The time weather prediction was kept secret
Long before satellites and supercomputers, humanity turned to the stars, animals, and intuition to predict the weather. Ancient peoples relied on signs from nature and the heavens, combining observation with myth to guide their agricultural and daily activities.
This mystical approach to weather forecasting was a blend of art and belief, setting the stage for the more scientific methods we recognize today.
Ancient Civilizations and Their Weather Predictions

The Babylonians were pioneers in using astronomical observations for weather predictions. They meticulously recorded cloud patterns and celestial events on clay tablets, believing that the sky held secrets to the weather.
Meanwhile, in China, the practice of feng shui incorporated weather predictions to ensure harmony with nature, using wind and water patterns to guide agricultural decisions.
The Role of Shamans and Oracles in Forecasting
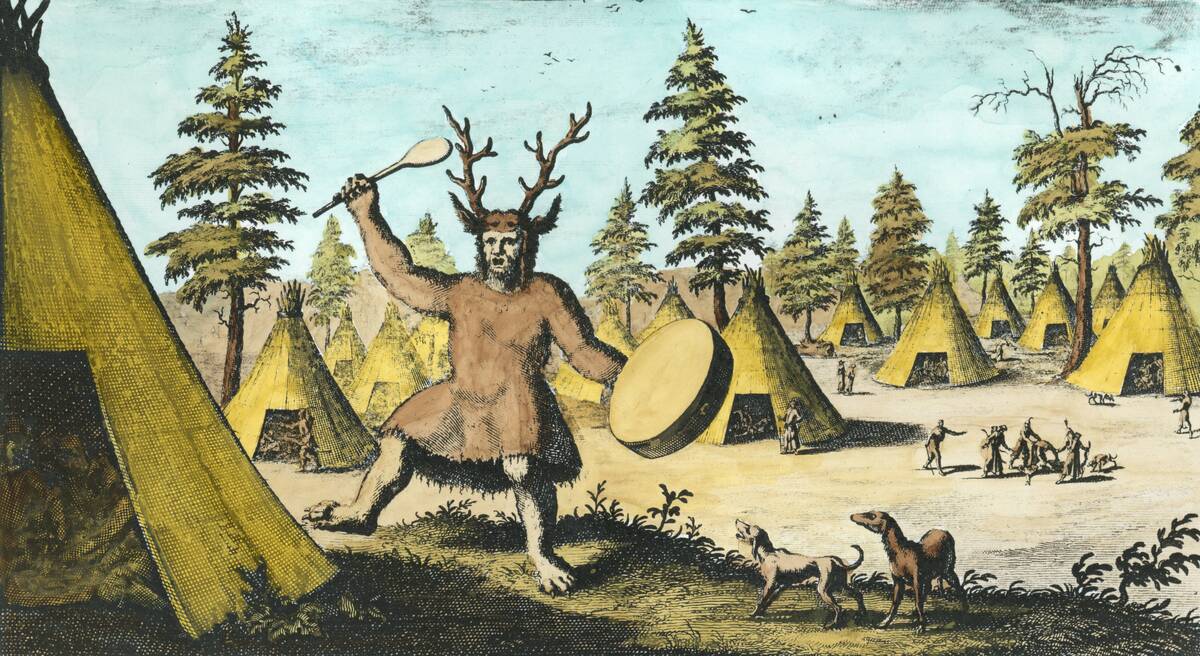

Shamans and oracles played a pivotal role in ancient weather forecasting, acting as intermediaries between the divine and the human.
In many indigenous cultures, shamans used rituals and trance states to interpret nature’s signs, while Greek oracles, such as those at Delphi, were sought for their prophetic insights, often linking weather predictions with divine favor or wrath.
The Curious Case of Weather Witches
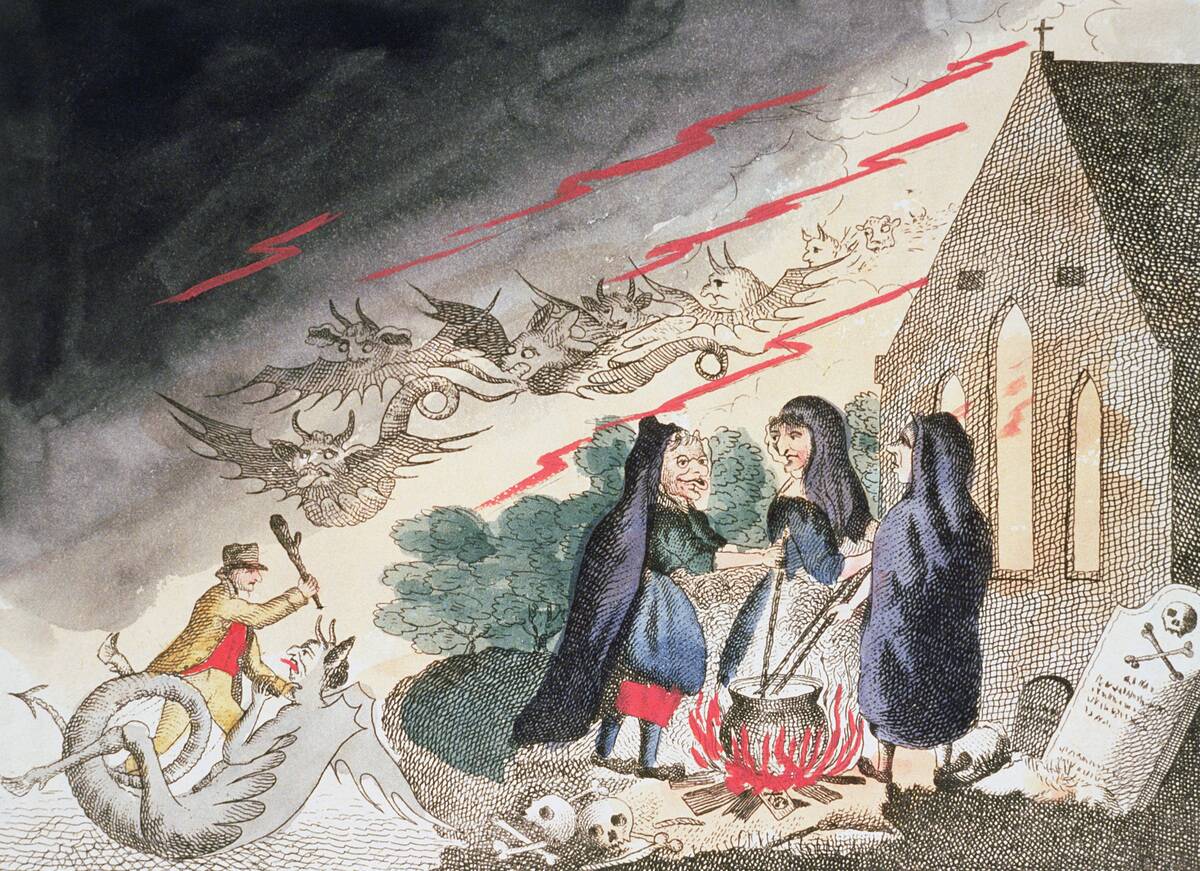

Weather witches, or ‘tempestarii’, were believed to control the weather through magical means. In medieval Europe, these individuals were often blamed for storms and adverse weather that affected crops and livelihoods.
Communities both feared and revered them, sometimes even seeking their services to ensure favorable weather, illustrating a fascinating blend of superstition and survival.
The Church’s Stance on Weather Forecasting
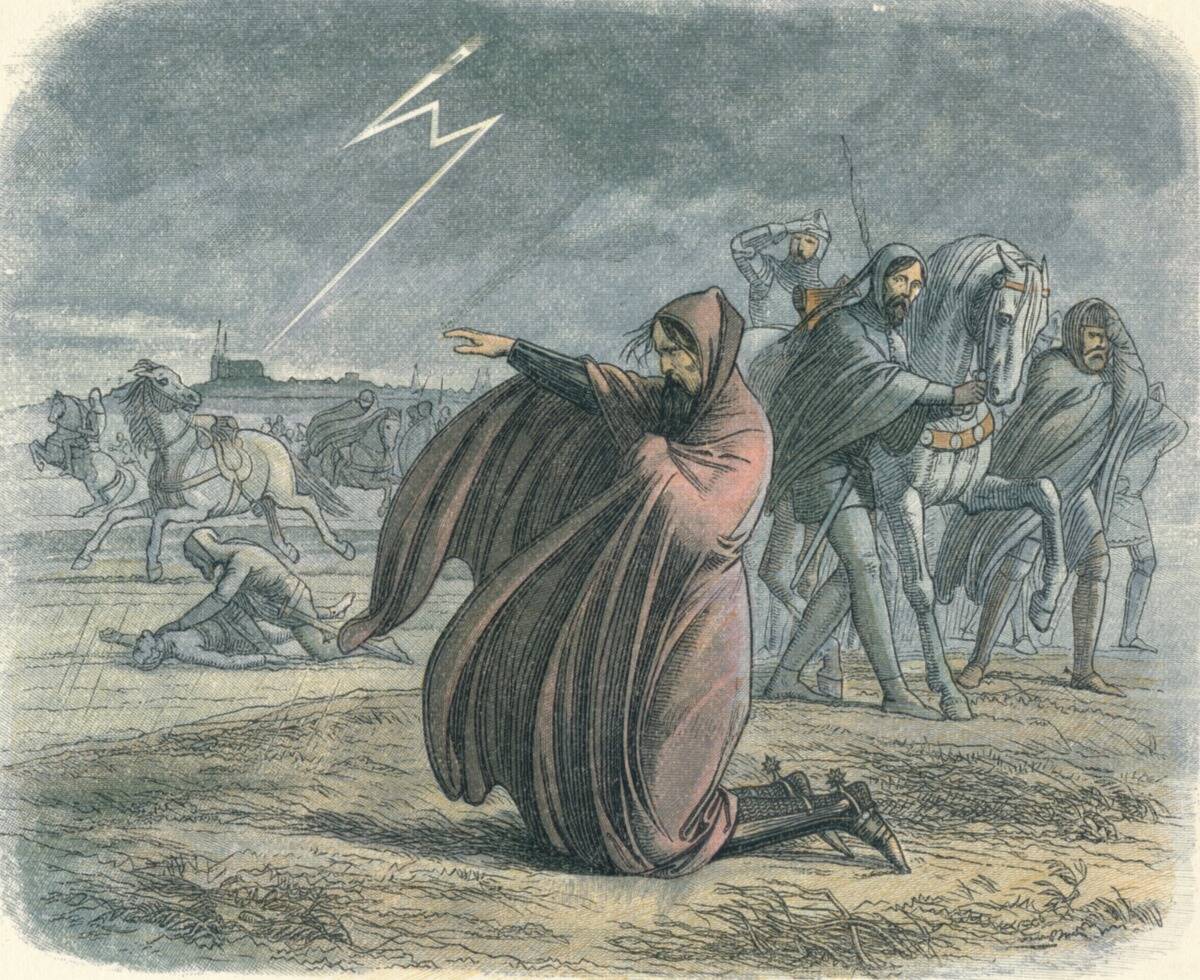

The Church held a complex view on weather forecasting during the medieval period. While some clergy saw it as dabbling in forbidden knowledge, others recognized its practical benefits for agricultural planning.
The tension between viewing weather forecasting as either divine insight or heretical practice mirrored broader conflicts between faith and emerging scientific inquiry, highlighting the era’s struggle with new ideas.
Scientific Revolution: A Shift in Perception

The Scientific Revolution marked a turning point in weather forecasting, as empirical observation began to challenge mystical methods. Figures like Galileo and Newton paved the way for a more systematic approach to understanding natural phenomena, emphasizing observation and experimentation.
This shift laid the groundwork for modern meteorology, as the mysteries of the sky gradually gave way to scientific inquiry.
The Birth of Meteorology as a Science

Meteorology began to emerge as a distinct science in the 17th century, as systematic observations and record-keeping became more common. Pioneers like Edmund Halley contributed to this shift by studying trade winds and monsoons, while the invention of the thermometer and barometer provided tools for precise measurements.
These advancements marked the beginning of a more structured and reliable approach to weather forecasting.
The Tale of Admiral FitzRoy and His Barometer

Admiral Robert FitzRoy, captain of the HMS Beagle, is a key figure in the history of meteorology. He developed the FitzRoy barometer, which became essential for early weather forecasting.
FitzRoy’s work with the Meteorological Department, now the UK’s Met Office, laid the foundation for systematic weather prediction. His barometer enabled sailors and farmers to anticipate weather changes, highlighting the practical application of scientific principles.
Weather Forecasting in the Age of Enlightenment
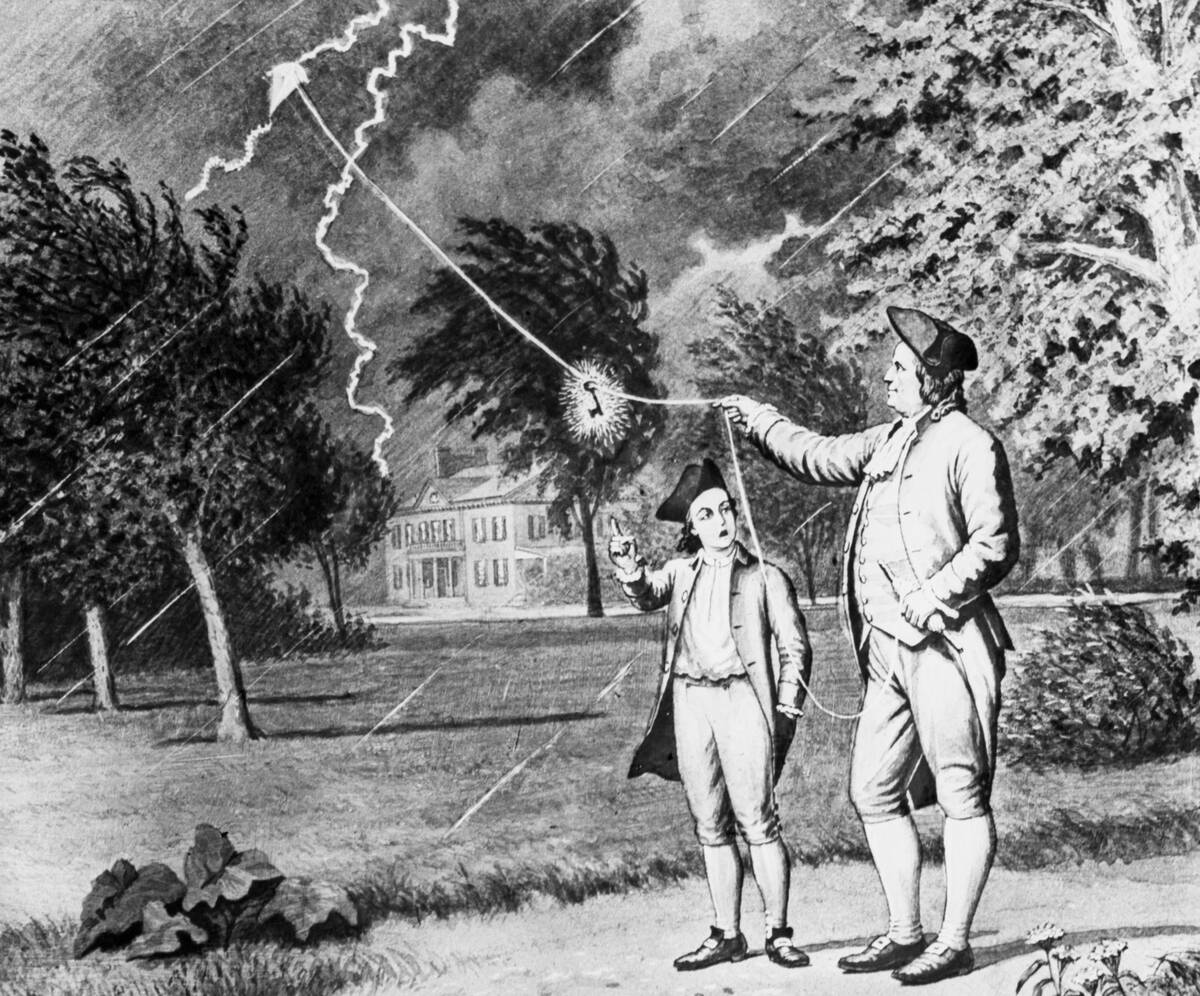

The Age of Enlightenment brought a surge of interest in understanding and predicting weather. Scientists like Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Jefferson made significant contributions, with Franklin’s kite experiment famously demonstrating the electrical nature of lightning.
This era emphasized rationality and empiricism, encouraging the development of more accurate and systematic methods for weather forecasting based on observation and analysis.
The Advent of Weather Instruments and Tools
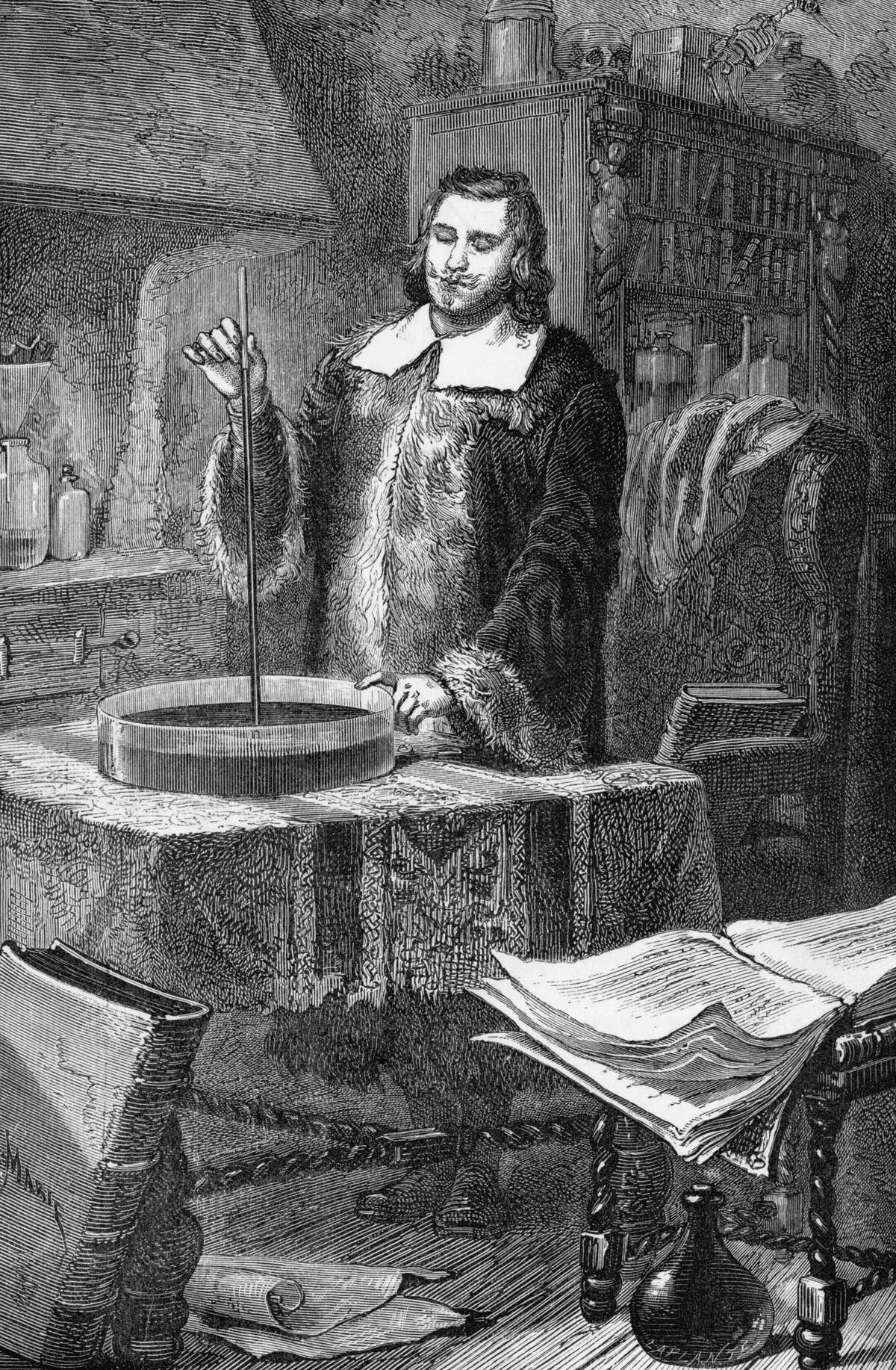

The invention of weather instruments revolutionized forecasting. The thermoscope, invented by Galileo, allowed for precise temperature readings, while Evangelista Torricelli’s barometer measured atmospheric pressure changes.
These tools enabled scientists to gather quantifiable data, moving weather forecasting from an art to a science. The proliferation of these instruments marked a new era in understanding and predicting atmospheric phenomena.
Early Public Reactions to Weather Forecasting

Initially, public reactions to weather forecasting were mixed, with skepticism and curiosity in equal measure. Many people were accustomed to traditional methods and viewed scientific predictions with suspicion.
However, as forecasts became more accurate and useful, especially for farmers and sailors, public trust grew. This shift in perception underscored the growing influence of science in everyday life.
How Newspapers Changed the Game for Forecasting

The advent of newspapers in the 19th century transformed weather forecasting by making it widely accessible. Newspapers began publishing regular forecasts, reaching a broad audience and integrating weather predictions into daily life.
This development not only informed the public but also increased pressure on forecasters to improve accuracy, spurring advancements in meteorological science and technology.
The Rise of Professional Weather Services
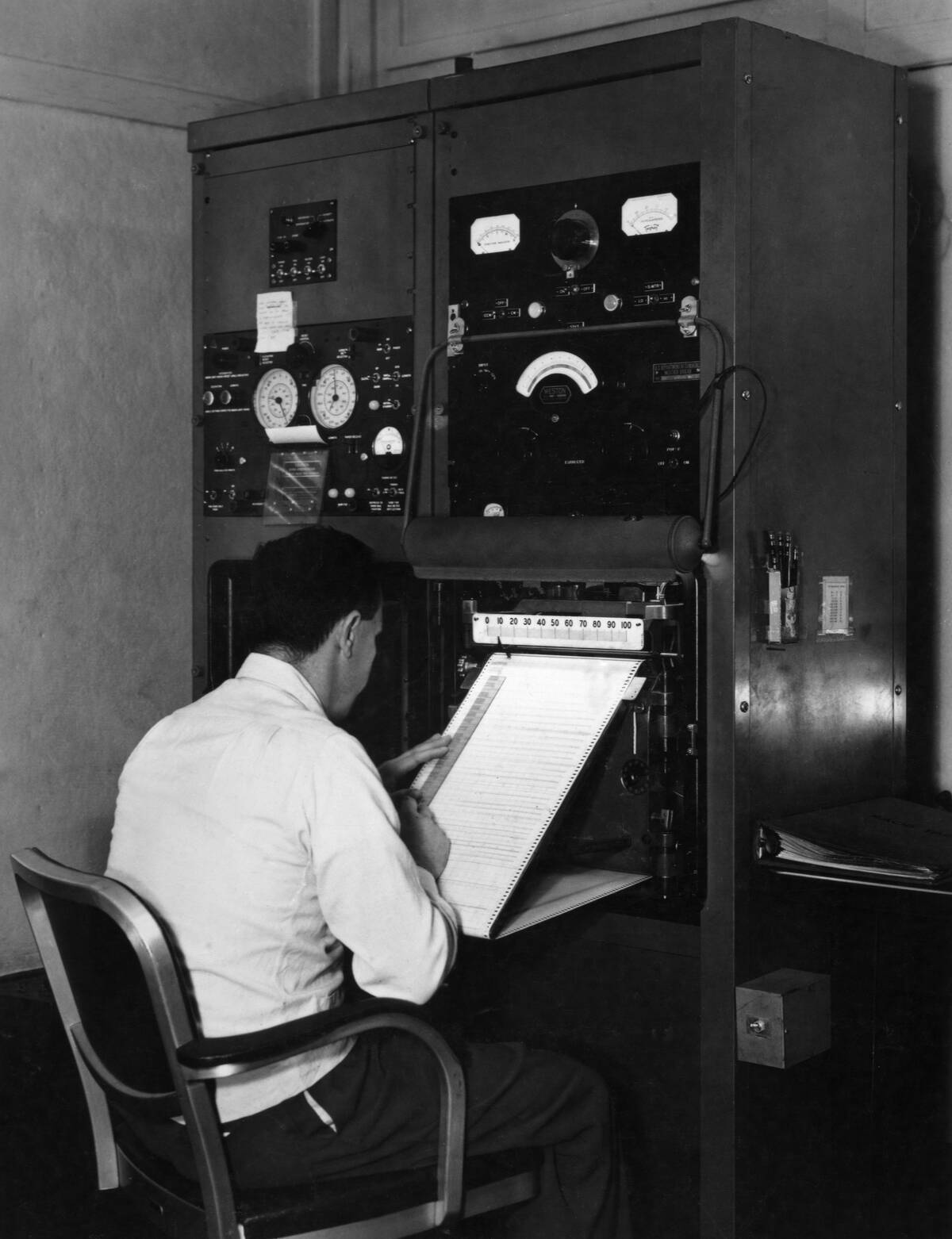

Professional weather services emerged in the late 1800s, with organizations like the United States Weather Bureau setting a standard for systematic data collection and forecasting.
These services employed trained meteorologists, utilizing telegraph networks for rapid communication of data. This professionalization facilitated more accurate and timely forecasts, cementing weather prediction as an essential public service.
Television: Bringing Weather Forecasting to the Masses

Television revolutionized weather forecasting by bringing it directly into living rooms. The visual medium allowed for dynamic presentations, with maps and animations making complex data understandable.
Weather personalities became household names, adding a new dimension of engagement and trust. This accessibility transformed public interaction with weather forecasts, making them an integral part of daily routines.
The Digital Era: Weather Apps and Instant Access

The digital era has made weather forecasting more immediate and personal. Weather apps provide real-time updates, personalized alerts, and detailed forecasts at our fingertips. This instant access empowers individuals to make informed decisions, whether planning a trip or preparing for extreme weather.
The convenience and accuracy of digital forecasting reflect the culmination of centuries of meteorological advancements.
From Forbidden Knowledge to Everyday Necessity
Weather forecasting has come a long way from its mystical and controversial origins. Once seen as forbidden knowledge, it is now a vital part of daily life, influencing everything from agriculture to global travel.
The evolution of weather prediction highlights humanity’s relentless quest for understanding and adapting to the natural world, transforming once arcane practices into indispensable tools for modern living.



