15 Photos revealing ancient trade routes across empires
Trade routes have long been the lifelines of civilizations, weaving intricate networks across continents. These ancient pathways weren’t just about commerce; they were conduits of culture, innovation, and ideas.
With goods like spices, silks, and precious metals, they connected distant lands, fostering interactions that shaped the course of history. Let’s embark on a journey through time to explore how these routes transformed societies and left a lasting legacy.
The Mysterious Beginnings of Early Commerce
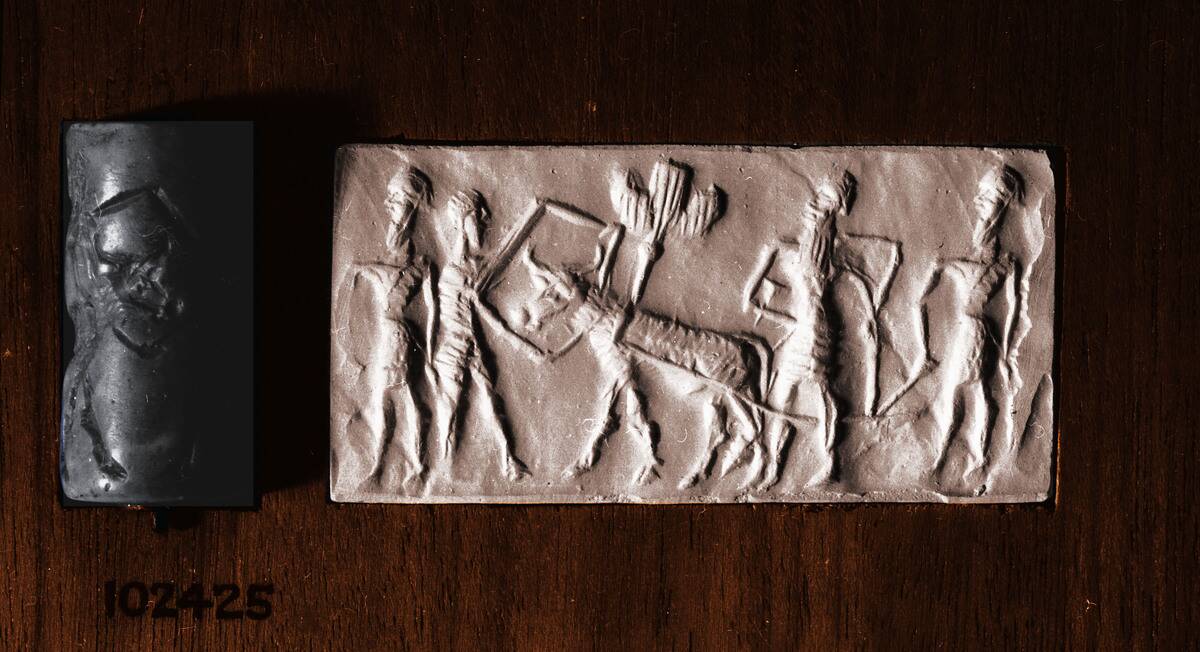

The origins of trade date back to prehistoric times, when humans first began exchanging goods and services. Early commerce was often conducted through bartering, with items like obsidian and flint being the currency of choice.
As societies grew, so did their need for more structured trade systems. This led to the development of the earliest known trade routes, which facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas between emerging cultures.
Ancient Civilizations: More Connected Than You Think
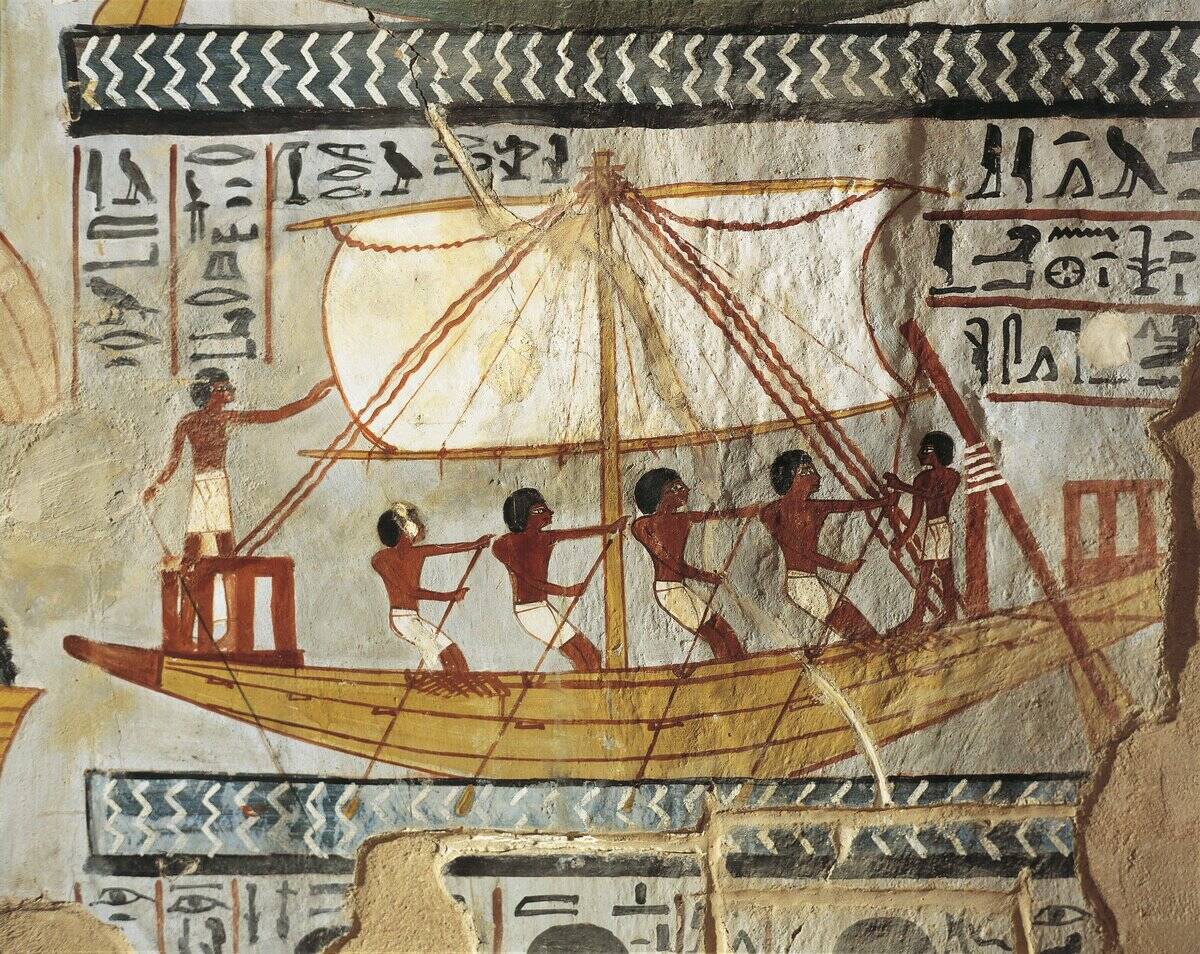

Far from being isolated, ancient civilizations were intricately linked through trade routes. The Egyptians traded with the Levantine coast, while the Mesopotamians exchanged goods with the Indus Valley.
These connections allowed for the transfer of not just goods, but also technology and knowledge. The spread of agricultural techniques, writing systems, and even religious beliefs can often be traced back to these early trade interactions.
The Silk Road: A Highway of History

The Silk Road is perhaps the most famous of all ancient trade routes, stretching over 4,000 miles from China to the Mediterranean. It wasn’t just a single road; rather, it was a network of routes that facilitated the exchange of goods, culture, and ideas.
Along this path, silk, spices, and tea traveled west, while wool, gold, and silver moved east. The Silk Road was instrumental in connecting the East and West, leaving a profound impact on the civilizations it touched.
Spices, Silks, and Silver: What Was Traded?

The commodities exchanged along ancient trade routes were as diverse as the cultures involved. Spices like cinnamon and pepper were highly prized, not just for flavoring food but also for their preservative qualities.
Silk, a luxurious fabric from China, was a major export, while silver and gold were universally valued for their scarcity and beauty. These items fueled economies and created a demand that encouraged further exploration and trade.
Navigating the Seas: The Maritime Silk Route
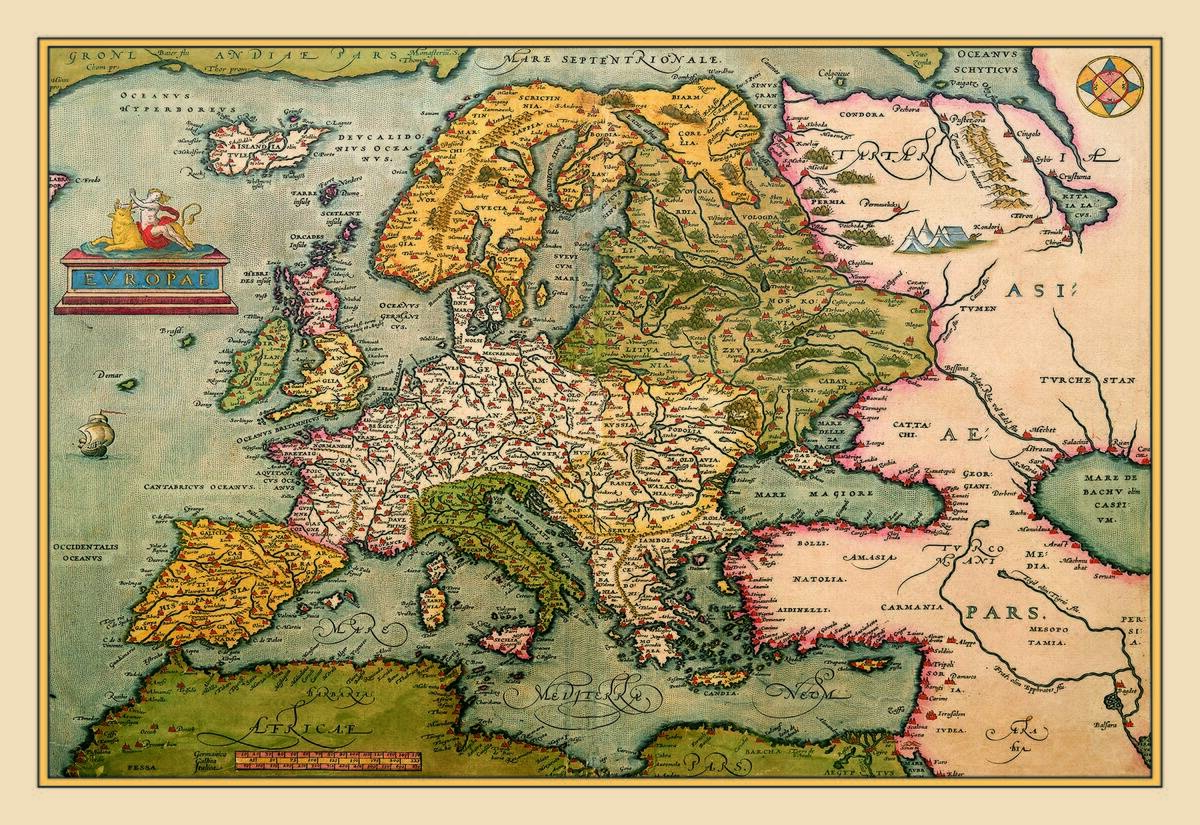
While the Silk Road is often associated with overland trade, the Maritime Silk Route played an equally crucial role. This sea route connected China, Southeast Asia, India, Arabia, and the East African coast.
Ships laden with silk, ceramics, and spices sailed these waters, taking advantage of the monsoon winds to facilitate travel. The Maritime Silk Route not only promoted trade but also encouraged cultural exchanges, influencing the art, architecture, and cuisine of the regions it touched.
The Role of the Camel Caravan in Desert Trade
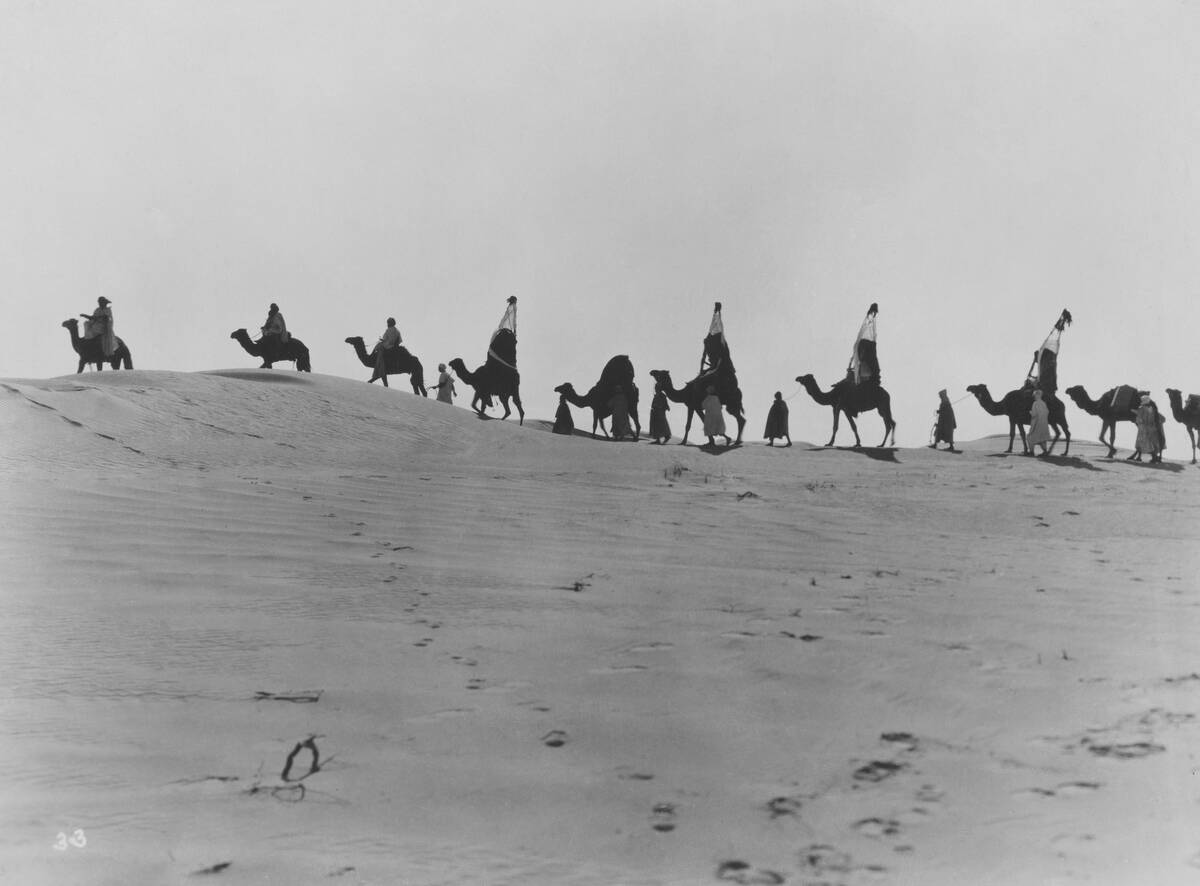

In the vast deserts of the Middle East and North Africa, the camel caravan was king. These hardy animals could travel long distances without water, making them ideal for transporting goods across arid regions.
Caravans often carried salt, gold, and textiles, linking sub-Saharan Africa with the Mediterranean and beyond. The camel caravan was essential in sustaining desert trade routes and helped facilitate the movement of goods, people, and ideas.
The Influence of Trade on Cultural Exchange

Trade routes were more than just conduits for goods; they were channels for cultural exchange. As merchants traveled, they brought with them stories, art, and religious beliefs. This exchange led to the blending of cultures, with elements of one civilization influencing another.
For example, the spread of Buddhism from India to China and beyond was facilitated by these routes, leaving a lasting impact on the spiritual and cultural landscapes of Asia.
How Trade Routes Shaped Ancient Economies

The economic impact of ancient trade routes was profound. They stimulated local economies by creating demand for exotic goods and encouraging production. Cities along these routes often flourished, becoming bustling centers of commerce and culture.
Taxing trade goods was a significant source of revenue for many empires, and control over key trade routes could determine the rise or fall of a civilization. Trade was a driving force behind economic growth and development in the ancient world.
Archaeological Evidence: Uncovering Trade Route Artifacts

Archaeologists have uncovered a wealth of artifacts that shed light on ancient trade routes. The discovery of Roman coins in India, Chinese silk in Egypt, and Persian pottery in Southeast Asia demonstrates the extensive reach of these networks.
These artifacts provide valuable insights into the goods that were traded and the interactions between different cultures. They also help historians piece together the complexities of ancient trade and its influence on the world.
The Power of the Monsoon Winds in Maritime Trade
The monsoon winds were a critical factor in the success of maritime trade routes. These seasonal winds allowed ships to sail from the Arabian Peninsula to India and Southeast Asia with relative ease.
By timing their voyages with the monsoons, traders could ensure faster and safer journeys. This natural phenomenon not only facilitated trade but also played a vital role in the cultural and economic exchanges that occurred along the Maritime Silk Route.
Trade Routes: The Ancient Internet

In many ways, ancient trade routes functioned like the internet of their time. They connected distant parts of the world, enabling the flow of information, ideas, and innovations. Just as the internet has transformed modern society, these routes transformed ancient civilizations.
They allowed for the rapid dissemination of new technologies and concepts, from papermaking to metallurgy, shaping the development of societies and laying the groundwork for future advancements.
The Roman Empire’s Far-Reaching Trade Connections

The Roman Empire was at the heart of a vast network of trade routes that spanned Europe, Asia, and Africa. Roman roads facilitated the movement of goods like olive oil, wine, and grain, while luxury items such as silk and spices flowed into the empire from the East.
This extensive trade network helped Rome to maintain its dominance and provided the resources needed to support its sprawling territories and burgeoning population.
The Impact of Trade on Language and Communication
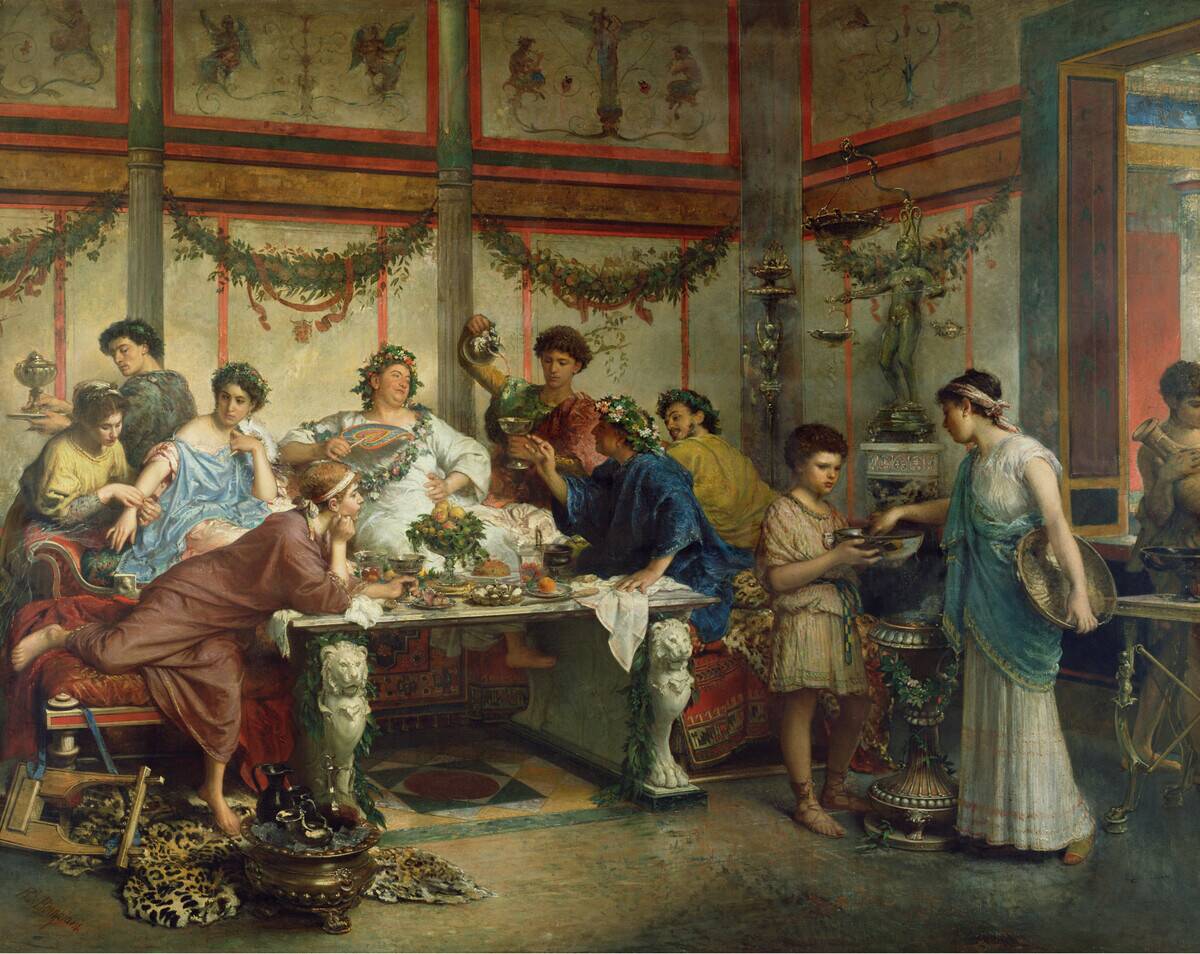

Trade routes not only facilitated economic and cultural exchanges but also impacted language and communication. As merchants interacted with people from different regions, they developed pidgins and lingua francas to facilitate trade.
These simplified languages allowed for basic communication and helped to overcome language barriers. Over time, some of these trade languages evolved into fully-fledged languages, leaving a lasting mark on the linguistic landscape of the areas they touched.
How Religion Spread Along Trade Routes
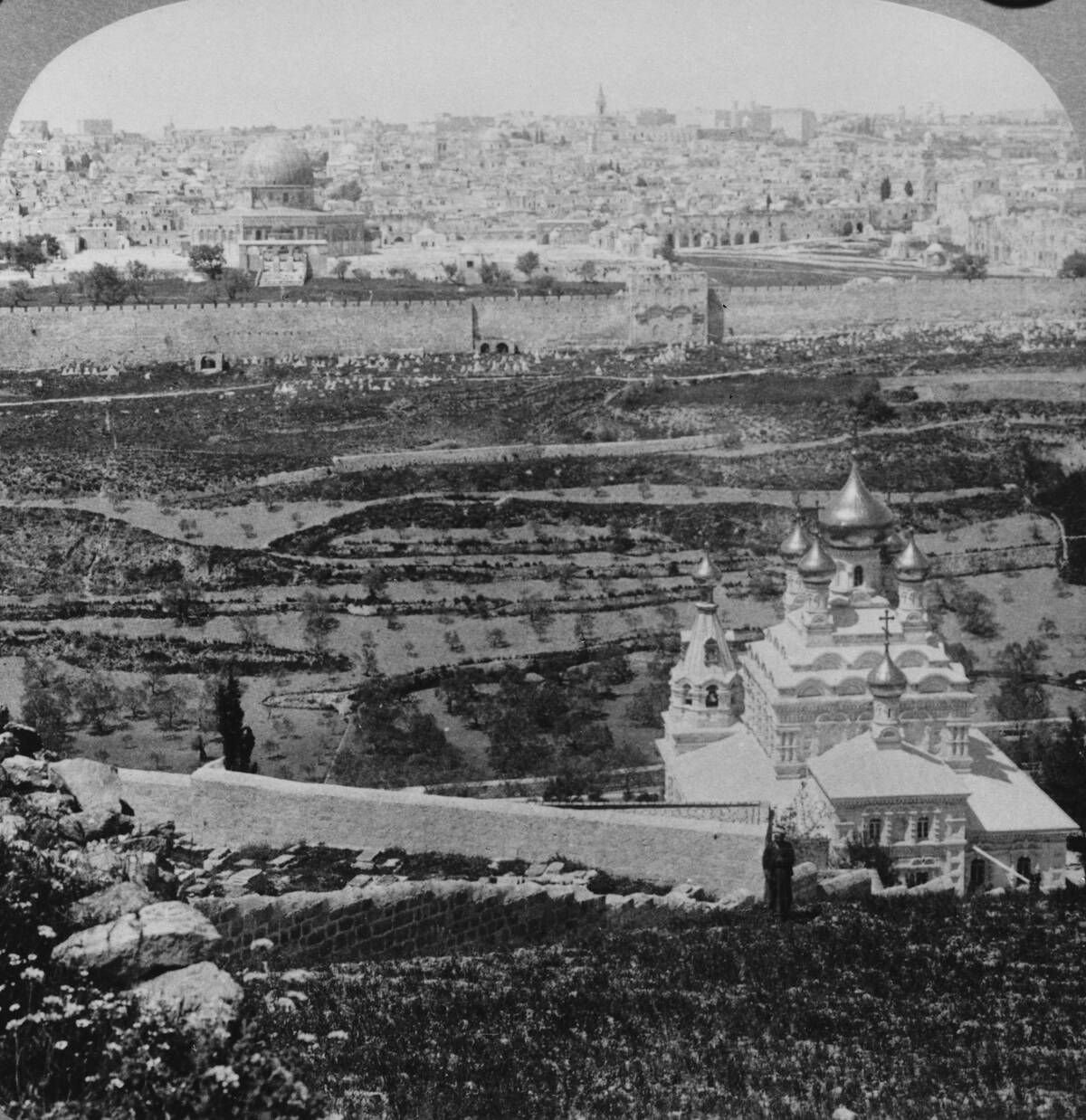

Religions often spread along trade routes, carried by merchants and travelers. Buddhism, for example, spread from India to Central Asia and China via the Silk Road. Similarly, Islam expanded through trade networks into Africa, Southeast Asia, and beyond.
These spiritual exchanges not only introduced new beliefs to different regions but also encouraged the blending of religious practices, leading to the development of new, syncretic traditions.
The Decline and Legacy of Ancient Trade Routes

Many ancient trade routes eventually declined due to various factors, such as the rise of new trade networks, changes in political power, and shifts in demand for goods. However, their legacy endures, as they laid the groundwork for modern global trade.
The routes fostered cultural exchanges that have left a lasting impact on art, technology, and society. Even today, the echoes of these ancient pathways can be seen in the interconnectedness of our modern world.



