The background of diplomatic immunity, simplified
Diplomatic immunity might sound like something out of a spy movie, but it’s a real and crucial part of international relations. Designed to allow diplomats to perform their duties without fear of coercion or harassment, this legal protection ensures that diplomats can focus on their work.
It’s a fascinating topic that blends law, history, and a touch of mystery, inviting us to explore how these protections came to be and how they function today.
The History of Diplomatic Immunity

The concept of diplomatic immunity has deep roots in human history, dating back thousands of years. It was born out of necessity, as societies realized that harming or imprisoning envoys could lead to disastrous consequences.
Over time, this understanding evolved, with different civilizations contributing to the framework that governs diplomacy today. From ancient treaties to modern conventions, the protection of diplomats has always been a priority for maintaining peace and communication between states.
Ancient Roots: A Look Back in Time

Diplomatic immunity traces its origins to ancient civilizations like Egypt and Greece, where envoys were considered sacred. The Greeks, for example, granted safe passage to heralds, and violators were often met with severe penalties.
This practice was crucial for maintaining dialogue and preventing conflicts. In ancient India, diplomatic immunity was defined in the Arthashastra, a treatise by Kautilya, emphasizing the need for the protection of messengers to ensure smooth diplomatic exchanges.
The Evolution of Diplomatic Practices

As societies grew more interconnected, the need for standardized diplomatic practices became evident. The Byzantine Empire played a key role in developing early diplomatic protocols, which influenced European practices during the Renaissance.
These protocols laid the groundwork for modern diplomatic immunity, focusing on the safety and privileges of diplomats. Through centuries of evolution, diplomatic practices have adapted to changing geopolitical landscapes, balancing tradition with innovation.
Diplomatic Immunity in the Middle Ages
During the Middle Ages, diplomatic immunity was still evolving, but it was recognized by most European monarchies. Envoys often traveled under the protection of royal decrees, ensuring their safety and freedom.
The concept of diplomatic immunity was further solidified by the Peace of Westphalia in 1648, which ended the Thirty Years’ War and established the principles of modern diplomacy. This period marked a significant step towards codifying the rights and protections of diplomats.
The Birth of Modern Diplomatic Immunity

The 19th century saw the birth of modern diplomatic immunity as nations recognized the need for formal agreements. The Congress of Vienna in 1815 was a pivotal moment, as it established protocols for diplomatic relations that influenced future treaties.
This era laid the foundation for the 20th-century agreements that would further define diplomatic immunity. As global politics became more complex, the need for universally recognized diplomatic protections became increasingly clear.
The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations

The Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations, adopted in 1961, is the cornerstone of modern diplomatic immunity. Ratified by nearly every country, it sets out the rules and privileges for diplomats, ensuring they can perform their duties without interference.
This convention provides a comprehensive framework governing diplomatic conduct, establishing the legal norms that protect diplomats worldwide. It marks a significant milestone in international law, promoting peaceful and cooperative global relations.
Diplomatic Immunity: A Global Standard

Diplomatic immunity has become a global standard, reflecting a shared commitment to maintaining diplomatic channels. Over 190 countries adhere to the principles outlined in the Vienna Convention, demonstrating their dedication to upholding international law.
This widespread acceptance ensures that diplomats can operate effectively across borders, fostering international cooperation. The global standardization of diplomatic immunity is essential for addressing today’s complex international issues, from trade negotiations to crisis management.
Understanding the Legal Framework

The legal framework of diplomatic immunity is intricate, balancing the rights of diplomats with the sovereignty of host countries. It grants diplomats immunity from arrest and prosecution, but also requires them to respect the laws of the host nation.
This delicate balance is maintained through mutual respect and adherence to international conventions. While diplomatic immunity offers significant protections, it also comes with responsibilities, ensuring that diplomats act in accordance with their host country’s regulations.
Who Qualifies for Diplomatic Immunity?

Diplomatic immunity is not just for ambassadors; it extends to various diplomatic staff and their families. This includes embassy officials, consular employees, and even technical staff in some cases.
The level of immunity varies depending on the diplomat’s rank and role, with higher-ranking officials enjoying broader protections. Understanding who qualifies for diplomatic immunity helps clarify the scope of these legal protections and ensures that diplomatic missions function smoothly and securely.
The Privileges and Benefits of Diplomats

Diplomats enjoy a range of privileges, from tax exemptions to inviolability of their residences. These benefits are designed to facilitate their work and protect them from local interference.
Diplomatic bags, for example, are not subject to search, ensuring the secure transmission of official communications. While these privileges are extensive, they are not absolute, and diplomats are expected to respect local laws. This balance of privileges and responsibilities is key to maintaining effective diplomatic relations.
Immunity in Practice: Real-World Examples

Real-world examples of diplomatic immunity highlight its practical applications and occasional controversies. In 2013, the case of Devyani Khobragade, an Indian diplomat in the U.S., sparked debate over the limits of immunity.
Such cases show how diplomatic immunity can sometimes lead to tension between countries. However, they also underscore the importance of clear communication and mutual respect in resolving disputes. These examples remind us that while diplomatic immunity is vital, it must be carefully managed.
Notable Cases and Controversies
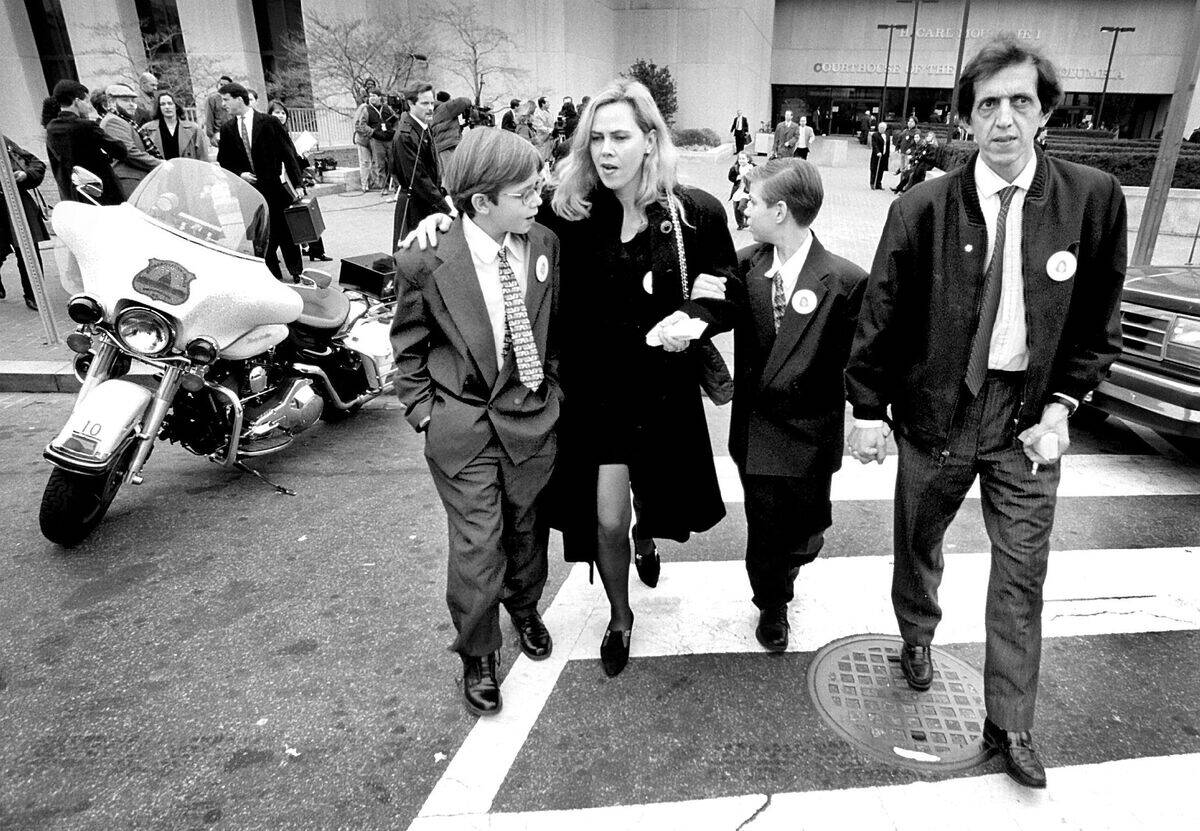

Diplomatic immunity has been at the center of many notable cases, often making headlines worldwide. One of the most infamous cases involved Georgian diplomat Gueorgui Makharadze, whose 1997 car accident in Washington, D.C., resulted in a fatality.
The incident led to public outcry and highlighted the challenges of balancing immunity with accountability. Such controversies illustrate the complexities of diplomatic immunity, prompting discussions on how to uphold justice while maintaining diplomatic norms.
The Role of Diplomats in International Relations

Diplomats play a crucial role in fostering international relations, acting as liaisons between governments. They negotiate treaties, promote peace, and facilitate cooperation on global issues like climate change and security.
Diplomatic immunity enables them to carry out these duties without fear of local interference, ensuring that international dialogue continues smoothly. By building bridges between nations, diplomats contribute to a more interconnected and cooperative world, highlighting the importance of their protected status.
The Impact of Diplomatic Immunity on Society

Diplomatic immunity has a significant impact on society, influencing how countries interact and resolve conflicts. It enables diplomats to engage in delicate negotiations and address international crises without the threat of legal repercussions.
This protection fosters open communication and collaboration, essential for addressing global challenges. While some may view diplomatic immunity as controversial, its role in promoting peace and stability cannot be understated, demonstrating its value in a complex world.
Diplomatic Immunity and the Media

The media often highlights cases of diplomatic immunity, shaping public perception and sparking debate. High-profile incidents can lead to scrutiny and criticism, influencing how diplomatic immunity is viewed by the public.
While media coverage can sometimes sensationalize issues, it also plays a vital role in holding diplomats accountable and ensuring transparency. By bringing attention to diplomatic immunity, the media encourages dialogue on its implications and the need for responsible use of these protections.
Common Misconceptions about Diplomatic Immunity

Diplomatic immunity is often misunderstood, leading to common misconceptions about its scope and application. One prevalent myth is that it allows diplomats to break any law without consequence, which is not true.
While diplomats are protected from prosecution, they are expected to respect local laws and can face expulsion for misconduct. Clarifying these misconceptions helps demystify diplomatic immunity and highlights its role as a tool for facilitating international relations, not evading justice.



