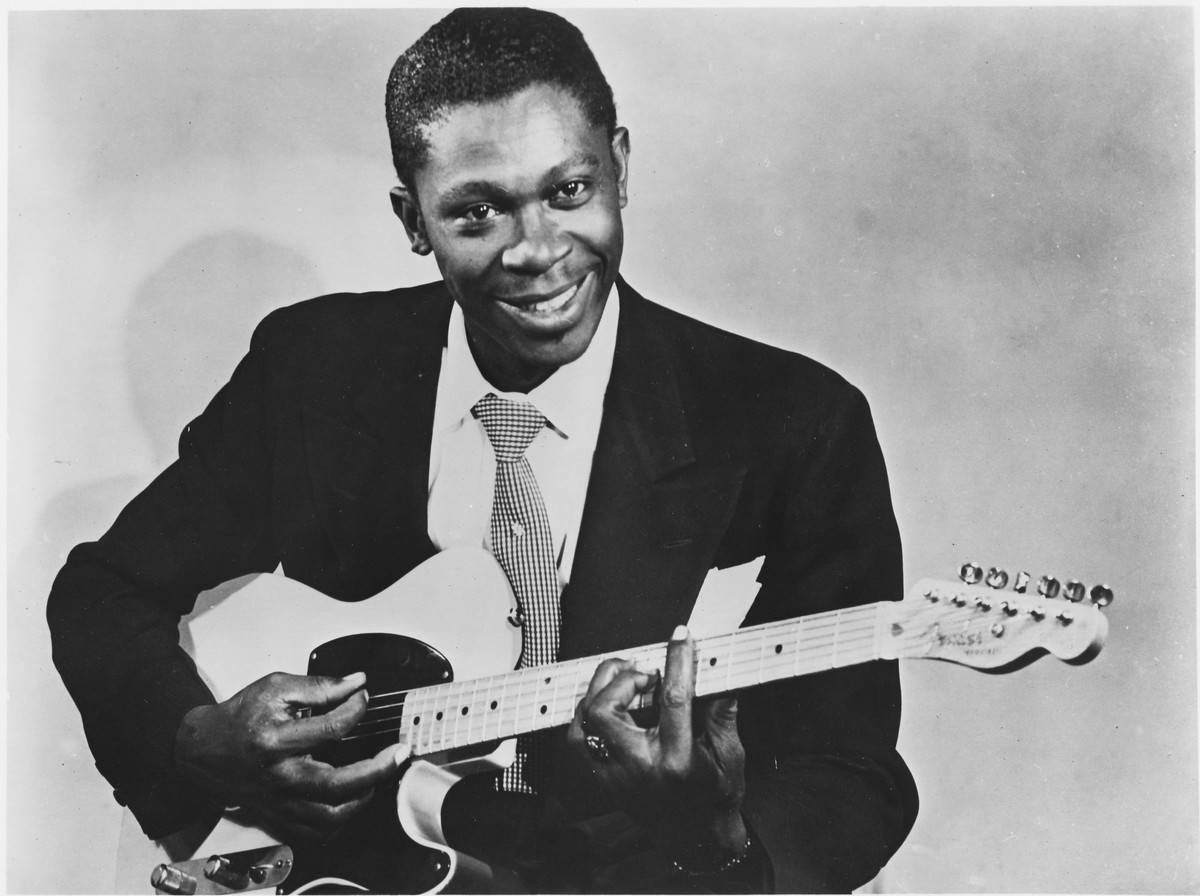

Blues music, with its roots in African American spirituals and work songs, emerged in the late 19th century. It is characterized by its use of the blues scale and specific chord progressions.
Artists like B.B. King (pictured) and Muddy Waters were instrumental in popularizing the genre. Blues laid the foundation for many modern music styles, including rock and roll, jazz, and hip-hop. Its themes of hardship and resilience resonate with listeners, reflecting the human experience in profound ways.
Rock ‘n’ Roll Revolution: Shaking Things Up
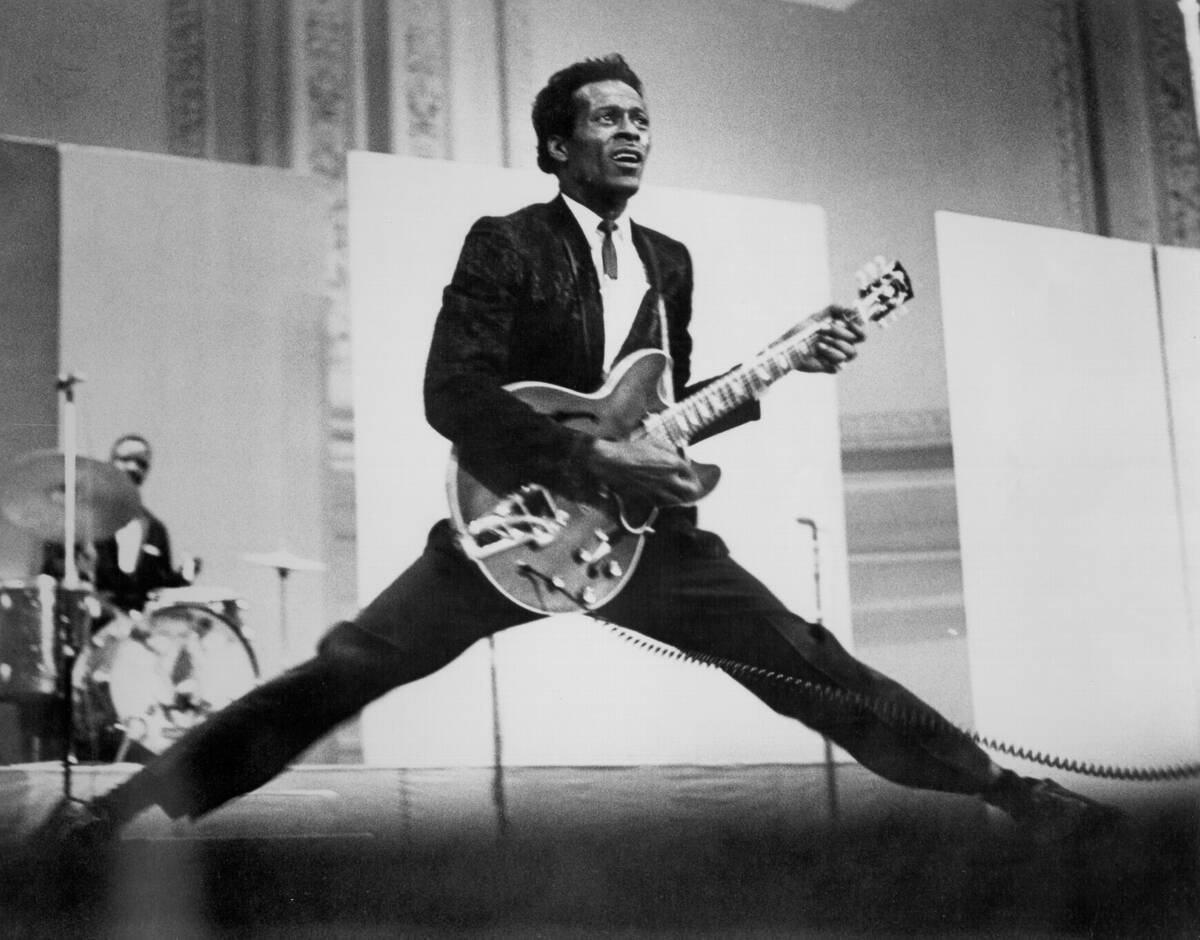

The 1950s witnessed the explosive rise of rock ‘n’ roll, a genre that combined elements of blues, country, and jazz. Pioneers like Elvis Presley, Chuck Berry, and Little Richard brought a rebellious energy to the music scene.
Rock ‘n’ roll was not just a musical revolution but a cultural one, influencing fashion, attitudes, and social norms. Its infectious rhythms and spirited performances captured the spirit of a generation and laid the groundwork for the diverse rock genres that followed.
The British Invasion: Beatles to Rolling Stones
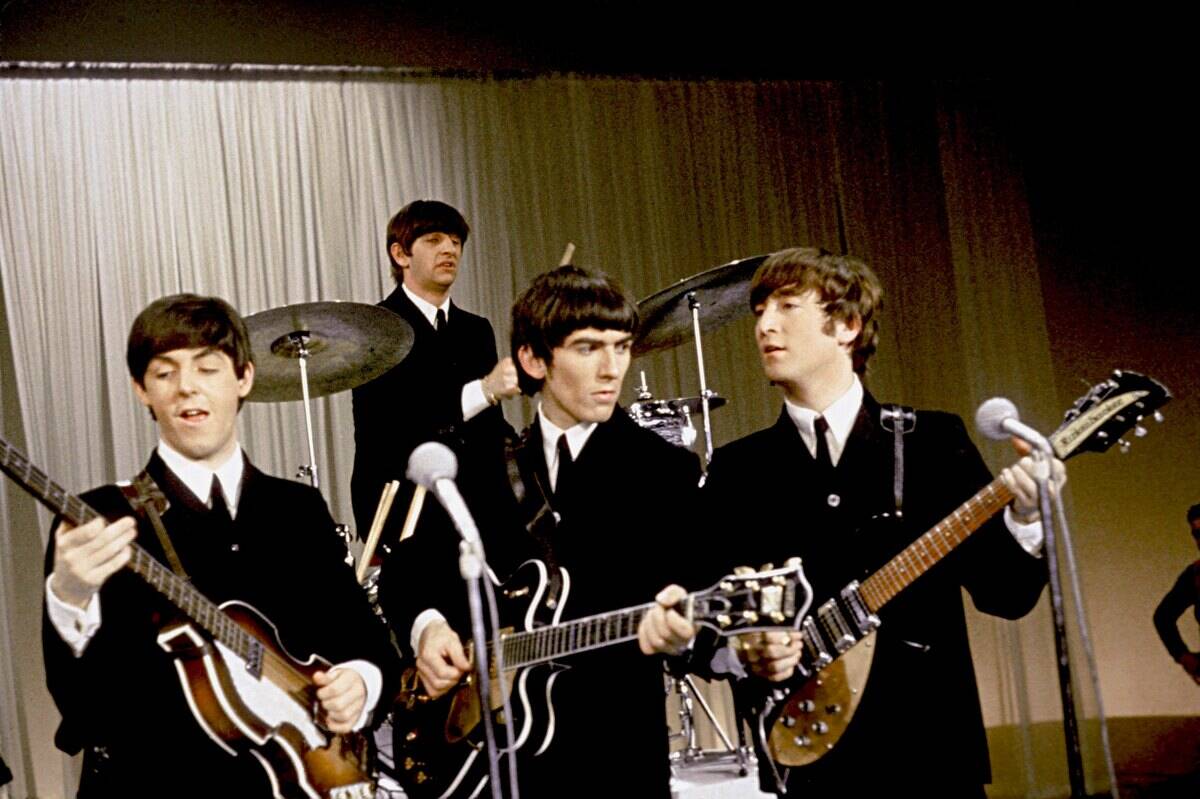

The 1960s saw the British Invasion, a wave of British bands that took the American music scene by storm. Leading the charge were The Beatles, whose innovative songwriting and charismatic performances redefined popular music.
The Rolling Stones brought a grittier, blues-influenced sound, challenging and expanding the boundaries of rock ‘n’ roll. The British Invasion sparked a musical revolution, influencing countless artists and forever changing the landscape of popular music.
Disco Fever: The Dance Craze of the 70s
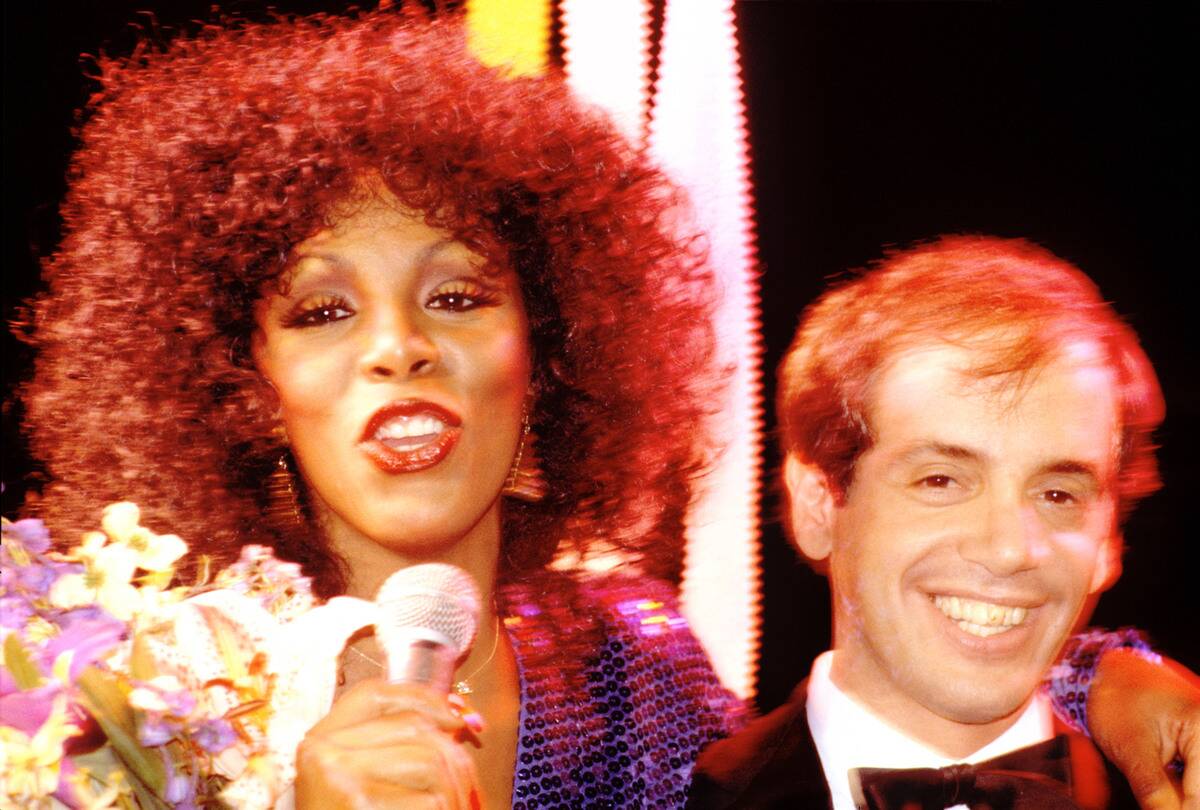

In the 1970s, disco fever swept across dance floors worldwide, characterized by its upbeat rhythms and infectious grooves. Artists like Donna Summer and the Bee Gees dominated the charts, creating anthems that still get people moving today.
Disco was more than just music; it was a lifestyle, with dance clubs like Studio 54 becoming cultural epicenters. The genre’s emphasis on rhythm and danceability influenced later electronic and pop music, leaving a lasting legacy.
Hip-Hop and Rap: Voices from the Streets
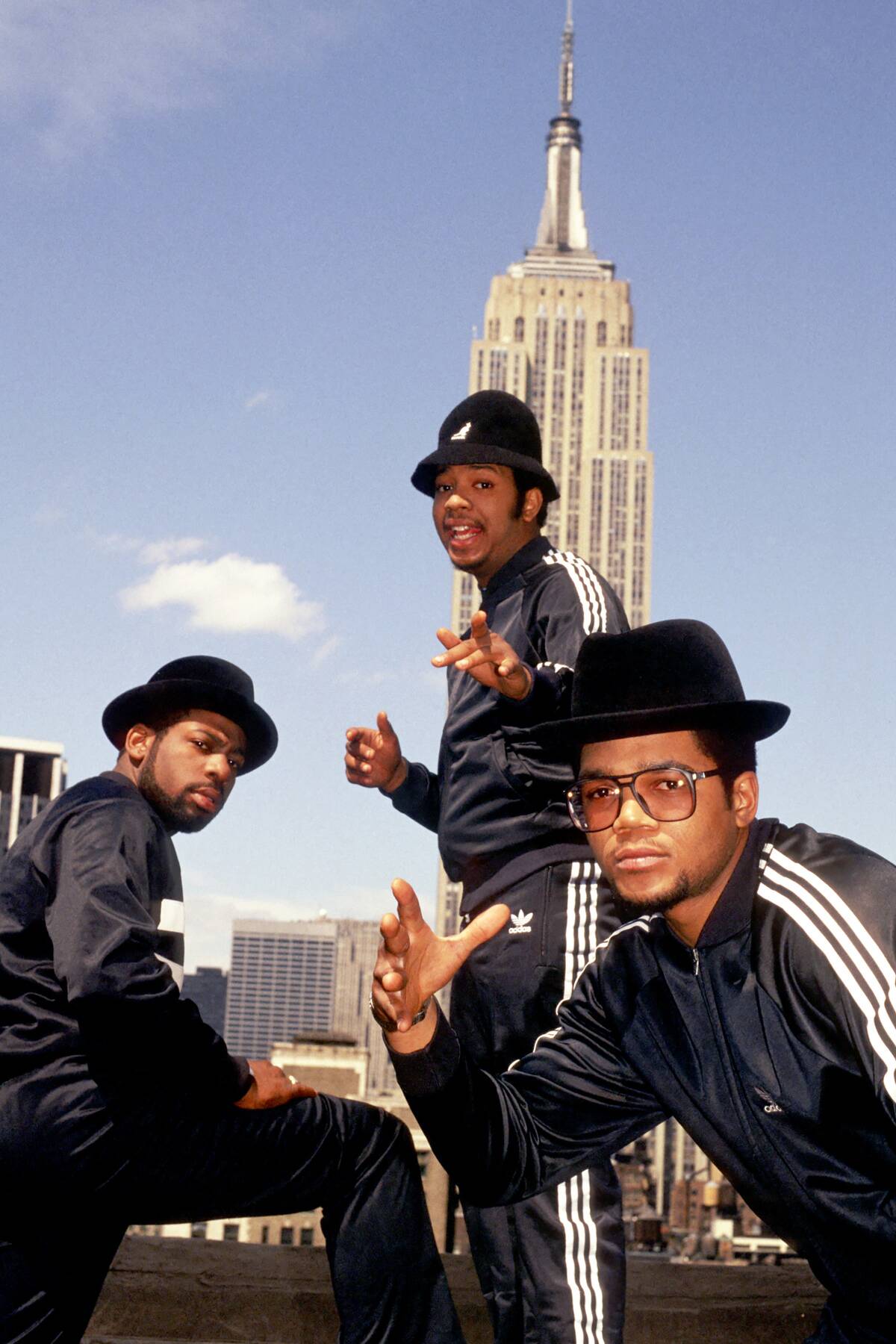

Hip-hop and rap emerged in the late 1970s in the South Bronx, New York City, as a voice for marginalized communities. Artists like DJ Kool Herc, Grandmaster Flash, and Run-D.M.C. pioneered this genre, combining rhythmic spoken word with beats created from samples and scratches.
Hip-hop quickly became a global phenomenon, addressing social issues and providing a platform for self-expression. Its cultural impact is immense, influencing fashion, language, and art, and it continues to evolve as a dominant force in the music industry.
Pop Music Explosion: From Madonna to Taylor Swift
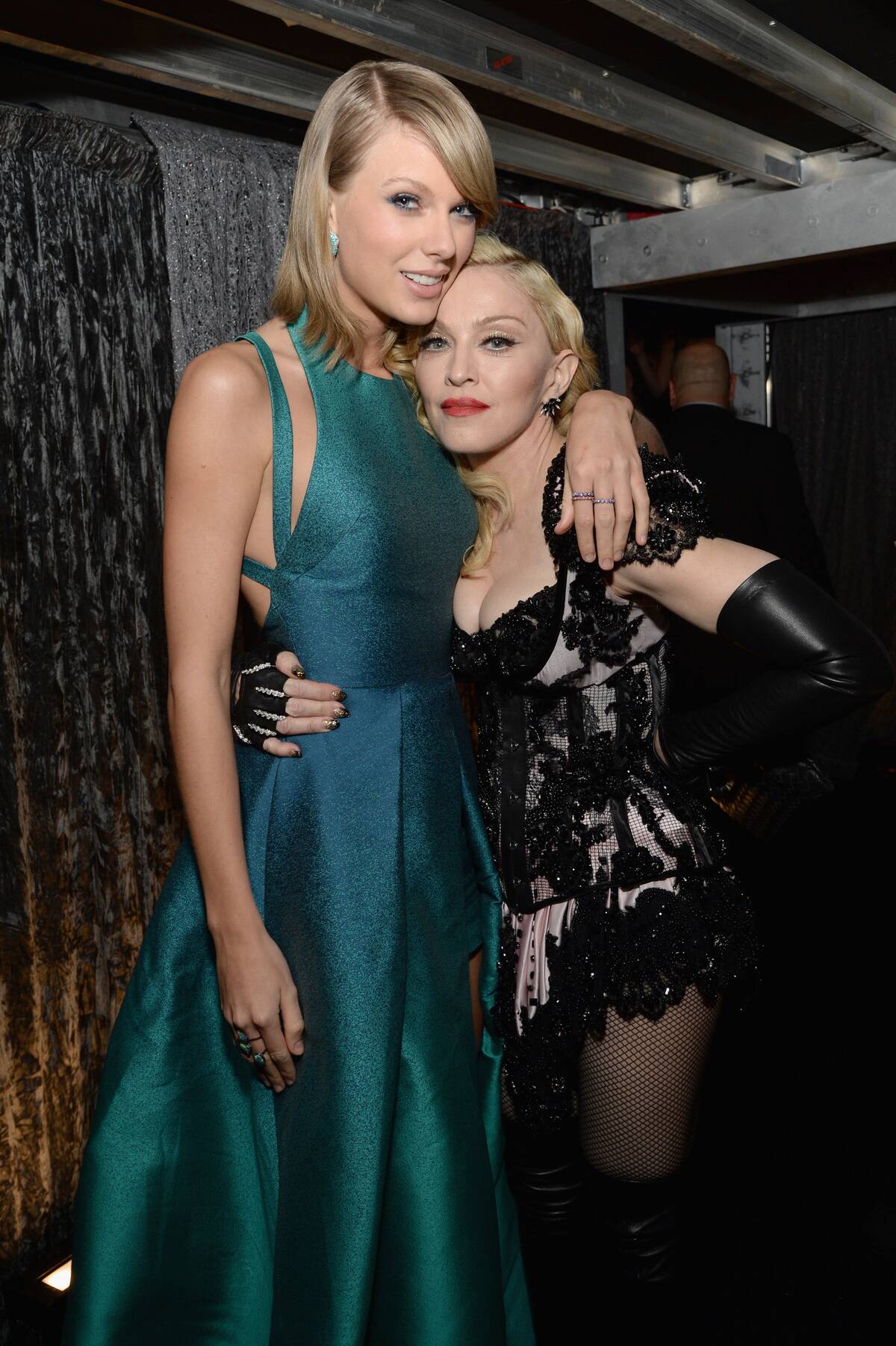

Pop music has become synonymous with catchy melodies and widespread appeal, dominating charts worldwide. Icons like Madonna in the 1980s and Taylor Swift in the 21st century have shaped the genre with their distinctive styles and ability to connect with audiences.
Pop’s adaptability has allowed it to incorporate elements from various genres, keeping it fresh and relevant. Its commercial success and cultural impact make pop music a defining force in the modern musical landscape.
The Digital Age: Music in the Era of Streaming and Downloads

The digital age has revolutionized the way we consume music, with streaming platforms like Spotify and Apple Music offering instant access to vast libraries of songs. This shift has changed the industry’s dynamics, emphasizing singles over albums and allowing independent artists to reach global audiences.
Music downloads and streaming have also impacted charts and revenue models, challenging traditional music distribution. Despite these changes, the digital age has democratized music, making it more accessible than ever before.
Global Influence: How World Music Shapes Modern Pop
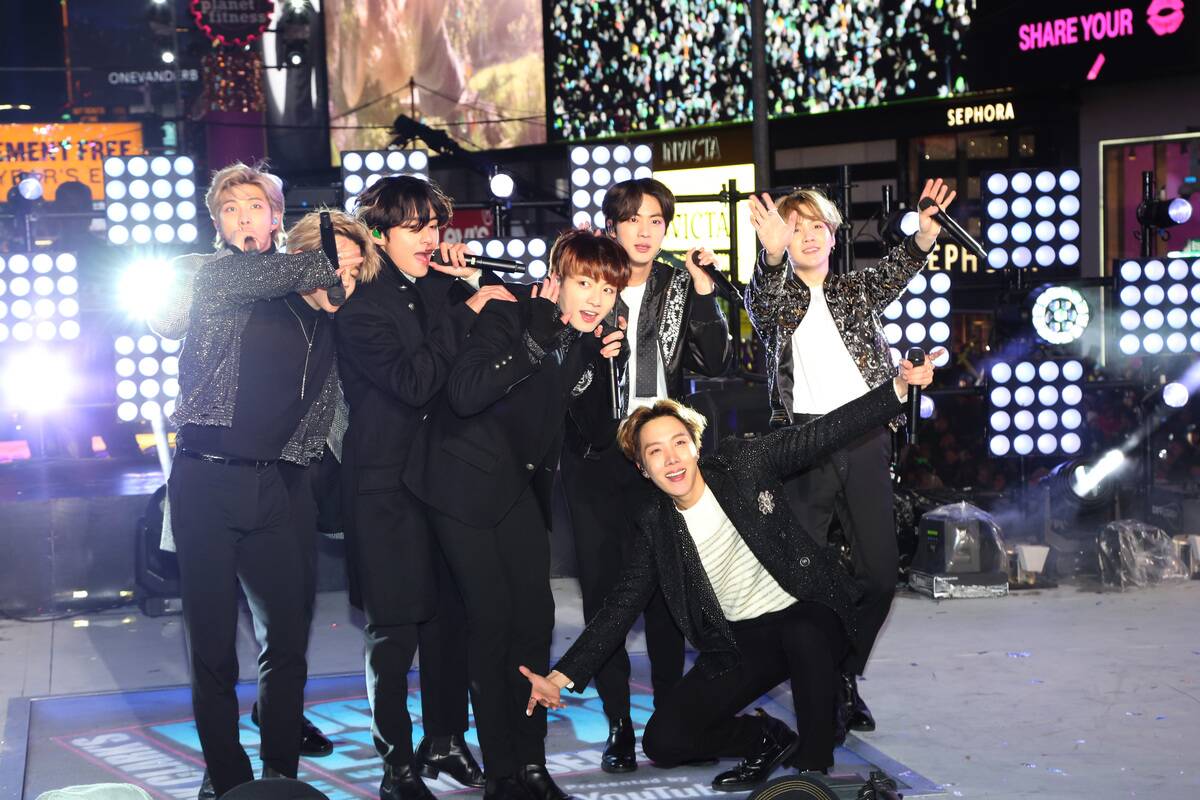

World music has increasingly influenced modern pop, bringing diverse sounds and cultural elements into mainstream music. Artists like Shakira and BTS have incorporated Latin and K-pop influences, respectively, into their work, achieving international success.
This blending of styles has enriched the pop genre, introducing listeners to new rhythms and instruments. As music becomes more globalized, the lines between genres continue to blur, creating a vibrant and dynamic musical landscape.
Technological Innovations: The Role of Synthesizers and Auto-tune
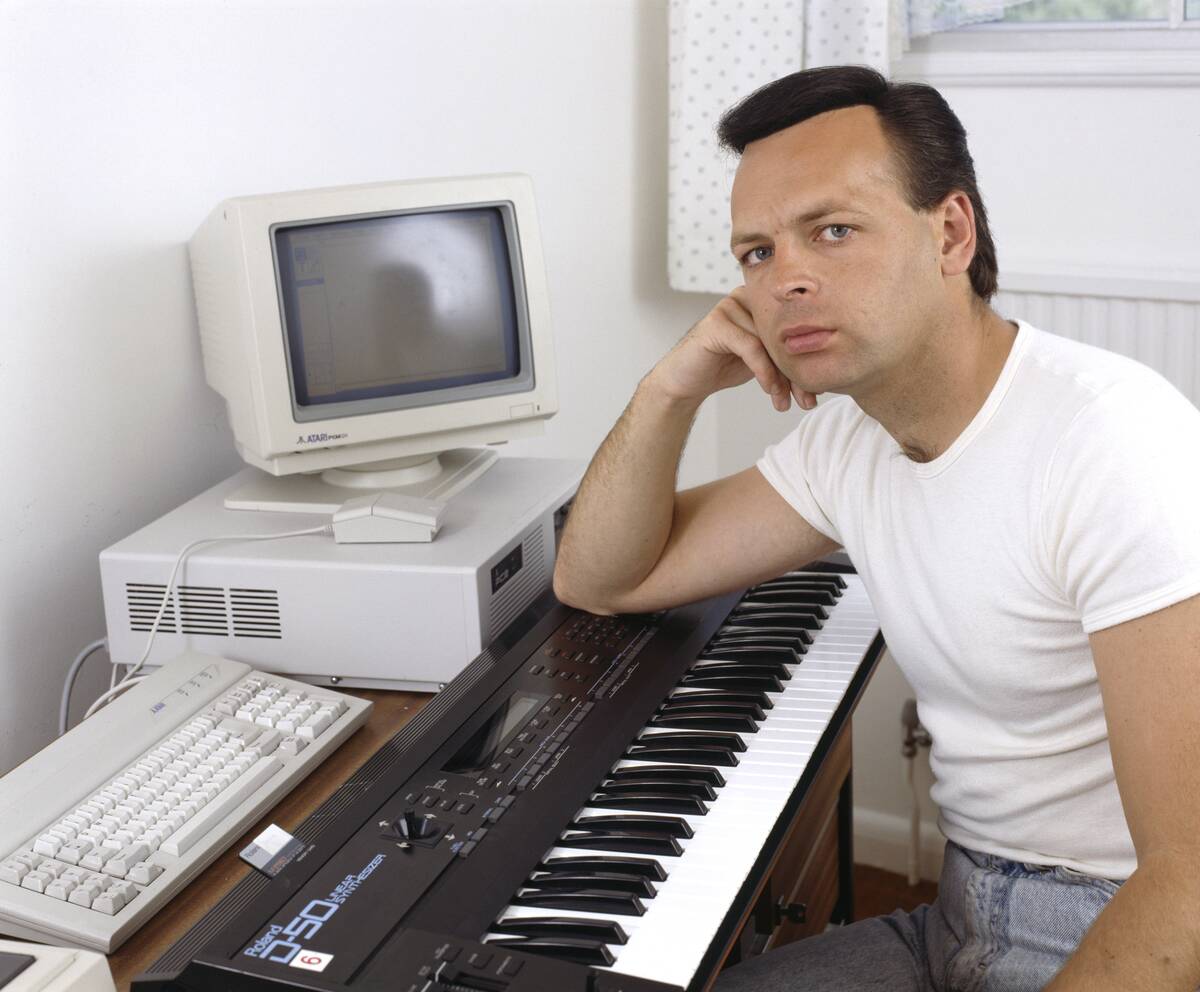

Technological innovations have significantly shaped modern music, with synthesizers and auto-tune being prominent examples. Synthesizers, popularized in the 1980s, allowed artists to explore new sonic possibilities and create electronic music.
Auto-tune, while initially used for pitch correction, has become a stylistic choice for many artists, adding a unique texture to vocals. These technologies have pushed the boundaries of creativity, enabling musicians to experiment with sound and redefine what is possible in music production.
The Rise of Indie and Alternative Scenes
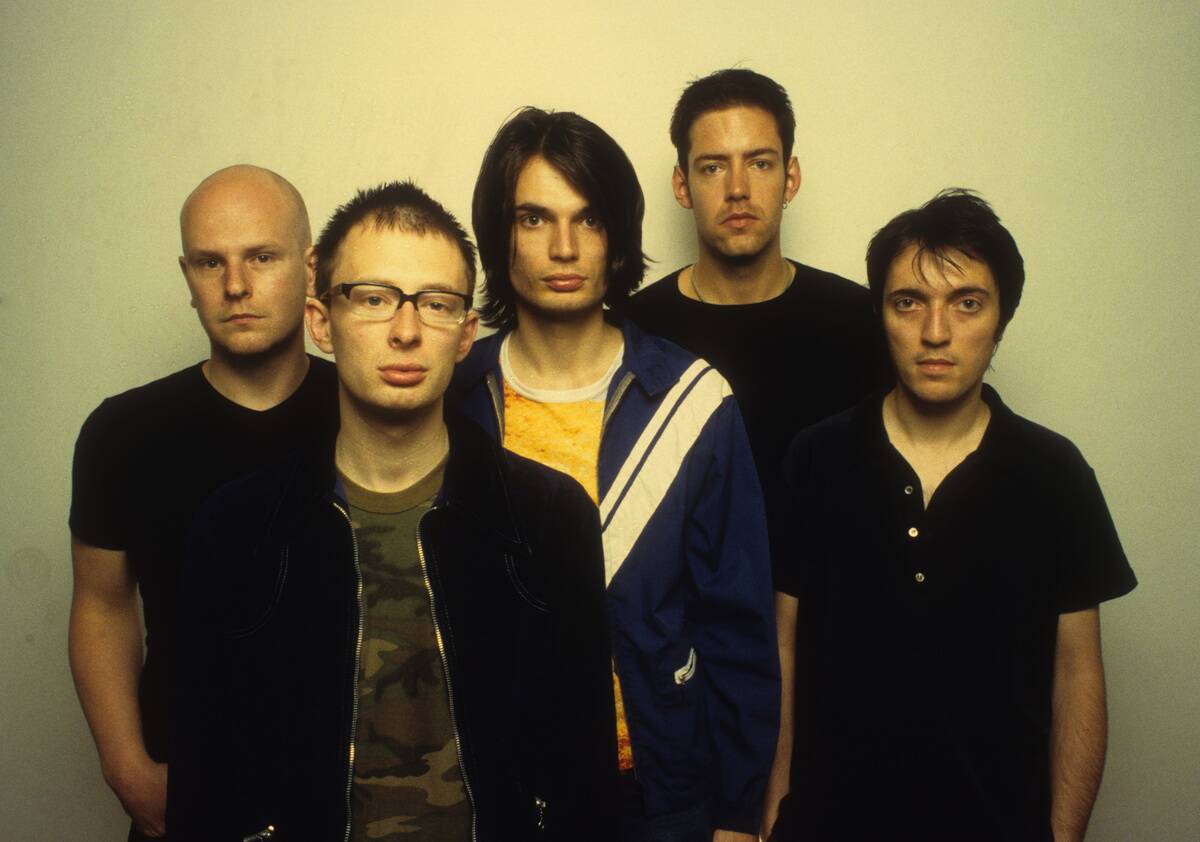

The indie and alternative music scenes have flourished since the 1990s, offering a counterpoint to mainstream pop. Bands like Radiohead and Arcade Fire have gained critical acclaim for their innovative sounds and artistic integrity.
These genres emphasize individuality and often explore unconventional themes and structures. The rise of independent labels and digital distribution has empowered artists to pursue their creative visions without commercial constraints, leading to a diverse and ever-evolving musical landscape.



