16 Photos of weather patterns science can’t explain
Welcome to the fascinating world of weather phenomena, where science and mystery intertwine. From mesmerizing light shows in the sky to peculiar stones that seem to move on their own, weather phenomena captivate our imagination.
Whether you’re a weather enthusiast or simply curious, these natural occurrences offer a glimpse into the dynamic and often unpredictable nature of our planet’s atmosphere. Join us as we explore some of the most intriguing weather phenomena across the globe.
A Brief History of Weather Prediction: From Folklore to Science

Long before modern meteorology, people relied on folklore and observation to predict the weather. Farmers looked to the behavior of animals and the color of the sky to forecast conditions, while sayings like “Red sky at night, sailor’s delight” offered guidance.
It wasn’t until the 19th century that scientific methods began to transform weather prediction. The invention of the telegraph and development of the barometer enabled more accurate forecasts, paving the way for the sophisticated models we use today.
The Bermuda Triangle: A Hotspot for Unpredictable Storms
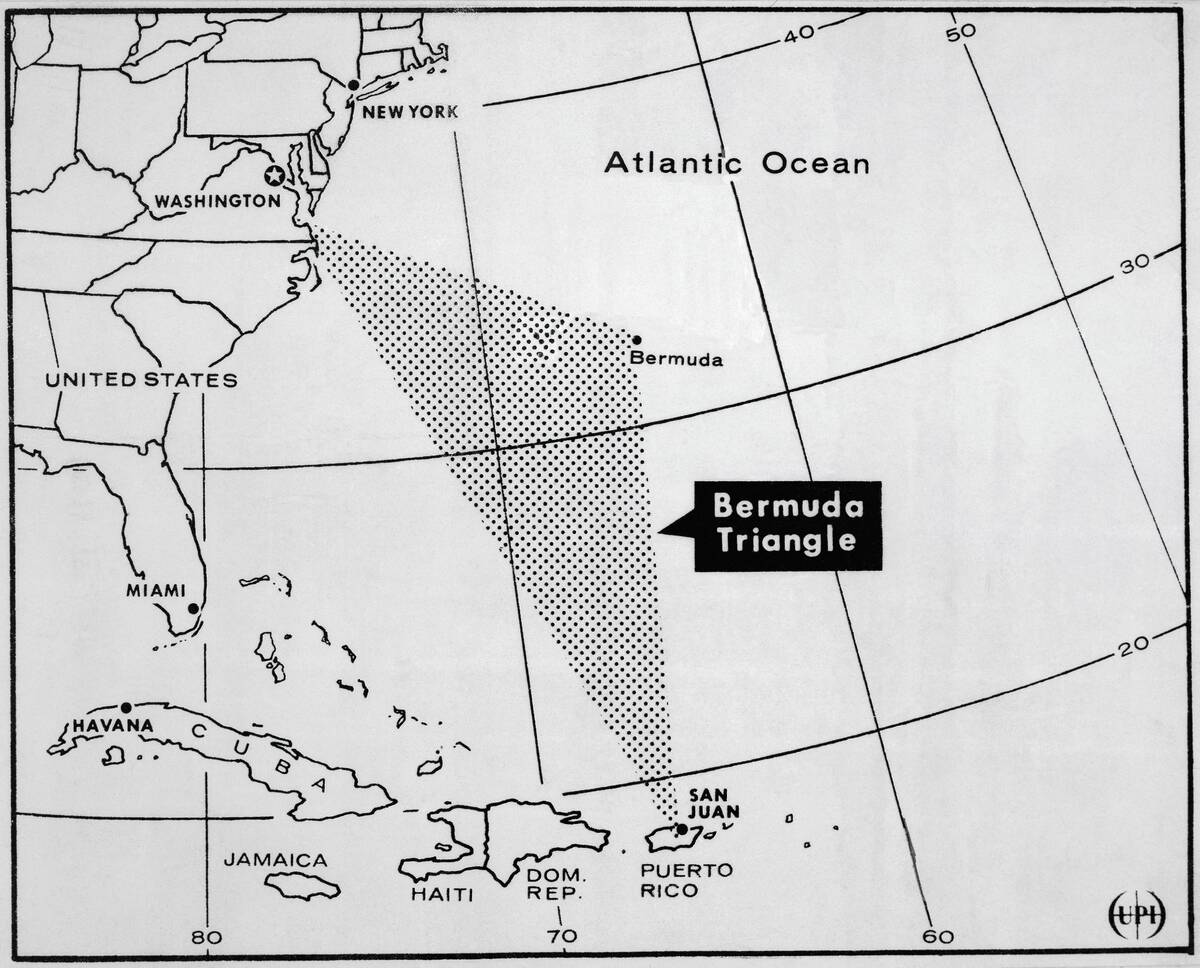
The Bermuda Triangle, a region in the North Atlantic Ocean, has long been associated with mysterious disappearances and unpredictable storms. Scientists have proposed various theories to explain the area’s volatile weather, including the presence of underwater methane hydrates and powerful Gulf Stream currents.
While many myths surround the Bermuda Triangle, it’s clear that the unique geography and climate of the region contribute to its reputation as a hotspot for sudden and severe weather changes.
Ball Lightning: The Electrifying Mystery

Ball lightning is one of the most enigmatic weather phenomena, often described as glowing, spherical objects that appear during thunderstorms. Although reports of ball lightning date back centuries, its elusive nature has made it difficult to study.
Recent theories suggest that it may be caused by the vaporization of silicon in the soil, resulting in a floating ball of plasma. While there is still much to learn, ball lightning continues to fascinate scientists and observers alike with its unpredictable and transient nature.
The Great Red Spot: Jupiter’s Eternal Storm
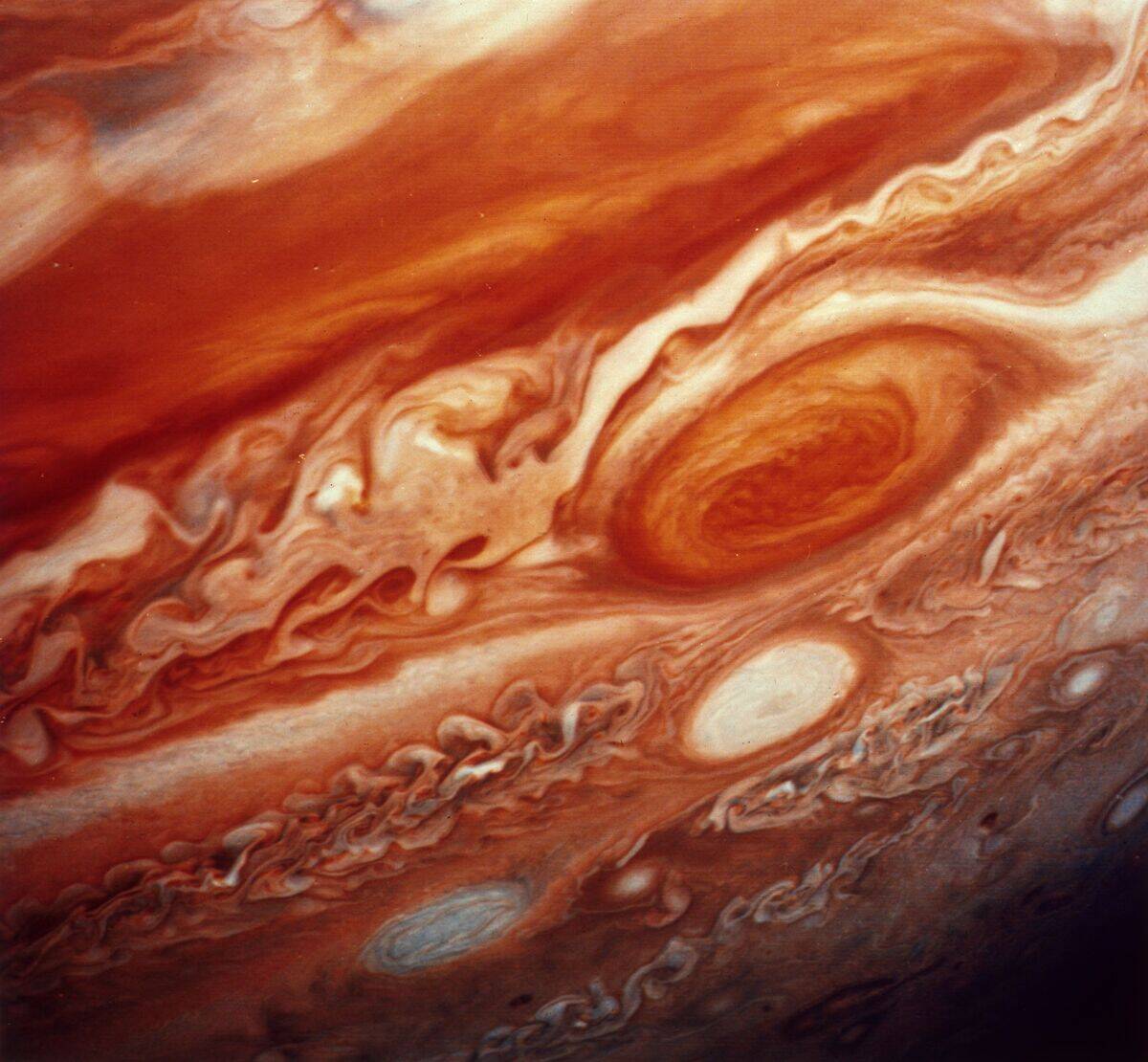

The Great Red Spot on Jupiter is an immense storm, larger than Earth, that has raged for at least 350 years. This persistent high-pressure region rotates counterclockwise and is characterized by its reddish hue, believed to be caused by chemical reactions in the planet’s atmosphere.
Despite its longevity, the storm is slowly shrinking, and scientists are eager to understand its dynamics. By studying the Great Red Spot, researchers hope to gain insights into atmospheric processes both on Jupiter and Earth.
Earth’s Wandering Poles and Their Climatic Impact
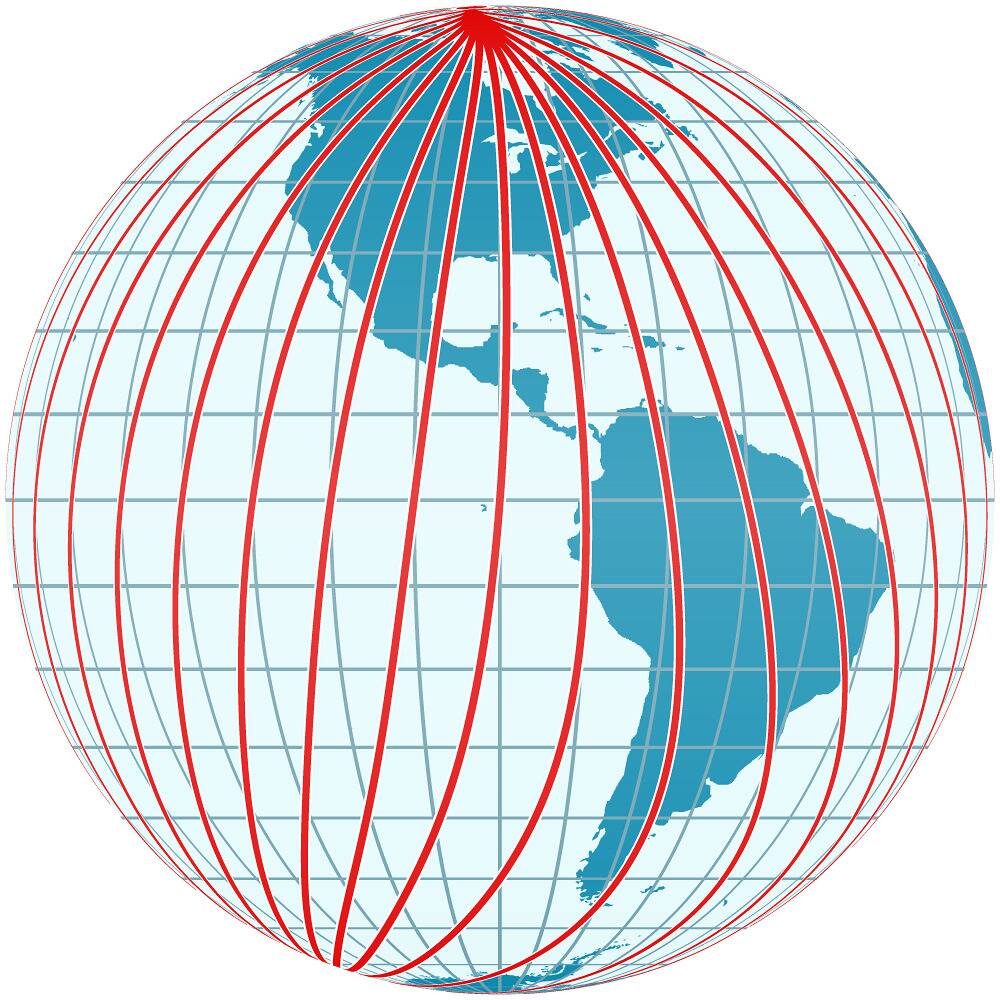
The Earth’s magnetic poles are not fixed; they wander over time due to changes in the planet’s core. This phenomenon, known as geomagnetic secular variation, could influence climate patterns by altering the distribution of solar radiation.
While a full pole reversal takes thousands of years, even small shifts can impact weather systems. Understanding these movements helps scientists predict changes in climate and prepare for potential disruptions in navigation systems that rely on magnetic fields.
The Anomalous Weather of the Sahara Desert
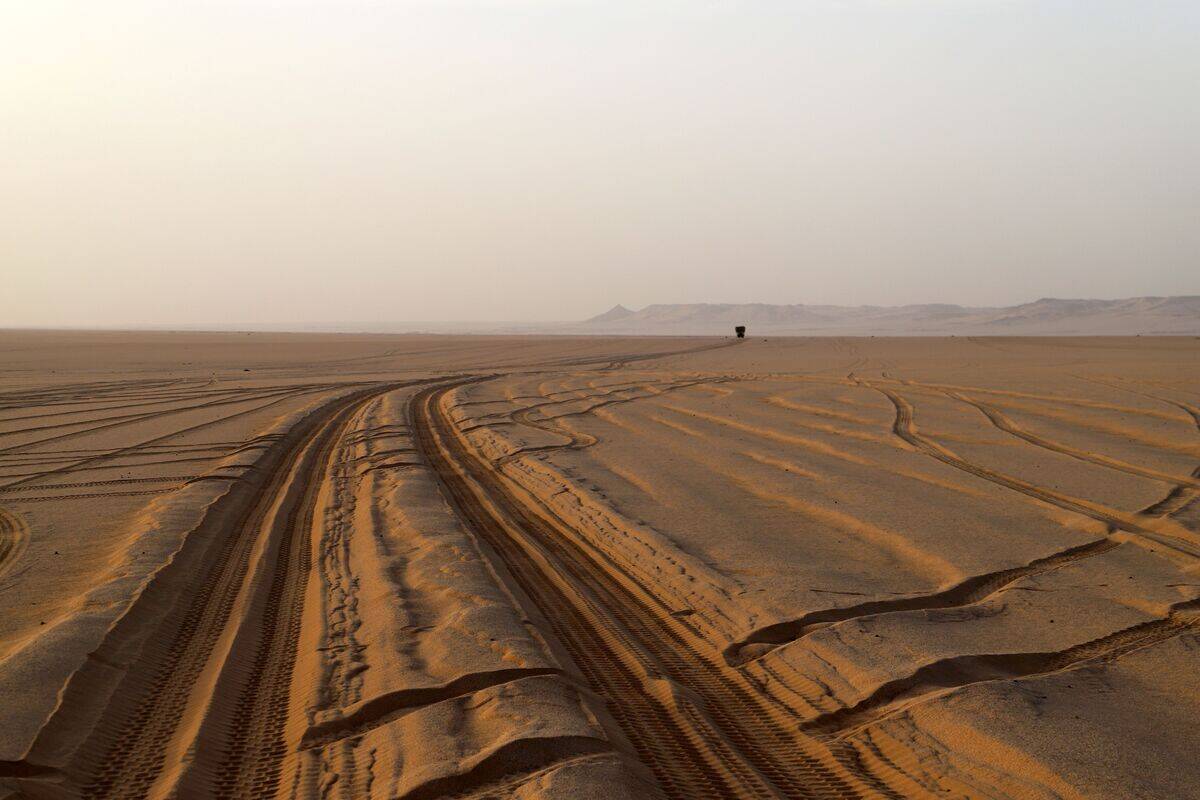

The Sahara Desert, one of the hottest regions on Earth, experiences some unexpected weather phenomena. While known for its scorching temperatures, the desert can also see sudden drops in temperature, even freezing conditions at night.
The unique landscape and atmospheric conditions create powerful dust storms that can travel across continents. These storms play a significant role in the Earth’s climate by transporting nutrients across the globe, affecting ecosystems far beyond the desert’s boundaries.
The Enigma of the Sailing Stones in Death Valley
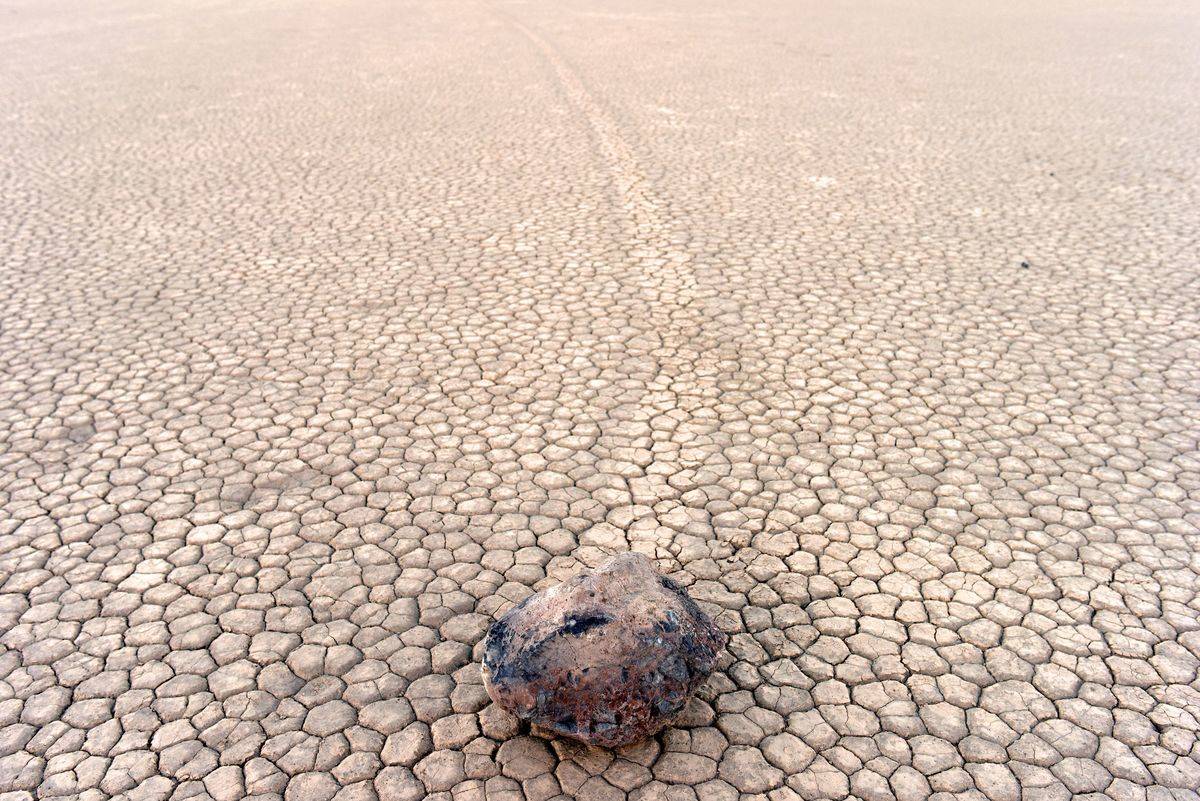

Death Valley’s Racetrack Playa is home to a curious phenomenon: rocks that move on their own across the desert floor, leaving trails behind them. Known as “sailing stones,” these rocks have puzzled scientists for decades.
Recent research suggests that a combination of ice, wind, and sunlight creates the perfect conditions for this movement. Thin sheets of ice form around the stones, and when the ice melts under the sun, even light winds can push the rocks across the slippery surface.
The Curious Case of the Vanishing Lake in Patagonia
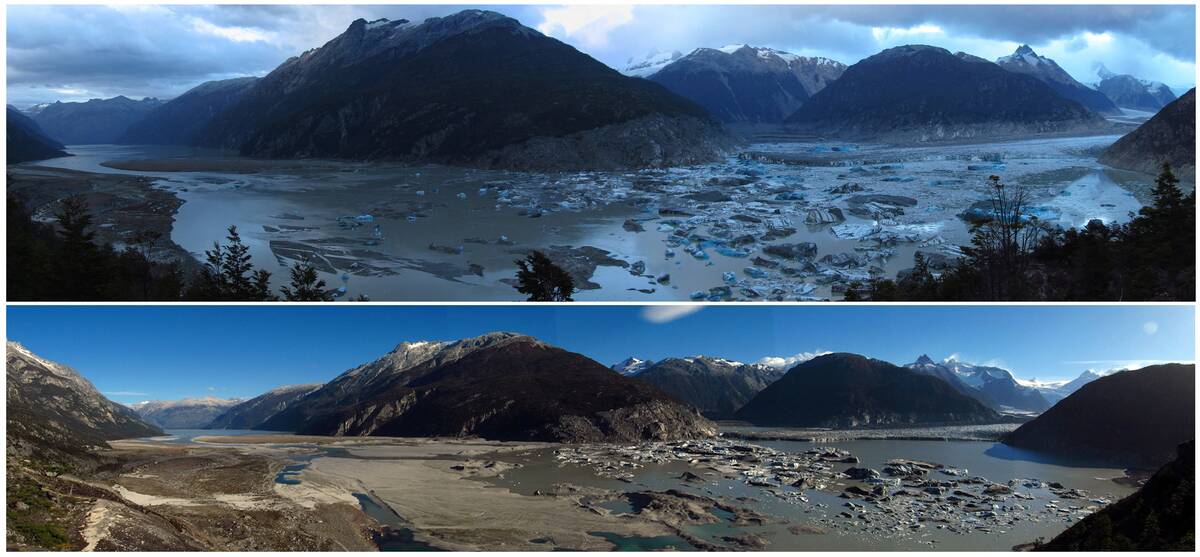

In Patagonia, Lake Cachet II has been known to mysteriously vanish overnight, leaving behind a dry lakebed. This phenomenon is a result of glacial meltwater flooding into a subglacial tunnel system, causing the lake to drain rapidly.
This draining can happen several times a year, dramatically altering the landscape. The vanishing lake serves as a stark reminder of the dynamic interactions between glaciers and climate, highlighting the importance of understanding these processes in a warming world.
The Aurora Borealis: More Than Just a Light Show
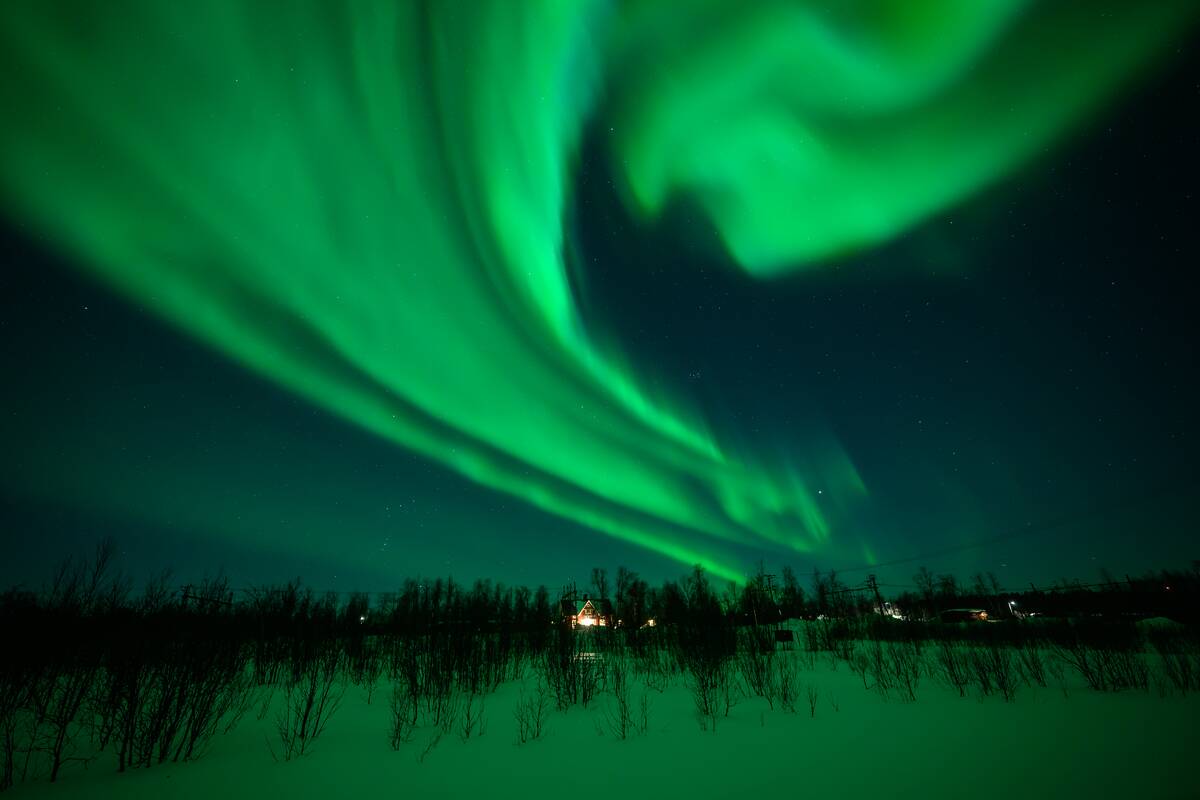

The Aurora Borealis, or Northern Lights, is a captivating natural light display that occurs near the polar regions. This dazzling phenomenon is caused by charged particles from the sun colliding with Earth’s magnetic field, creating vibrant colors in the sky.
While the auroras are a stunning spectacle, they also offer valuable insights into solar activity and space weather. Scientists study the auroras to better understand the sun’s influence on Earth’s magnetic environment and its impact on satellite communications.
Weather Whiplash: Sudden Climate Swings
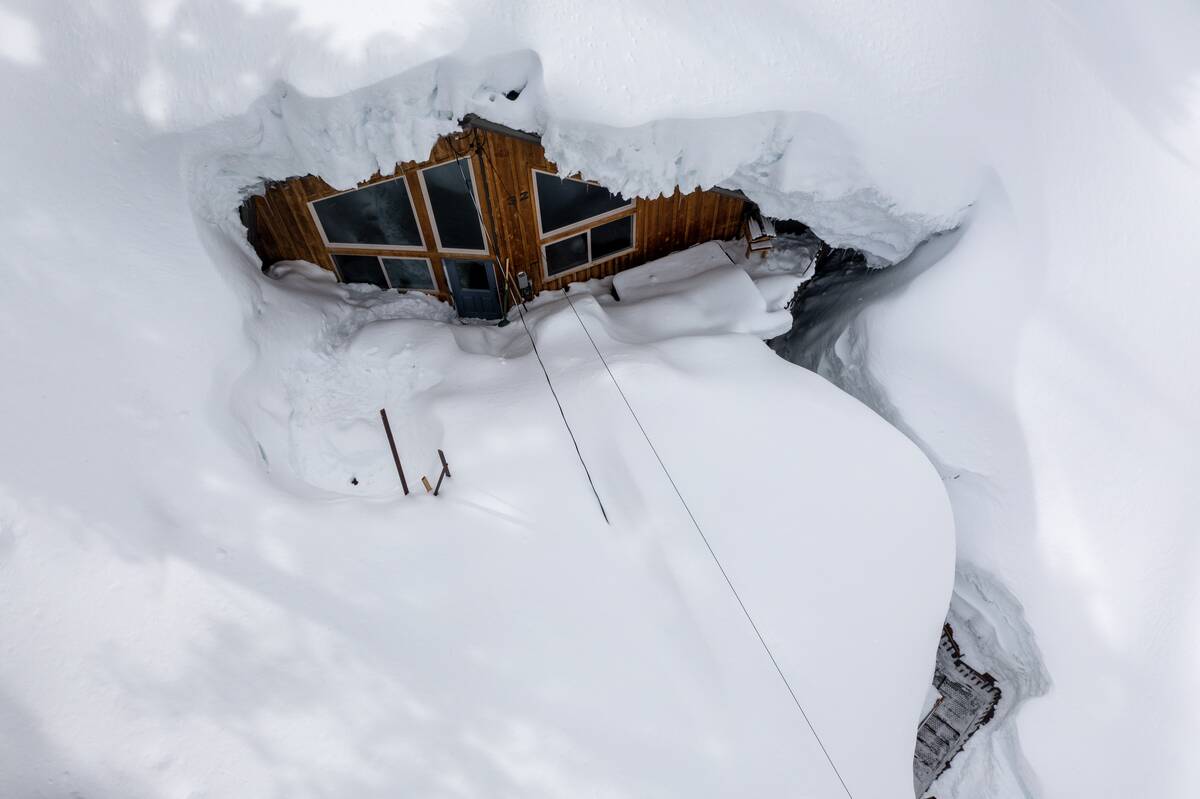

Weather whiplash refers to rapid and extreme shifts in weather conditions, such as sudden temperature changes or unexpected storms. These swings can be caused by a variety of factors, including atmospheric pressure systems and ocean currents.
Climate change is believed to be increasing the frequency and intensity of weather whiplash events, posing challenges for agriculture, infrastructure, and emergency preparedness. Understanding the mechanisms behind these abrupt changes is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate their impact.
The Mystery of the Silent Thunderstorms
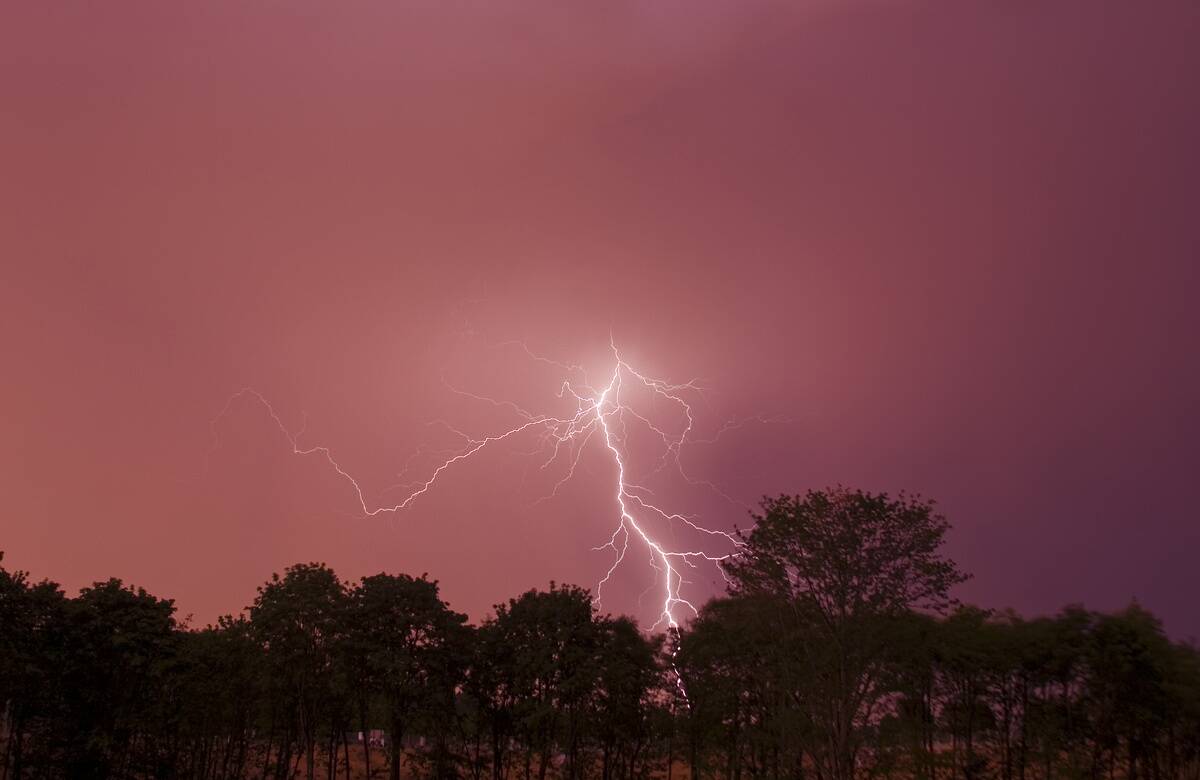

Silent thunderstorms, also known as heat lightning, are a peculiar phenomenon where distant lightning is visible but no thunder is heard. This occurs when the storm is too far away for the sound of thunder to reach the observer.
The lightning is often reflected off clouds, creating an eerie, silent display. While not directly threatening, silent thunderstorms are a reminder of the vastness and power of weather systems, highlighting the interconnectedness of atmospheric events even at great distances.
The Year Without a Summer: Volcanic Eruptions and Global Cooling
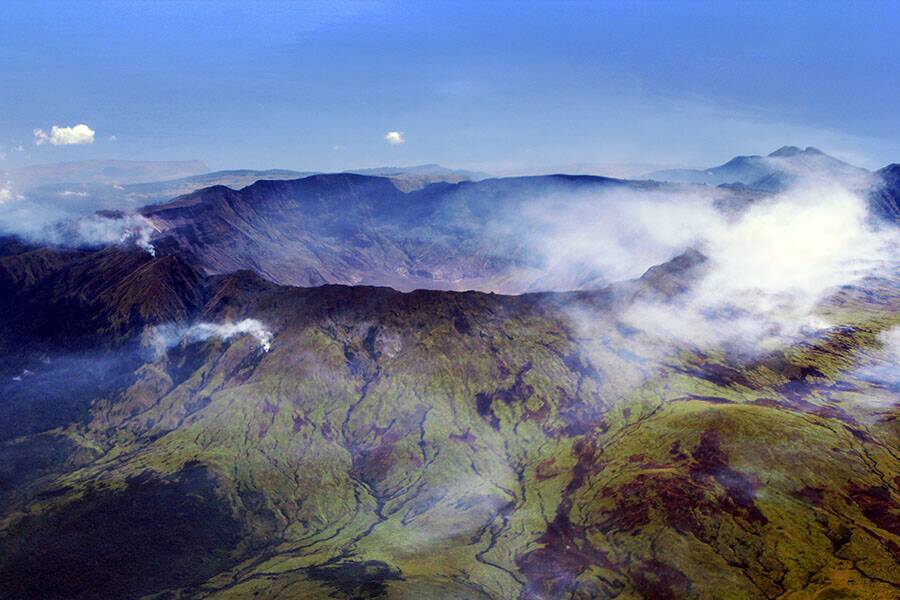

The year 1816 is known as “The Year Without a Summer,” marked by severe climate abnormalities that led to widespread crop failures and food shortages. This was largely due to the eruption of Mount Tambora in Indonesia, which injected vast amounts of volcanic ash into the atmosphere.
The ash blocked sunlight, causing a temporary global cooling effect. This event underscores the profound influence volcanic activity can have on Earth’s climate, offering lessons for understanding and predicting future climatic disruptions.
The Role of Ocean Currents in Unpredictable Weather Patterns
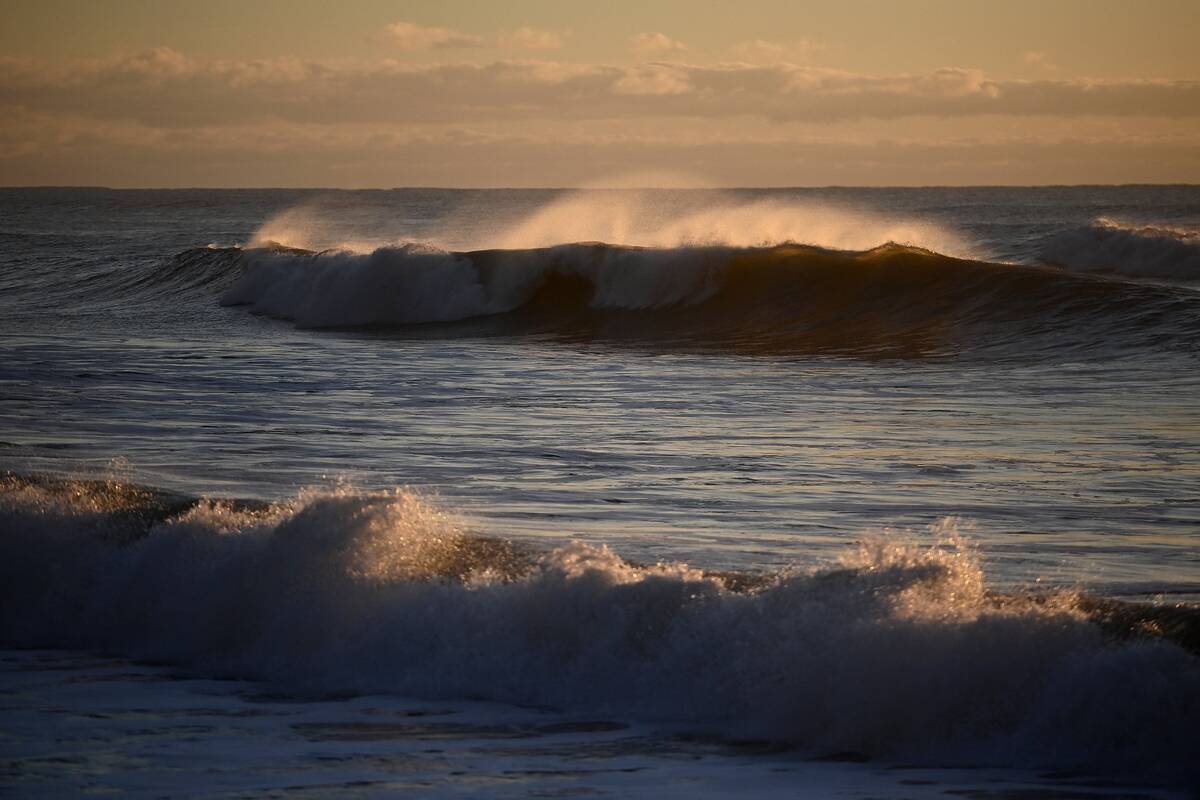

Ocean currents play a crucial role in regulating climate and weather patterns around the globe. They transport warm and cold water across vast distances, influencing atmospheric conditions and precipitation.
Changes in these currents, such as those caused by El Niño and La Niña events, can lead to significant shifts in weather, including droughts, floods, and hurricanes. Studying ocean currents helps scientists predict these shifts and improve long-term climate models, essential for preparing for extreme weather events.
The Unforeseen Impact of Solar Flares on Earth’s Climate
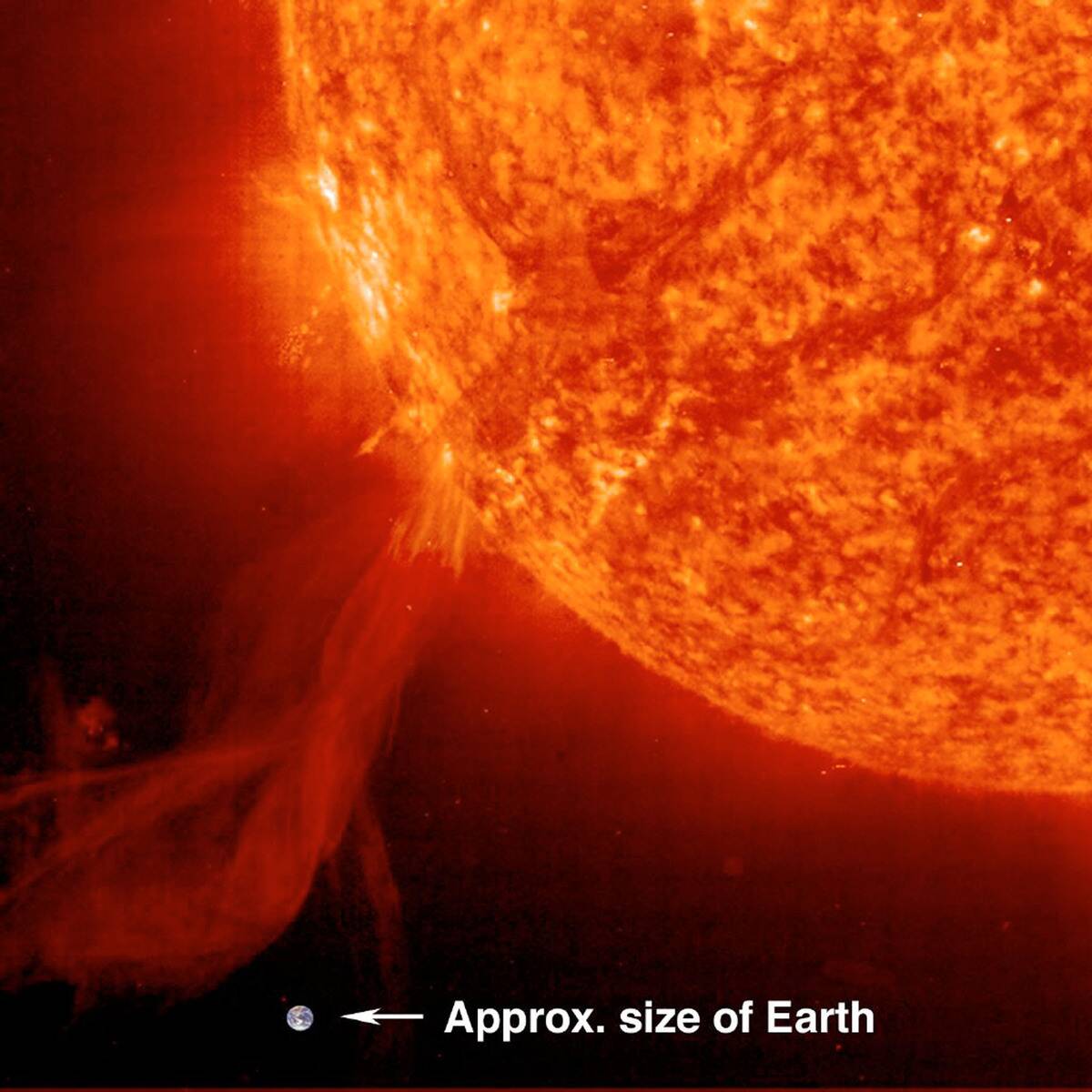
Solar flares, powerful bursts of radiation from the sun, can have unexpected effects on Earth’s climate. While primarily known for disrupting satellite communications and power grids, solar flares can also influence weather patterns.
The increase in solar activity can alter the Earth’s ionosphere, affecting radio signal propagation and even atmospheric circulation. Understanding these impacts is vital for predicting space weather and its potential effects on our planet, highlighting the interconnectedness of solar and terrestrial phenomena.
Microclimates: Tiny Pockets of Atmospheric Oddities

Microclimates are small areas with distinct atmospheric conditions that differ from the surrounding region. These variations can be caused by factors such as topography, vegetation, and human activity. Urban areas, for example, often experience higher temperatures than rural surroundings due to the heat-retaining properties of concrete and asphalt.
Microclimates can have significant ecological and agricultural impacts, influencing local biodiversity and crop yields. Studying these localized climates helps scientists understand broader climate dynamics and their implications for ecosystems.
The Role of Urban Heat Islands in Meteorological Anomalies

Urban heat islands are areas within cities that experience higher temperatures than their rural counterparts, primarily due to human activities and infrastructure. The concentration of buildings, roads, and vehicles generates and traps heat, leading to warmer conditions. This phenomenon can exacerbate heatwaves, increase energy consumption, and affect local weather patterns.
Understanding urban heat islands is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate their impact, such as incorporating green spaces and reflective materials into city planning to reduce temperatures and improve urban living conditions.



