How the battleship era came to a sudden end
The battleship era, a time when colossal steel giants ruled the seas, came to an abrupt end faster than many had anticipated. Once the pride of naval fleets, these massive vessels were the embodiment of military power and technological prowess.
Yet, they became relics almost overnight due to rapid advancements in warfare technology and tactics. Understanding this shift provides insight into how innovation can overturn longstanding traditions in a blink of an eye.
The Golden Age of Battleships: A Brief Overview
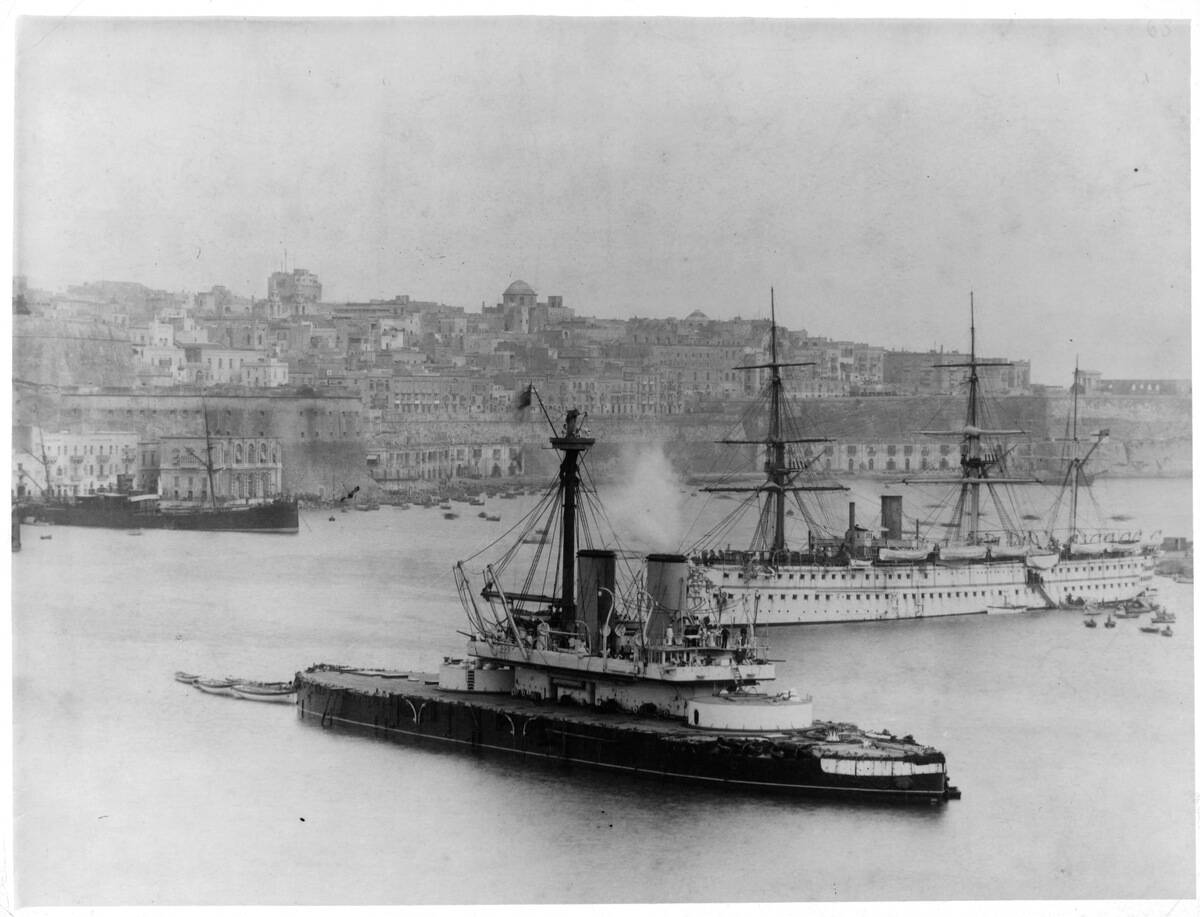

From the late 19th century to the early 20th century, battleships were the pinnacle of naval strength. Countries like Britain, Germany, and the United States invested heavily in these warships, leading to an arms race on the high seas.
The Dreadnought (pictured), launched in 1906, revolutionized naval warfare with its all-big-gun armament and steam turbine propulsion. This period saw battleships as the ultimate status symbol for naval supremacy.
The Mighty Battleships: Symbols of Naval Dominance
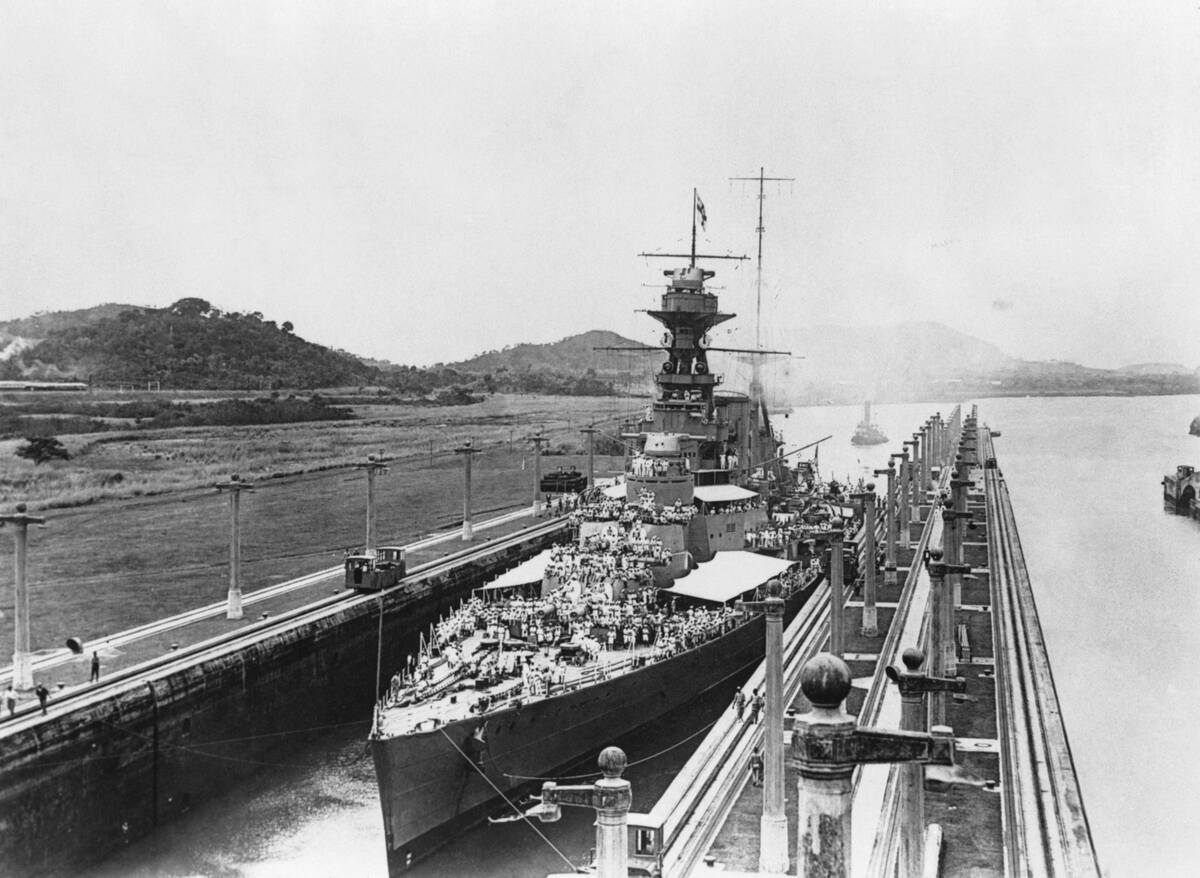

Battleships were more than just war machines; they were symbols of national pride and naval dominance. Their sheer size and firepower commanded respect and often deterred conflict.
Nations showcased them during naval reviews to demonstrate their maritime strength. The HMS Hood, for example, was known as the ‘Mighty Hood’ and served as a powerful deterrent during its time. Such ships were floating fortresses, capable of engaging enemy fleets with devastating effect.
Technological Marvels: What Made Battleships Stand Out?
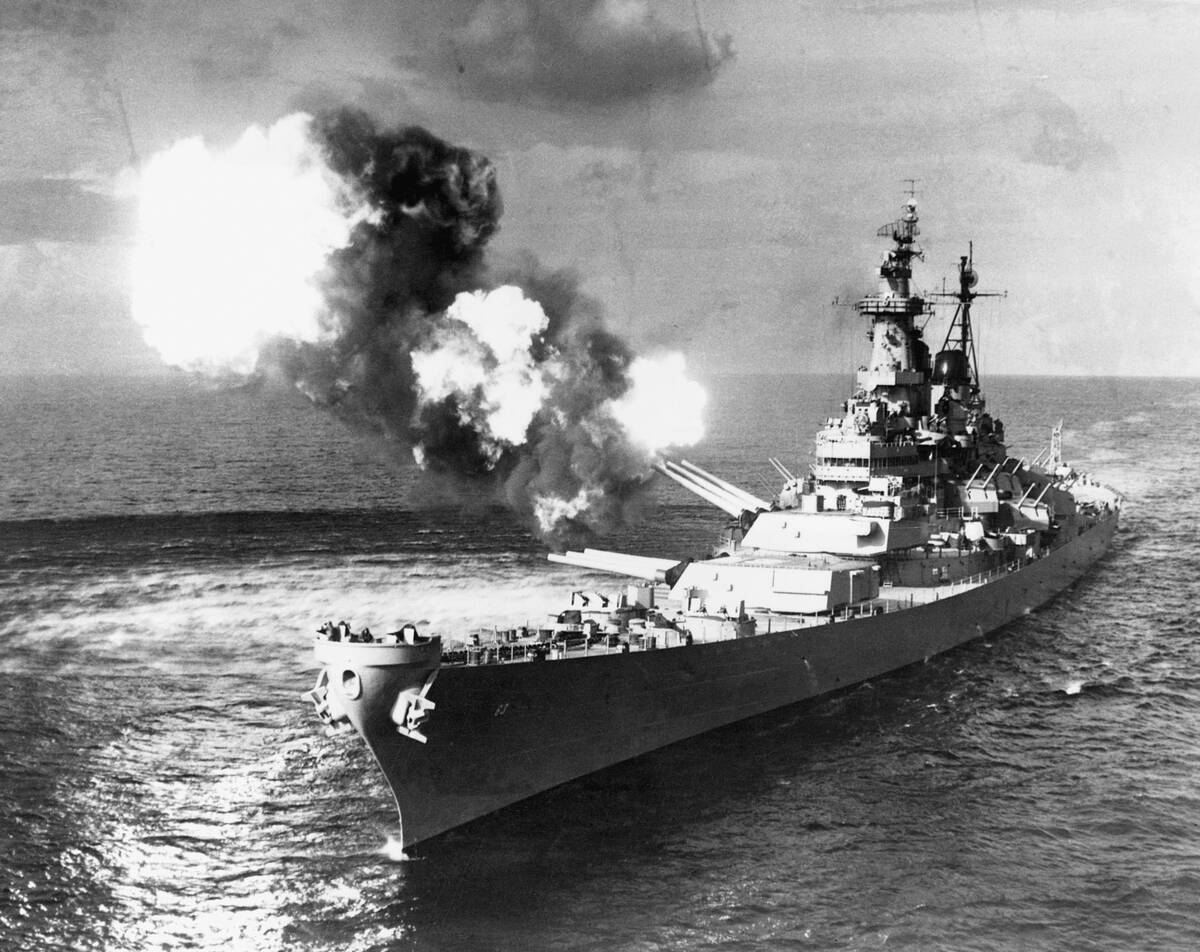

Battleships were technological marvels, incorporating the latest in naval engineering and armament. They boasted thick armor plating and massive guns capable of firing shells over 20 miles.
Advanced fire-control systems were developed to improve accuracy at long ranges, and innovations like radar further enhanced their combat capabilities. These features made battleships formidable opponents, combining offense and defense in a way that few other vessels could match at the time.
A Shift in Naval Warfare: The Winds of Change
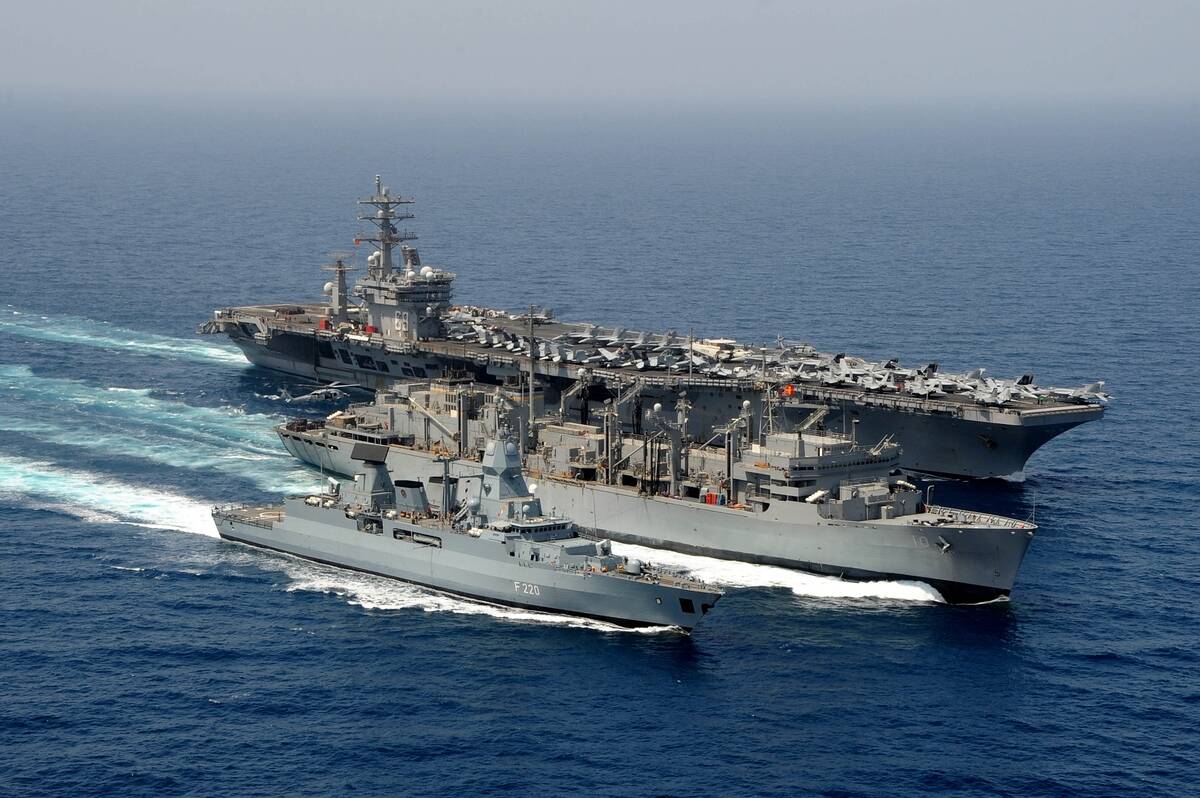

Despite their power, battleships were not immune to the changing tides of warfare. The interwar years saw technological advances that began to challenge the battleship’s dominance.
Naval strategists started questioning their effectiveness as aircraft carriers and submarines proved themselves in exercises and smaller conflicts. The shift was subtle at first, but it became apparent that the era of big-gun ships was under threat from new, more versatile forms of naval power.
The Rise of Air Power: A Game Changer for Naval Forces
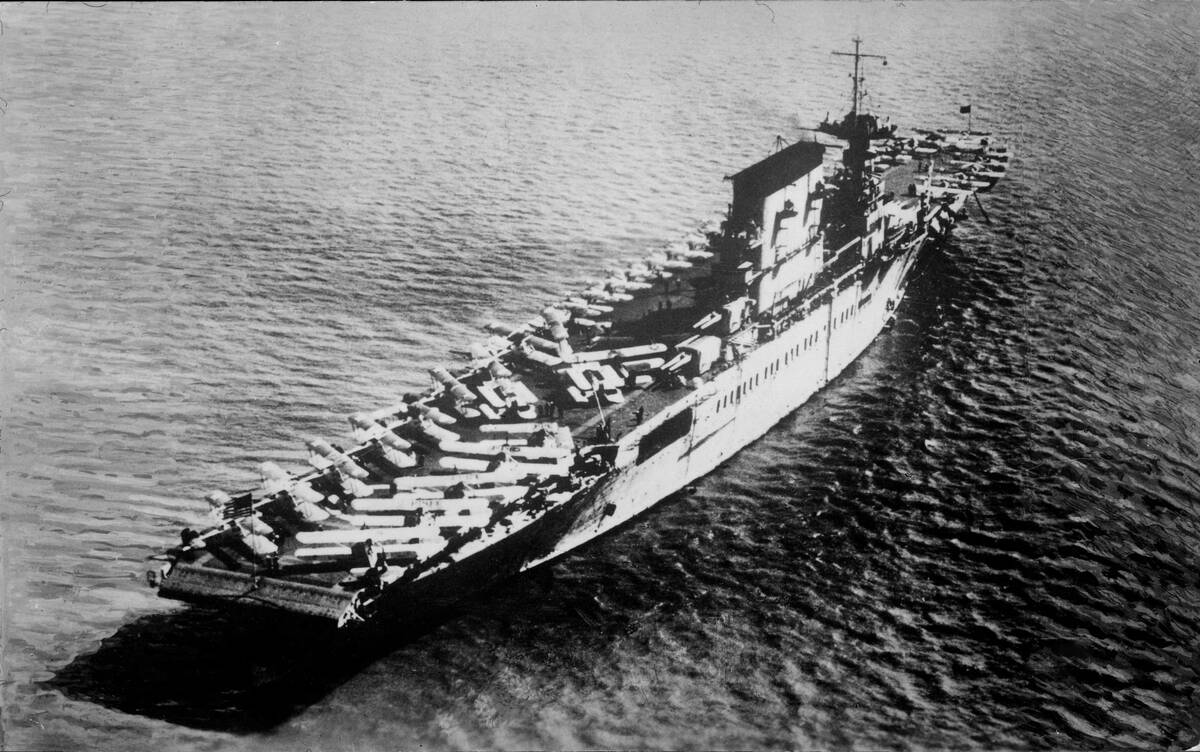

Air power emerged as a game changer in naval warfare, offering capabilities that battleships could not match. Aircraft could scout vast areas of ocean and attack from above, bypassing the thick armor of battleships.
The ability to strike from above rendered traditional naval artillery less effective. The U.S. Navy’s use of carrier-based aircraft in the 1920s and 30s demonstrated the potential of air power to revolutionize naval strategy and tactics.
The Advent of Aircraft Carriers: Stealing the Spotlight
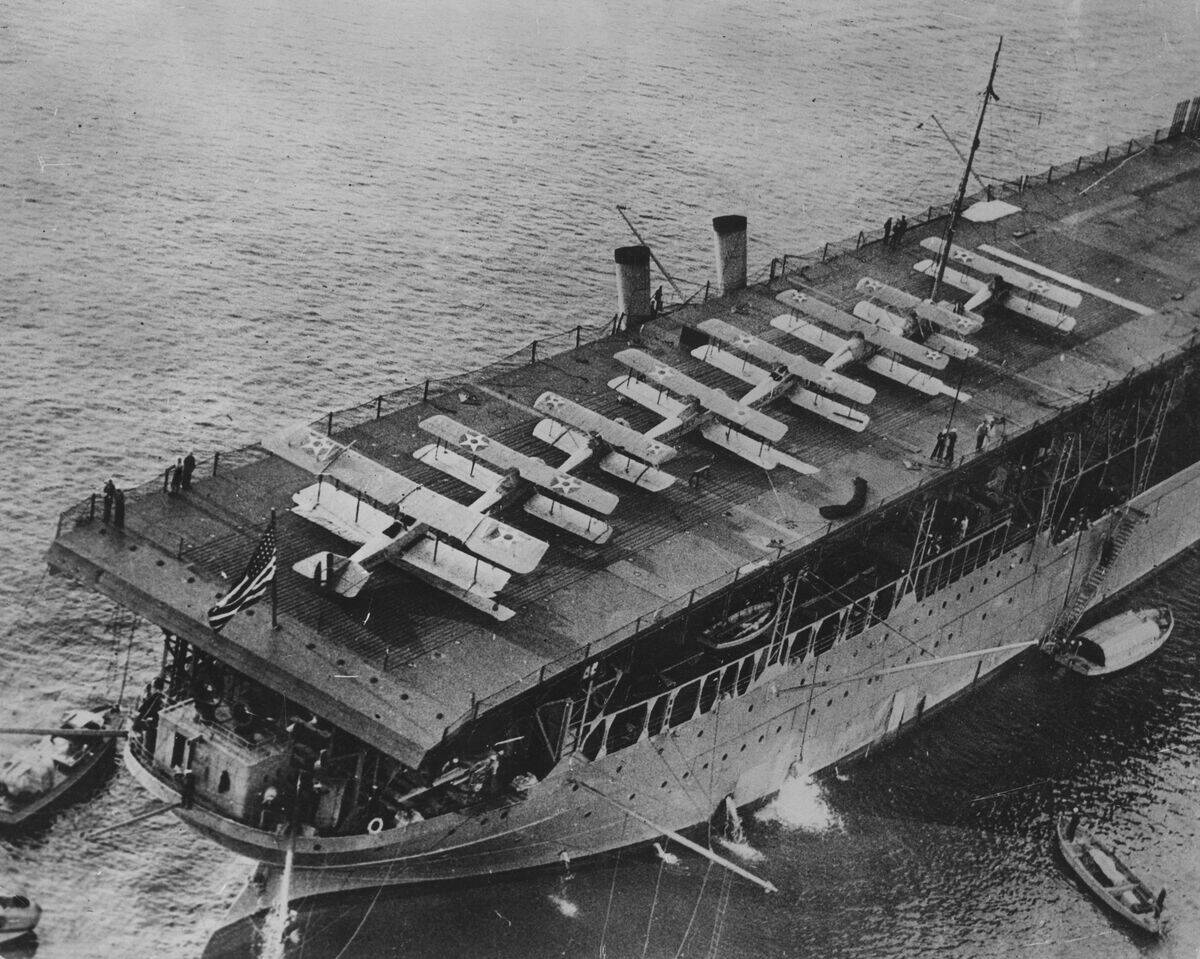

Aircraft carriers soon stole the spotlight from battleships, proving themselves as the new capital ships of navies. With the ability to launch and recover aircraft, carriers extended a fleet’s reach and provided unmatched flexibility in combat.
The USS Langley, commissioned in 1922, was the first U.S. aircraft carrier (the first purpose-built one, anyway) and marked the beginning of a new era. Carriers could project power across great distances, making them invaluable in naval operations.
The Battle of Taranto: A Turning Point in Naval Strategy
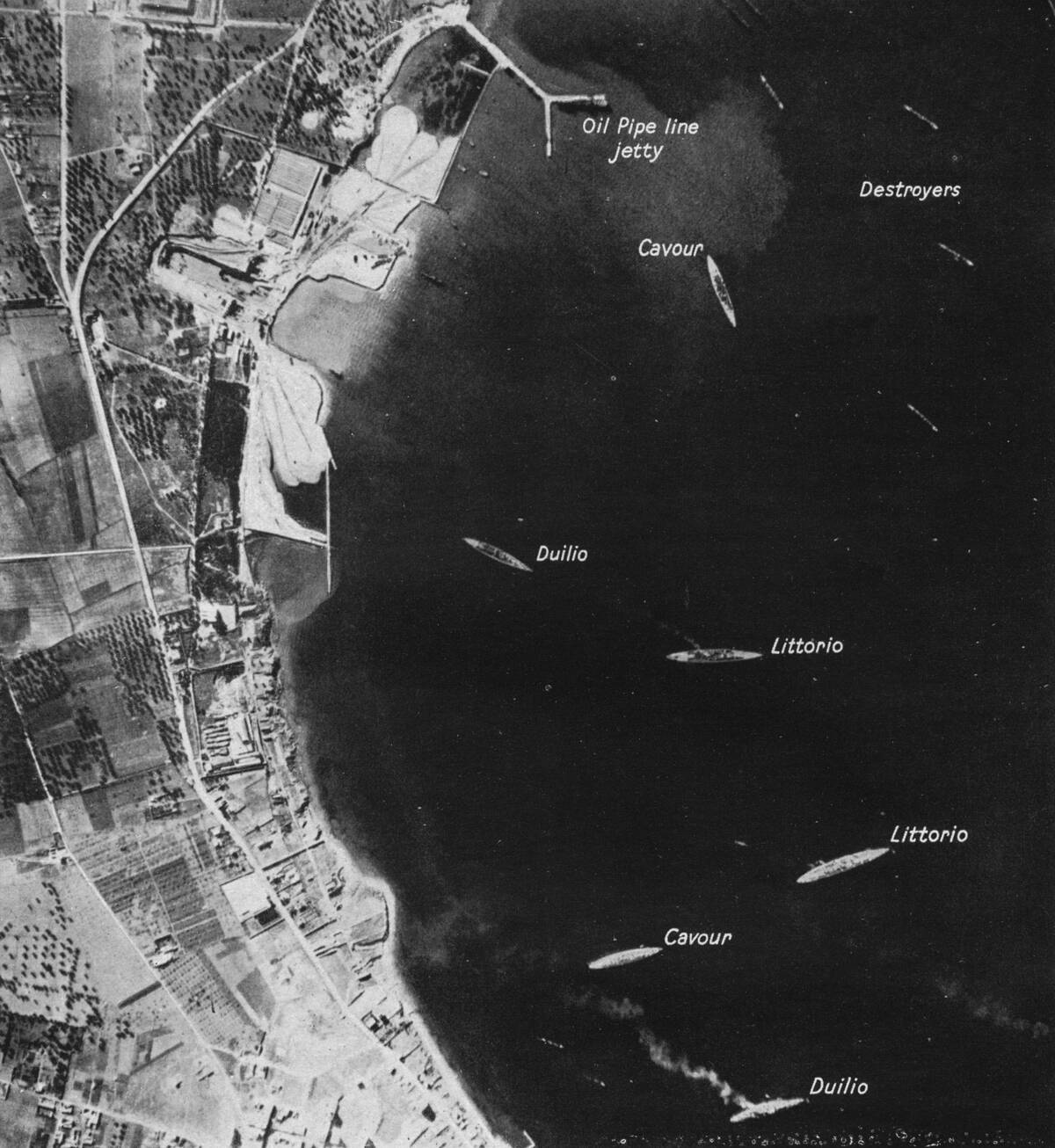

The Battle of Taranto in 1940 was a turning point that showcased the vulnerability of battleships to air attacks. British aircraft from the carrier HMS Illustrious launched a surprise nighttime raid on the Italian fleet, severely damaging three battleships and costing Italy half of its capital ships.
This daring assault demonstrated the effectiveness of carrier-based aircraft and forced navies worldwide to reconsider their reliance on battleships. Taranto highlighted the need for air superiority in modern naval warfare.
Pearl Harbor: A Wake-Up Call for Battleship Advocates
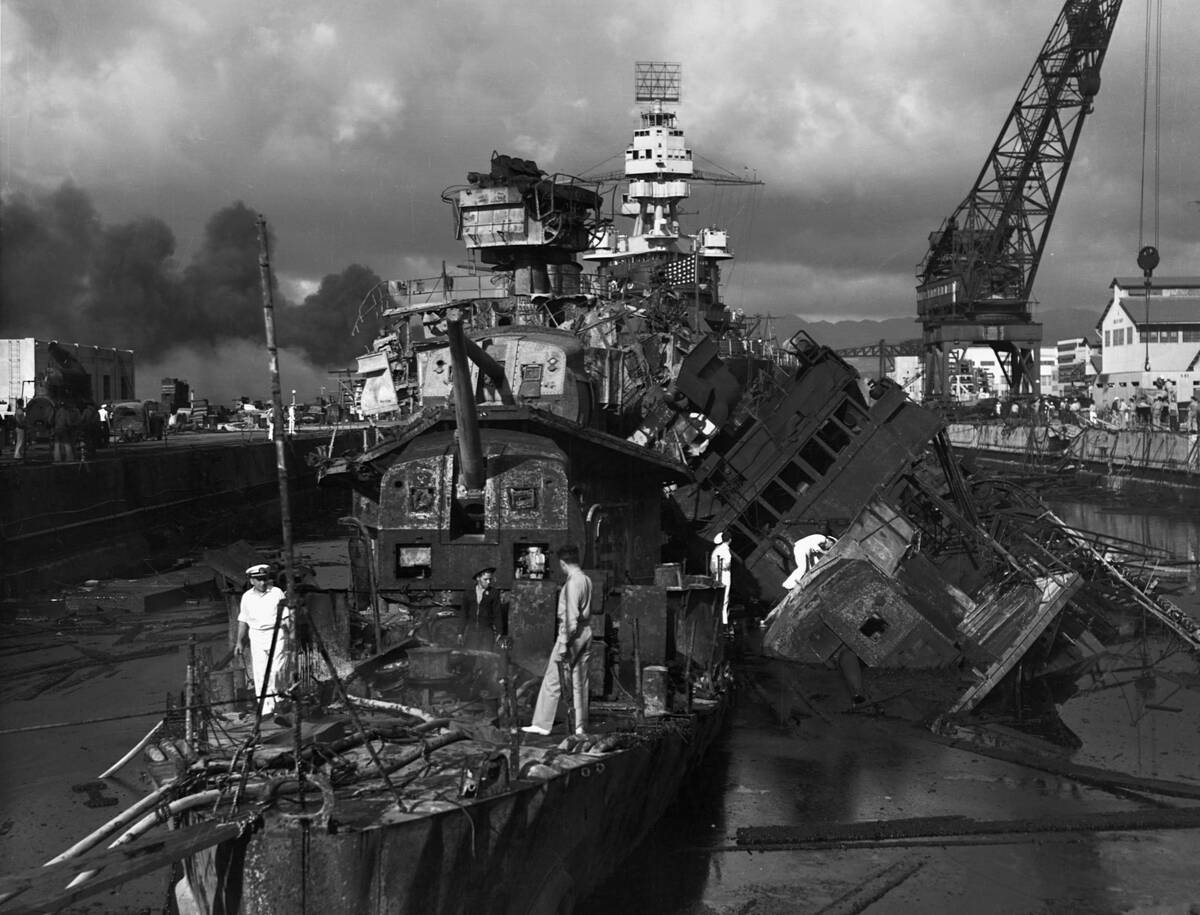

The attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, served as a stark wake-up call for battleship advocates. Japanese aircraft launched from carriers decimated the U.S. Pacific Fleet, sinking or damaging eight battleships.
This devastating blow underscored the battleship’s vulnerability to air attacks and accelerated the shift toward carrier-based warfare. Pearl Harbor was a pivotal moment that reshaped naval strategy and confirmed the ascendancy of air power in naval operations.
Submarines on the Prowl: The Underwater Threat
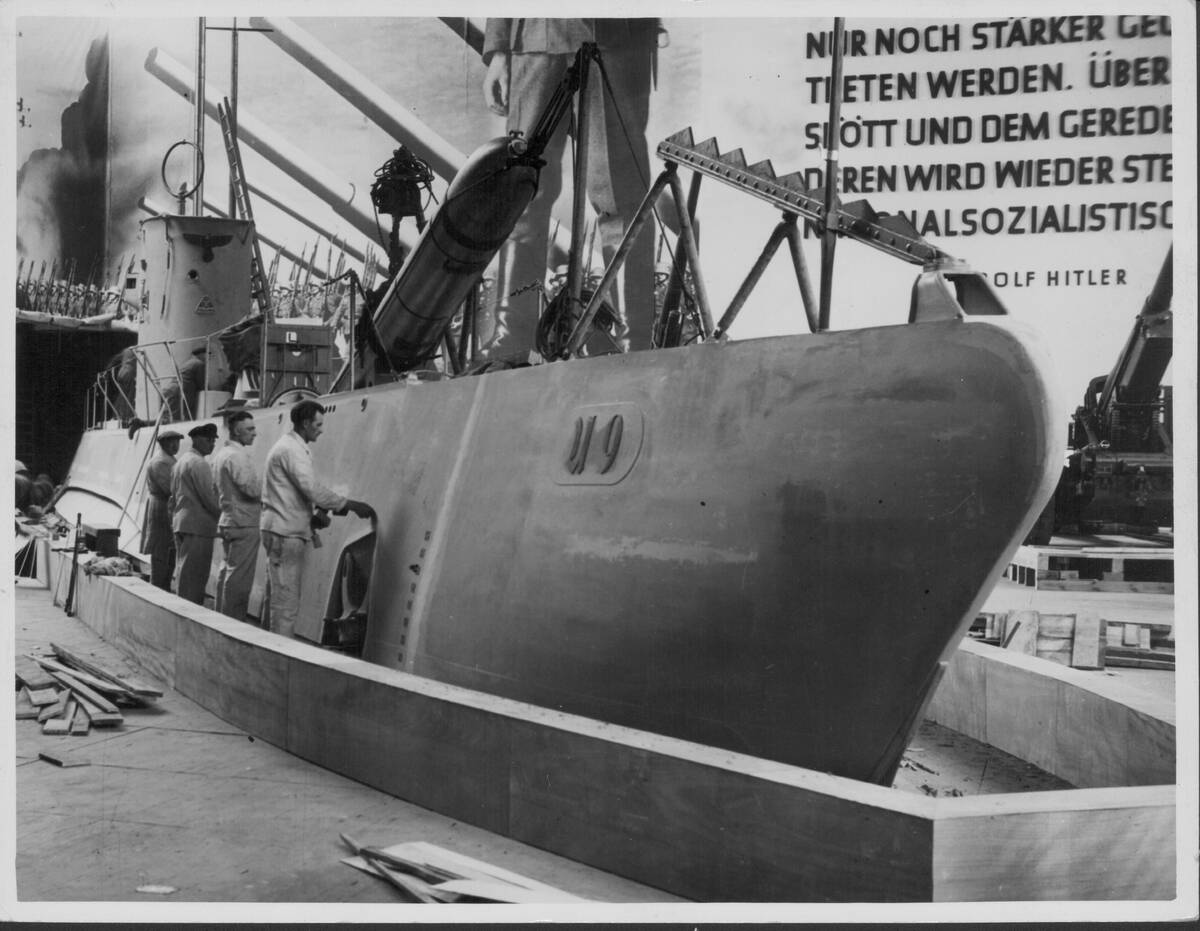
Submarines emerged as a formidable underwater threat, further diminishing the battleship’s role. Able to operate undetected, submarines could launch torpedoes with deadly accuracy, sinking even the most heavily armored ships.
The German U-boat campaigns during both World Wars highlighted the effectiveness of submarine warfare. As stealthy predators, submarines forced navies to develop new tactics and technologies to counter this invisible menace.
The Cost Factor: Economic Burdens of Maintaining Battleships
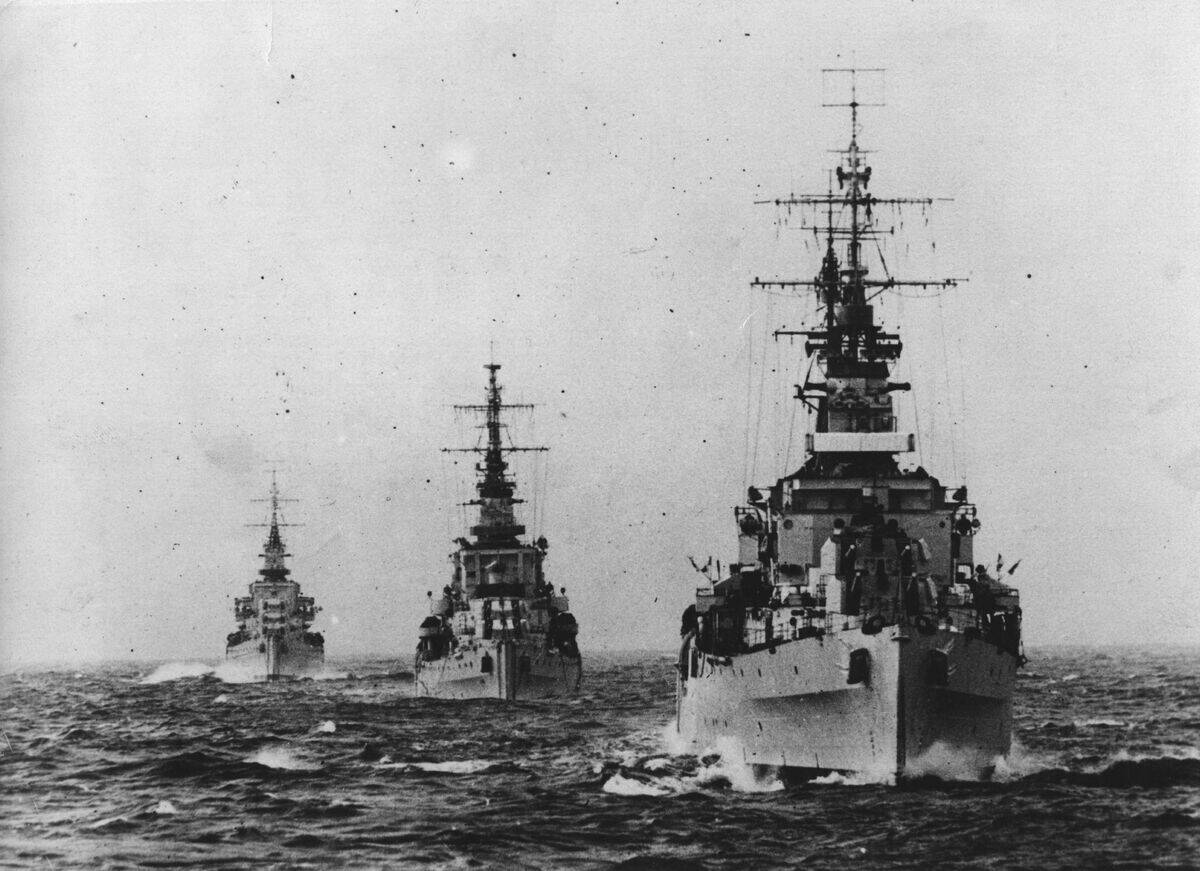
Maintaining a fleet of battleships was an enormous economic burden for any nation. The construction, upkeep, and operational costs of these behemoths were staggering. As budgets tightened, navies found it increasingly difficult to justify the expense.
Aircraft carriers and submarines, while also costly, provided more strategic value for their investment. The economic realities of the post-war world hastened the decline of battleships as nations sought more efficient ways to project power.
World War II Lessons: Adapt or Be Left Behind
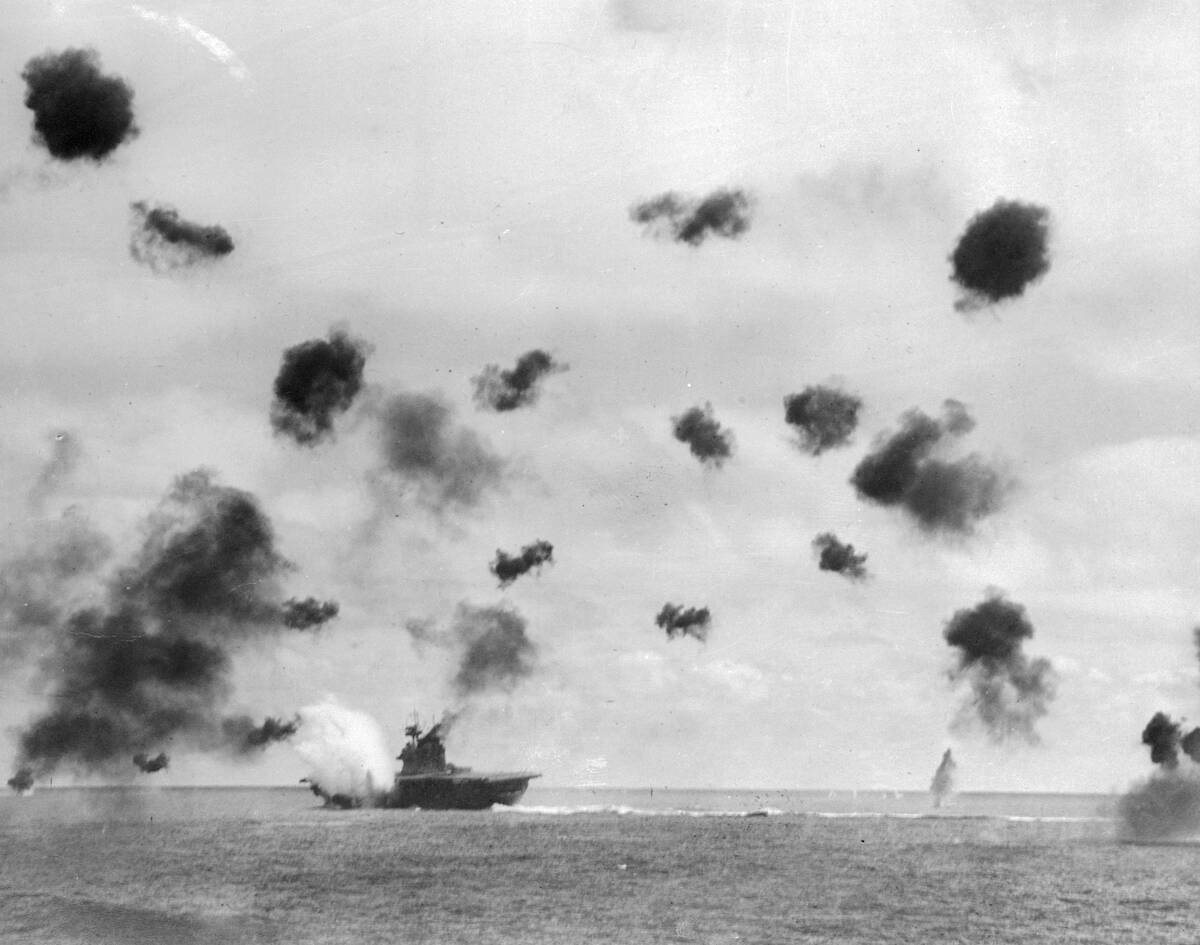

World War II taught invaluable lessons about the need to adapt to new technologies and strategies. Navies that clung to traditional battleship doctrines found themselves struggling against more agile and innovative forces.
The war highlighted the importance of flexibility and the ability to integrate new technologies like radar, sonar, and aircraft into naval operations. Adaptation became key to survival and success in the rapidly evolving landscape of military conflict.
The Dawn of Missile Technology: The New Frontier
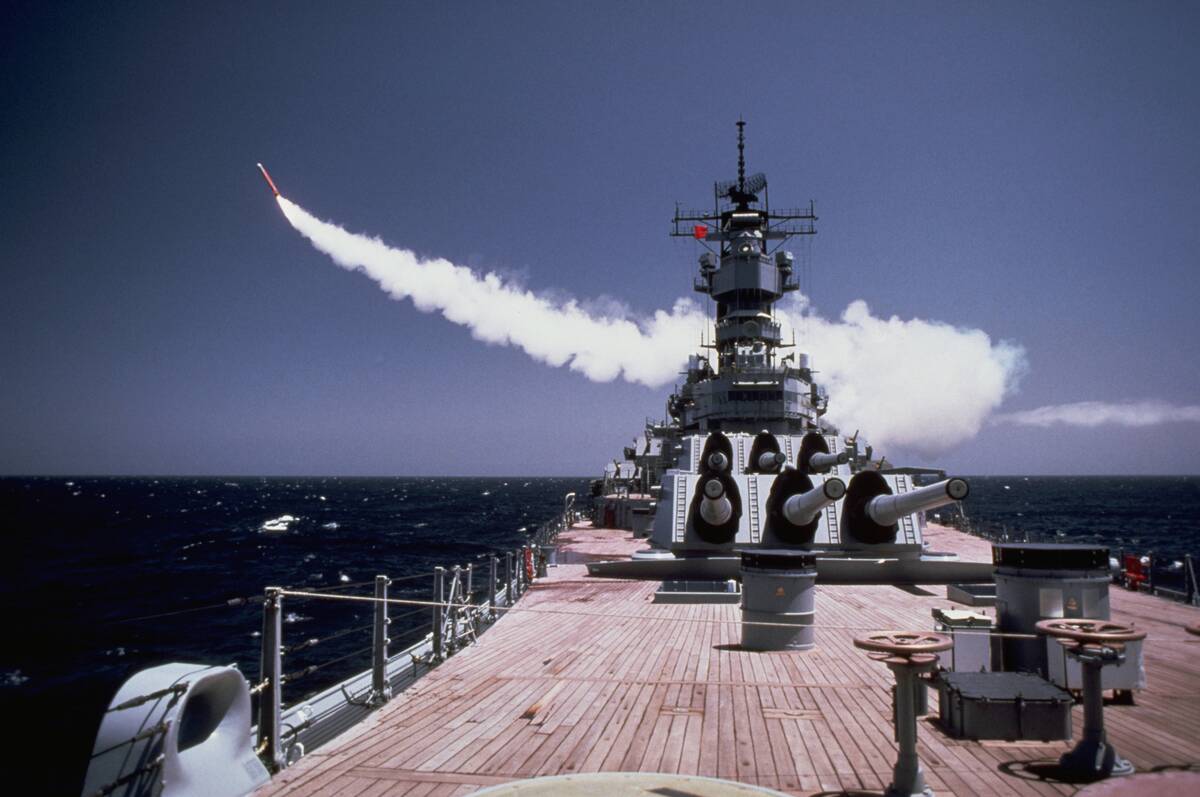

Missile technology ushered in a new frontier that further eclipsed the battleship’s role. Guided missiles offered unparalleled precision and range, capable of striking targets with devastating effect.
The introduction of missile-equipped ships allowed for long-distance engagements without the need for direct line-of-sight. This technological leap reinforced the shift away from large surface combatants, as navies embraced the versatility and effectiveness of missile systems in modern warfare.
The Evolution of Naval Tactics: Beyond Battleships
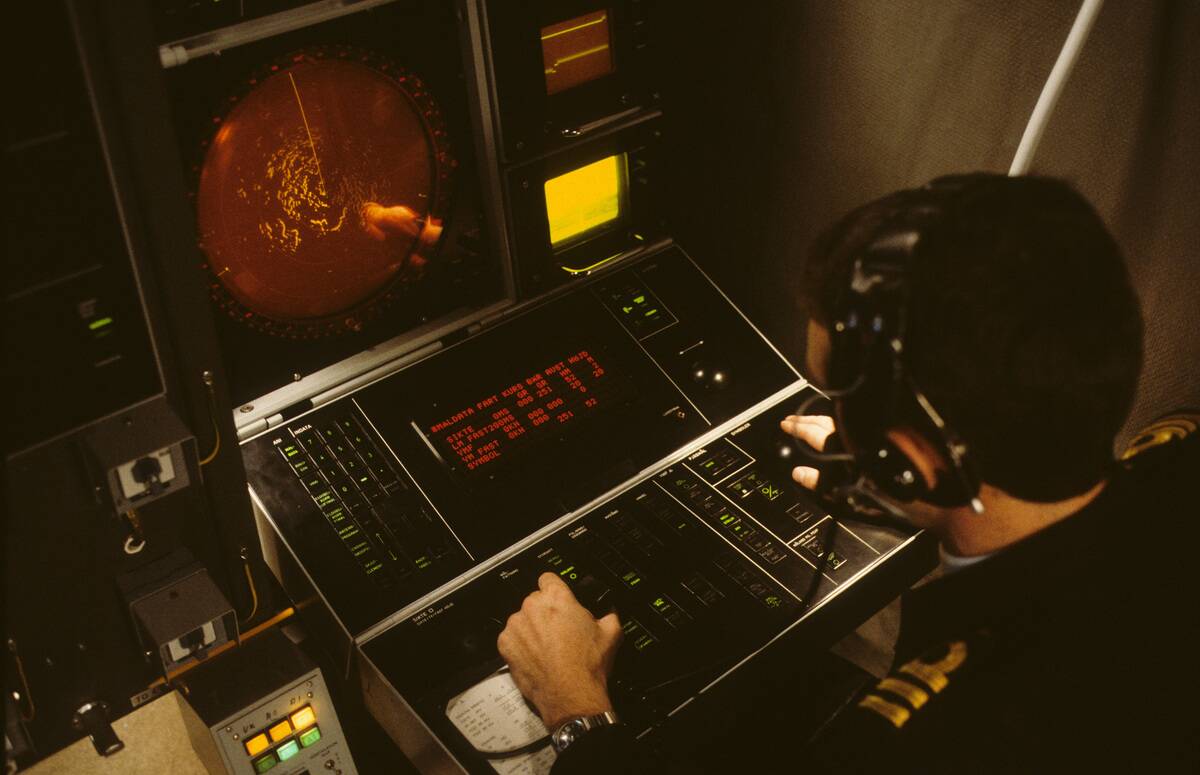
Naval tactics evolved beyond the battleship-centric strategies of old, embracing new technologies and doctrines. The focus shifted toward integrated fleet operations, combining aircraft carriers, submarines, and missile ships into cohesive task forces.
This holistic approach allowed for greater flexibility and adaptability in responding to threats. The evolution of naval tactics underscored the importance of innovation and highlighted the need for navies to remain agile in the face of changing warfare dynamics.



